博文
ABBS: Doxycycline&doxorubicin inhibits prostate cancer
|||
Chao Zhu, Xueting Yan, Ao Yu, and Yongjian Wang
Key Laboratory of Bioactive Materials, Ministry of Education, College of Life Sciences, Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, China
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 2017, 49: 999–1007; doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmx097
Castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) is fatal and there is currently no effective clinical treatment. The antibiotic doxycycline has shown anti-cancer effect in several kinds of solid tumors including prostate cancer. In this study, a combination of doxycycline and doxorubicin was used to investigate the synergistic effect on CRPC cells. MTT assay was employed to determine the viability of cells in two-dimensional (2D) cultures. Apoptosis was determined by Annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) double staining assay. Cell cycle was analyzed by PI staining, and reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) was used to determine the expressions of apoptosis-related genes at mRNA level. Western blot analysis was used to analyze the expressions of Bcl-2, Bax, and Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase proteins. Cytotoxicity assay and morphological observation of PC3 cells in three-dimensional (3D) cultures were used to determine the effect of combination treatment. Results showed that doxycycline combined with doxorubicin significantly inhibited PC3 cells in both 2D and 3D cultures, enhanced apoptosis, and increased the accumulation of cells in G2/M phase. RT-PCR showed down-regulation of Bcl-2 and up-regulation of Bax mRNA after combination treatment. Meanwhile, western blot analysis showed that combination treatment resulted in down-regulation of Bcl-2 protein and up-regulation of Bax protein, and that PARP cleavage was obviously exhibited after combination treatment. Confocal imaging analysis indicated that doxorubicin penetrated deeply into the core of spheroids when combined with doxycycline. These data indicated that doxycycline in combination with doxorubicin had a synergistic effect on PC3 cells and may provide a potential novel strategy for the treatment of CRPC.
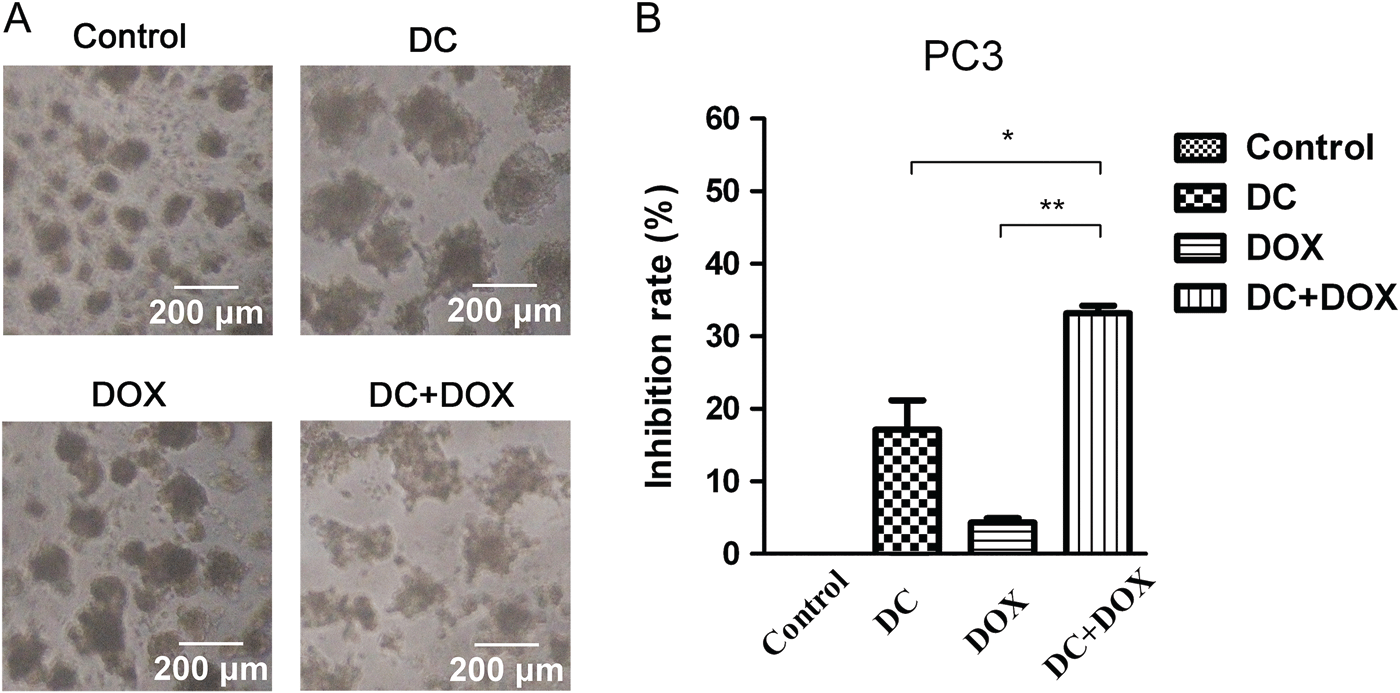
Combination treatment of DC and DOX on the morphology and cytotoxicity against spheroids formed by PC3 cells
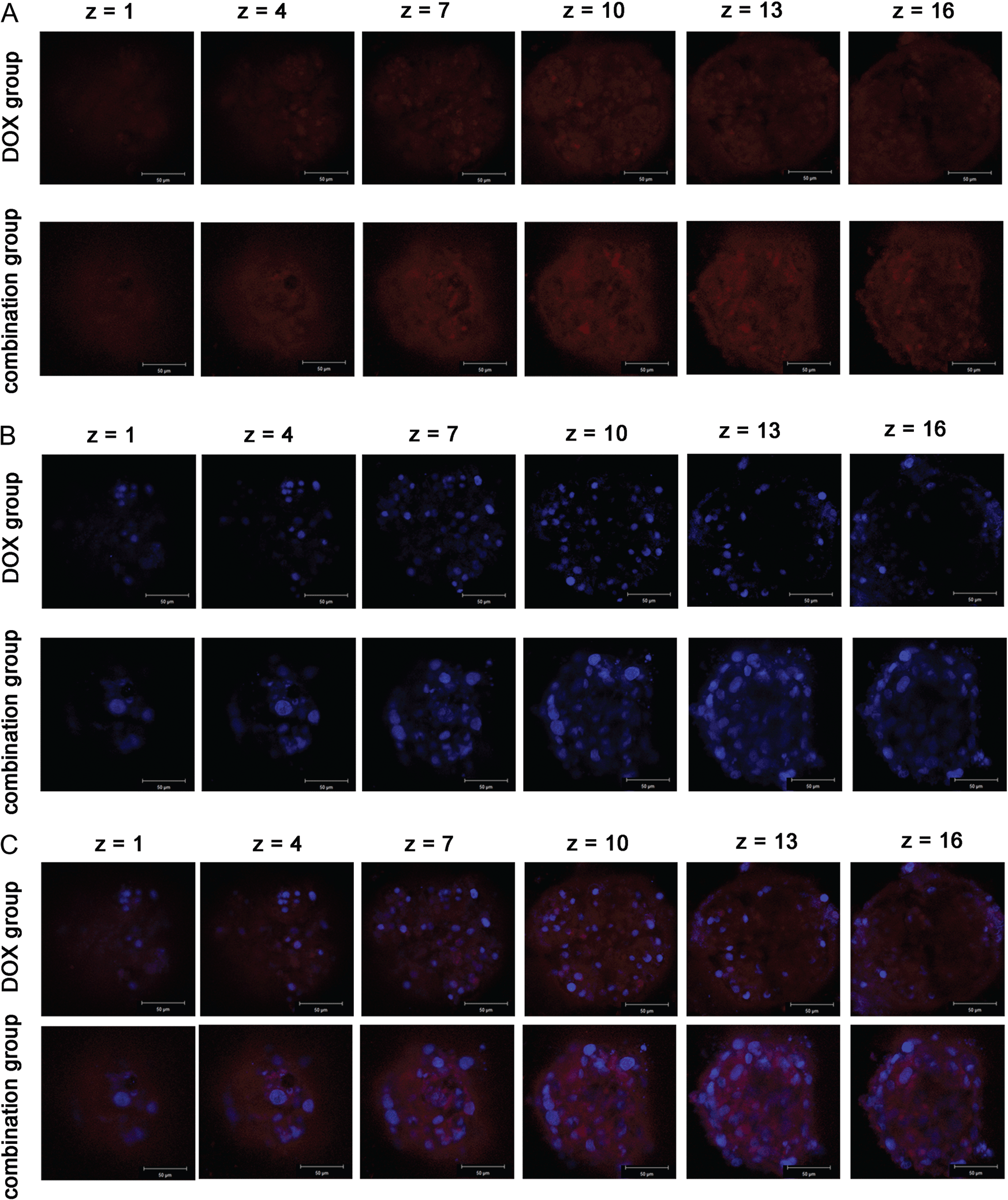
Z-series confocal imaging of the cellular uptake of DOX in the spheroids formed by PC3 cells
阅读原文: http://www.abbs.org.cn/arts.asp?id=4225
获取全文: abbs@sibs.ac.cn
相关论文:
1 Design of an allosterically modulated doxycycline and doxorubicin drug-binding protein

https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-592748-1185961.html
上一篇:ABBS: Heavy ion beam on liver cancer
下一篇:ABBS: Resveratrol attenuates bone cancer pain by ASIC3