博文
简单可靠的糖尿病早期预测  精选
精选
||
简单可靠的糖尿病早期预测
诸平
据世界卫生组织(World Health Organization简称WHO)网站报道,糖尿病患者人数从1980年的1.08亿上升至2014年的4.22亿。低收入和中等收入国家的患病率上升速度高于高收入国家。糖尿病是失明、肾衰竭、心脏病发作、中风和下肢截肢的主要病因。2000~2019年期间,糖尿病导致的死亡增加了3%。2019年,糖尿病以及糖尿病引起的肾脏疾病估计造成200万人死亡。贾伟平院士也指出:我国糖尿病患者1.25亿,患病率达11.9%。之前,本人也写过一些与糖尿病有关的博文:
今天介绍德国波鸿鲁尔大学(Ruhr University Bochum, Bochum, Germany)2024年1月19日提供的消息,由德国、印度、新加坡以及英国的研究人员合作完成的一项新研究——简单可靠的糖尿病早期预测方法(Simple and Reliable Early Prediction of Diabetes),基于数学建模,简单的血液测试可以比复杂的测试表现得更好。
糖尿病通常在器官或神经受损后才会被发现。部分原因是早期诊断既耗时又困难。由德国波鸿市圣约瑟夫医院鲁尔大学医学系(Department of Medicine I of Ruhr University Bochum at St. Josef Hospital in Bochum, Germany)约翰内斯·迪特里希(Johannes Dietrich)助理领导的一个国际研究小组表明,仅根据从血液样本中提取的两个值进行数学计算,就可以在早期阶段可靠而廉价地诊断糖尿病。研究人员在2024年1月2日的《糖尿病杂志》(Journal of Diabetes)上发表了他们的研究结果——Johannes W. Dietrich, Assjana Abood, Riddhi Dasgupta, Shajith Anoop, Felix K. Jebasingh, R. Spurgeon, Nihal Thomas, Bernhard O. Boehm. A novel simple disposition index (SPINA-DI) from fasting insulin and glucose concentration as a robust measure of carbohydrate homeostasis. Journal of Diabetes, 2024. DOI: 10.1111/1753-0407.13525. First published: 02 January 2024. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/1753-0407.13525
参与此项研究的除了来自德国波鸿鲁尔大学的研究人员之外,还有来自德国哈廷根的 布兰肯斯泰因圣伊丽莎白医院(St. Elisabeth-Hospital Blankenstein, Hattingen, Germany)、德国波鸿鲁尔大学和威滕/赫德克大学鲁尔罕见病中心{Ruhr Centre for Rare Diseases (CeSER), Ruhr University Bochum and Witten/Herdecke University, Bochum, Germany}、德国波鸿天主教医院(Catholic Hospitals Bochum, Bochum, Germany);印度韦洛尔的基督教医学院(Christian Medical College, Vellore, India)、印度班加罗尔浸信会医院(Bangalore Baptist Hospital, Bangalore, India);新加坡南洋理工大学(Nanyang Technological University Singapore, Singapore, Singapore)以及英国伦敦大学国王学院生命课程与人口科学学院(King's College London, School of Life Course & Population Sciences, London, UK)的研究人员。
糖尿病往往长期未被发现(Diabetes often remains long undetected)
约翰内斯·迪特里希指出:“30%的糖尿病患者尚未被诊断出来,因此没有接受任何治疗。”
这是因为在早期很难发现该病。“糖尿病是逐渐发病的,我们的诊断方法不够灵敏,无法检测到它;此外,它们不够具体,这意味着也可能出现假阳性结果,”约翰内斯·迪特里希强调说。
约翰内斯·迪特里希与来自德国、印度、新加坡和英国的同事一起,研究了一种早期检测糖尿病的新方法。这种方法被称为SPINA Carb,是基于数学建模的。所需要的只是血液样本,这是在早上病人吃早餐之前采集的。在样品中测量的两个值是相关的:胰岛素值(insulin value)和葡萄糖值(glucose value)。约翰内斯·迪特里希解释说:“我们将这些值输入一个方程,该方程描述了身体对糖代谢的控制循环,并根据某个变量将其分解。”结果就是所谓的静态配置指数(static disposition index, SPINA-DI)。
比其他标记更可靠(More reliable than other markers)
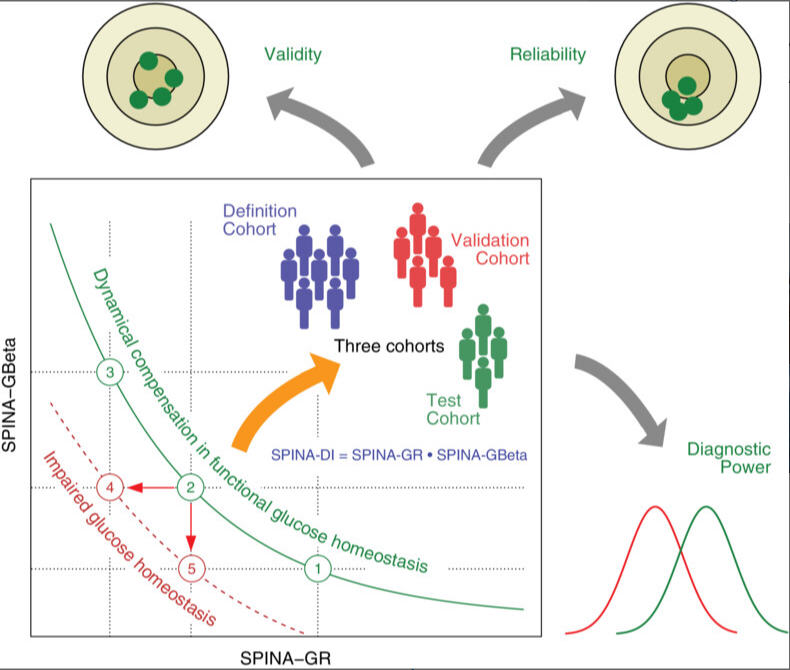
