博文
Open Force Field Consortium using direct chemical perceptio
|
, , , , , , , , , , and
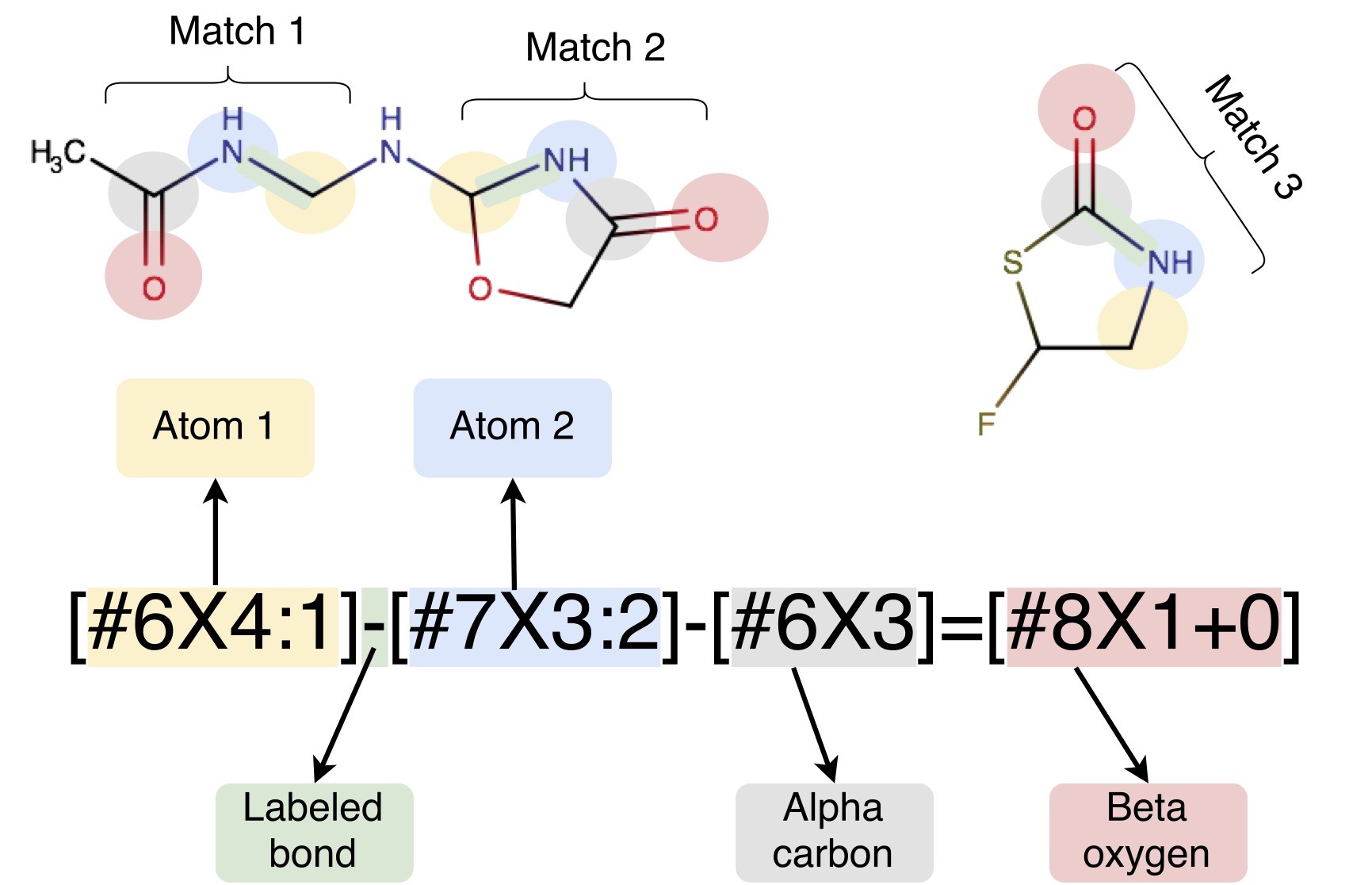
A key issue affecting the accuracy and transferrability of these force fields is the use of atom typing. Traditional approaches to defining molecular mechanics force fields must encode, within a discrete set of atom types, all information which will ever be needed about the chemical environment; parameters are then assigned by looking up combinations of these atom types in tables. This atom typing approach leads to a wide variety of problems such as inextensible atom-typing machinery, enormous difficulty in expanding parameters encoded by atom types, and unnecessarily proliferation of encoded parameters. Here, we describe a new approach to assigning parameters for molecular mechanics force fields based on the industry standard SMARTS chemical perception language (with extensions to identify specific atoms available in SMIRKS). In this approach, each force field term (bonds, angles, and torsions, and nonbonded interactions) features separate definitions assigned in a hierarchical manner without using atom types. We accomplish this using direct chemical perception, where parameters are assigned directly based on substructure queries operating on the molecule(s) being parameterized, thereby avoiding the intermediate step of assigning atom types — a step which can be considered indirect chemical perception. Direct chemical perception allows for substantial simplification of force fields, as well as additional generality in the substructure queries. This approach is applicable to a wide variety of (bio)molecular systems, and can greatly reduce the number of parameters needed to create a complete force field. Further flexibility can also be gained by allowing force field terms to be interpolated based on the assignment of fractional bond orders via the same procedure used to assign partial charges. As an example of the utility of this approach, we provide a minimalist small molecule force field derived from Merck’s parm@Frosst (an Amber parm99 descendant), in which a parameter definition file only approximately 300 lines long can parameterize a large and diverse spectrum of pharmaceutically relevant small molecule chemical space. We benchmark this minimalist force field on the FreeSolv small molecule hydration free energy set and calculations of densities and dielectric constants from the ThermoML Archive, demonstrating that it achieves comparable accuracy to the Generalized Amber Force Field (GAFF) that consists of many thousands of parameters.
Official website: http://openforcefield.org/
Software
openforcefield: A Python toolkit from the Open Force Field Initiative for the development and use of modern molecular mechanics force fields based on direct chemical perception and parameterized with rigorous statistical methods. This also provides the SMIRNOFF force field format.
open-forcefield-tools: Development space for property calculation and force field parameterization tools.
SMARTY: A simple prototype implementation Bayesian atom type sampling using reversible-jump Markov chain Monte Carlo (RJMCMC) over SMARTS types. This also provides the SMIRKY tool, which samples over SMIRKS patterns for chemical perception of parameter types.
Datasets
open-forcefield-data: Curated datasets from the NIST ThermoML database to be used for force field parameterization.
MiniDrugBank: A repository to track the creation and evolution of the MiniDrugBank Molecule set, filtered from DrugBank Release Version 5.0.1.
Forcefileds
smirnoff99Frosst: The first general-purpose implementation of a SMIRKS Native Open Force Field (SMIRNOFF) as implemented by the SMIRNOFF
ForceFieldclass (in openforcefield.typing.engines.forcefield) for parameterizing small molecules for OpenMM and (via ParmEd and InterMol) a wide variety of other simulation packages.
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-355217-1115541.html
上一篇:A postdoc position in GPCR modelling
下一篇:openSUSE Leap 15.0 released