博文
Several Assumptions of P-wave Velocity Anomaly in Tomography
||
Several Assumptions of P-wave Velocity Anomaly in Seismic Tomography
Lijun Chen
1. The conception of the velocity of P-waves[1]
The velocity of P-waves in a homogeneous isotropic medium is given by
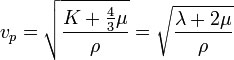
where K is the bulk modulus (the modulus of incompressibility), μ is the shear modulus (modulus of rigidity, sometimes denoted as G and also called the second Lamé parameter), ρ is the density of the material through which the wave propagates, and λ is the first Lamé parameter.
Of these, density shows the least variation, so the velocity is mostly controlled by K and μ.
The elastic moduli P-wave modulus, M, is defined so that M = K + 4μ / 3 and thereby
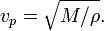
Typical values for P-wave velocity in earthquakes are in the range 5 to 8 km/s.[2] The precise speed varies according to the region of the Earth's interior, from less than 6 km/s in the Earth's crust to 13 km/s through the core.[3]
2. Several assumptions of P-wave velocity anomaly
Thermal column has become a broad consensus, but also are confirmed by the large number of seismic tomography results, therefore:
Assumption 1: In the appropriate phase of the angular velocity of the Earth rotation changes, part of the deep mantle heavy material along a habitual channel are released to the surface direction, formed thermal column in upper mantle and the main energy source of earthquakes, volcanoes and continental drift; in the appropriate phase of the angular velocity of the Earth rotation change, the upwelling heavy material down by gravity; go round and begin again, form activity rhythm of thermal column.
The assumption need to appropriate revision after in contrast to the relations of the angular velocity of the Earth rotation changes and earthquakes or volcanoes.
With upwelling invasive body and assumed the elastic moduli P-wave modulus, M, is constant, then vp is relevant only with density ρ, accordingly:
Assumption 2: Under the condition of phase charnge, nucleation and cavitation, a part of thermal columns can produce cavitating bubbles or flows and form seismic cylinders. The bubbles in the seismic cylinders grow gradually with heat engine and collapse at certain depth, resulting intermediate and deep earthquake activities as well as the driving force from the bottom layer to the top. As a result of cavitating bubbles or flows, the density of seimic cylinders is lower than that of substances of external environment, leading to the formation of P-wave fast velocity anomaly.
This Assumption is similar to the mechanisms of heat engine and is applicable to all the twenty-four seismic cylinders worldwide. The size of cavitating bubbles or cloud is thought to be large to trigger intermediate and deep earthquakes of magnitude of 5-7 .Therefore, seismic cylinders with higher seismic activities lead to larger P-wave fast velocity anomalies.
Under this assumption, the primary energy source of crust seismicity and volcano eruptions comes from intermediate and deep earthquake activity.
Assumption 3: A part of thermal columns do not satisfy the condition of cavitation and do not have intermediate or deep earthquakes. However, the density of upwelling substances is high slightly compared to surroundings, resulting P-wave slow velocity anomaly.
The assumption applies for Iceland, Hawaii as well as the mid-ocean ridges with volcanoes and shallow earthquake activities.
Under this assumption, volcano eruptions and seafloor spreading of mid-ocean ridge can promote slow movement of continental shift worldwide.
These 3 assumptions constitute basic assumptions of the Seismic Geothermics.
These 3 assumptions are needed to collect information and further proof.
(The first draft 2011.11.24)
Reference:
1. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/P-wave
2. http://hypertextbook.com/facts/2001/PamelaSpiegel.shtml
3. http://earthquake.usgs.gov/learn/topics/seismology/keeping_track.php
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-552558-511314.html
上一篇:冰岛和夏威夷地震层析图像的共性
下一篇:关于地震层析中P波波速异常的若干假定