博文
ABBS: TNF-α in intervertebral disc degeneration
|||
Tumor necrosis factor-α: a key contributor to intervertebral disc degeneration
Cheng Wang, Xiaohua Yu, Yiguo Yan, Wei Yang, Shujun Zhang, Yongxiao Xiang, Jian Zhang and Wenjun Wang
Department of Spine Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, University of South China, Hengyang 421001, China
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 2017, 49: 1–13; doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmw112
Intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration (IDD) is the most common cause leading to low back pain (LBP), which is a highly prevalent, costly, and crippling condition worldwide. Current treatments for IDD are limited to treat the symptoms and do not target the pathophysiology. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) is one of the most potent pro-inflammatory cytokines and signals through its receptors TNFR1 and TNFR2. TNF-α is highly expressed in degenerative IVD tissues, and it is deeply involved in multiple pathological processes of disc degeneration, including matrix destruction, inflammatory responses, apoptosis, autophagy, and cell proliferation. Importantly, anti-TNF-α therapy has shown promise for mitigating disc degeneration and relieving LBP. In this review, following a brief description of TNF-α signal transduction, we mainly focus on the expression pattern and roles of TNF-α in IDD, and summarize the emerging progress regarding its inhibition as a promising biological therapeutic approach to disc degeneration and associated LBP. A better understanding will help to develop novel TNF-α–centered therapeutic interventions for degenerative disc disease.
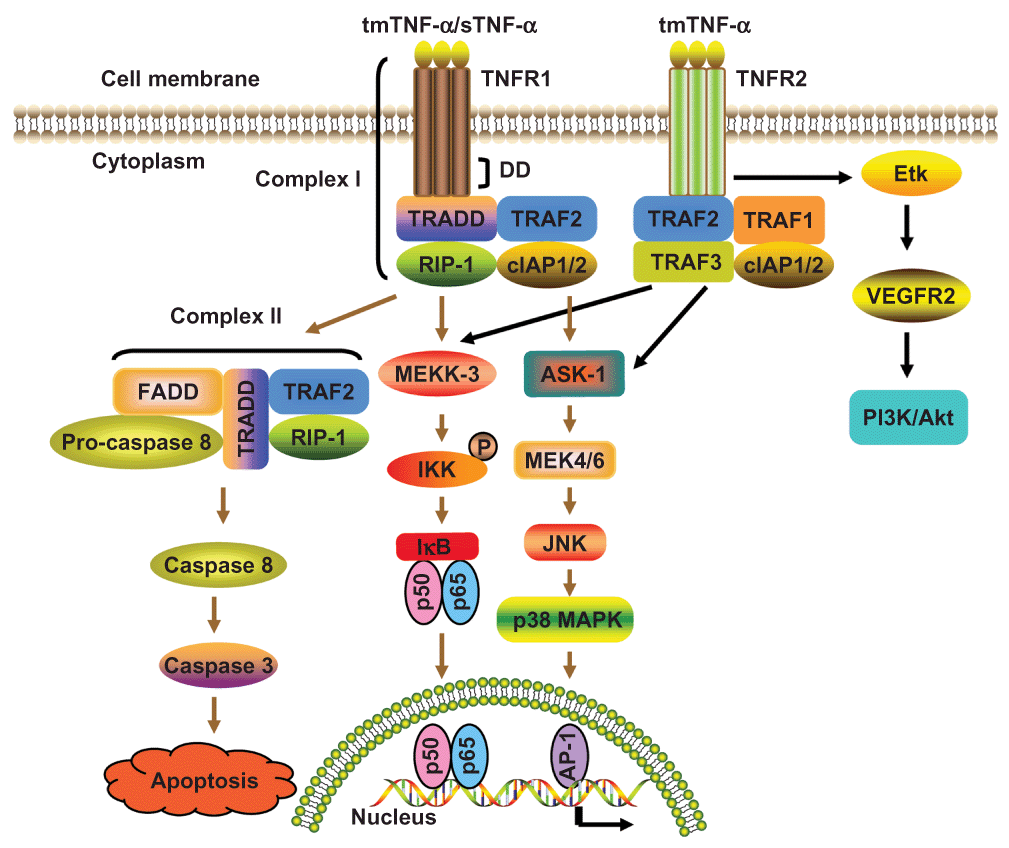
A schematic presentation of TNF-α signaling pathways
阅读全文: http://www.abbs.org.cn/arts.asp?id=4102
获取全文: abbs@sibs.ac.cn
相关论文:
1 Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: pain and disc content
2 Advancing the cellular and molecular therapy for intervertebral disc disease
3 Inflammation in intervertebral disc degeneration and regeneration
5 Advancing the cellular and molecular therapy for intervertebral disc disease

关注ABBS
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-592748-1133887.html
上一篇:ABBS: Abrin P2 suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosi
下一篇:ABBS: Embryonic epicardial cells during embryonic day