在计算机模拟中,研究小组证明了新参数证实了动态补偿理论(theory of dynamical compensation),该理论预测代谢综合症患者的胰岛素抵抗(Insulin resistance)是通过胰腺β细胞(pancreatic beta cells)增加其活性来补偿的。随后对来自美国、德国和印度的三组志愿者进行的研究支持了这一假设。“在所有三组中,我们发现计算的SPINA-DI与代谢功能的相关指标相关,例如对口服葡萄糖耐量试验的反应,”约翰内斯·迪特里希概述道。
最重要的是,SPINA-DI被证明比其他计算的葡萄糖代谢标记物更可靠,并且可以更准确地诊断。
作者们总结道:“新方法不仅成本效益高,而且精确可靠。它可以补充,甚至在许多情况下取代更复杂的既定方法。”。
本研究得到了新加坡教育部(Ministry of Education - Singapore)、德国研究基金会(DFG GRK 1041/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft)、德国乌尔姆大学客座教授(Universität Ulm, Visiting Professorship)、德国波鸿鲁尔大学的开放获取出版基金(Open Access Publication Funds #6119/Ruhr-Universität Bochum)的资助。
上述介绍,仅供参考。欲了解更多信息,敬请注意浏览原文或者相关报道。
Aims
The widely used dynamic disposition index, derived from oral glucose tolerance testing, is an integrative measure of the homeostatic performance of the insulin-glucose feedback control. Its collection is, however, time consuming and expensive. We, therefore, pursued the question if such a measure can be calculated at baseline/fasting conditions using plasma concentrations of insulin and glucose.
Methods
A new fasting-based disposition index (structure parameter inference approach-disposition index [SPINA-DI]) was calculated as the product of the reconstructed insulin receptor gain (SPINA-GR) times the secretory capacity of pancreatic beta cells (SPINA-GBeta). The novel index was evaluated in computer simulations and in three independent, multiethnic cohorts. The objectives were distribution in various populations, diagnostic performance, reliability and correlation to established physiological biomarkers of carbohydrate metabolism.
Results
Mathematical and in-silico analysis demonstrated SPINA-DI to mirror the hyperbolic relationship between insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function and to represent an optimum of the homeostatic control. It significantly correlates to the oral glucose tolerance test based disposition index and other important physiological parameters. Furthermore, it revealed higher discriminatory power for the diagnosis of (pre)diabetes and superior retest reliability than other static and dynamic function tests of glucose homeostasis.
Conclusions
SPINA-DI is a novel simple reliable and inexpensive marker of insulin-glucose homeostasis suitable for screening purposes and a wider clinical application.
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-212210-1418833.html
上一篇:化学合成: 吡啶类骨架编辑的新策略
下一篇:HIV疫苗突破:创新研究中的抗体保护动物