博文
mLife专题分享 | 病原微生物研究
|

mLife已正式出版6期,报道内容涵盖微生物学领域的各个学科,下面分享的文章聚焦病原微生物研究,欢迎阅读!
Assessing global fungal threats to humans
Jianping Xu

该文评估了真菌对人类的主要危害类型,以及引起各种危害的主要驱动因素;同时讨论了控制真菌危害的最新进展和潜在的研究领域,以推动其定量评估和预测,激发人们更好地研究和预测所有微生物对人类的威胁。

Xu J. Assessing global fungal threats to humans. mLife. 2022; 1: 223–240.
Human skin bacterial microbiota homeostasis: A delicate balance between health and disease
Yibin Zhu, Xi Yu, Gong Cheng
该文总结了皮肤微生物菌群和人类健康的关系,讨论了由皮肤微生物菌群失衡导致的多种疾病,并介绍了利用皮肤微生物进行疾病治疗的最新进展。文章提出,深入理解人类健康和疾病与皮肤微生物菌群稳态的互作机制,将提供以皮肤细菌为疾病治疗思路的新策略。

Zhu Y, Yu X, Cheng G. Human skin bacterial microbiota homeostasis: a delicate balance be-tween health and disease. mLife. 2023; 2: 107–120.
Delivery of an Rhs-family nuclease effector reveals direct penetration of the gram-positive cell envelope by a type VI secretion system in Acidovorax citrulli
Tong-Tong Pei, Yumin Kan, Zeng-Hang Wang, Ming-Xuan Tang, Hao Li, Shuangquan Yan, Yang Cui, Hao-Yu Zheng, Han Luo, Xiaoye Liang, Tao Dong

该研究发现了一种兼具杀伤细菌和真菌功能的T6SS,揭示了其对革兰氏阳性菌的细胞壁穿透作用,对开发抑制耐药病原菌的新手段有重要意义。

Pei, T-T, Kan, Y, Wang, Z-H, Tang, M-X, Li, H, Yan, S, et al. Delivery of an Rhs-family nuclease effector reveals direct penetration of the gram-positive cell envelope by a type VI secretion system in Acidovorax citrulli. mLife. 2022; 1: 66–78.
https://doi.org/10.1002/mlf2.12007
Legionella pneumophila temporally regulates the activity of ADP/ATP translocases by reversible ADP-ribosylation
Jiaqi Fu, Pengwei Li, Hongxin Guan, Dan Huang, Lei Song, Songying Ouyang, Zhao-Qing Luo
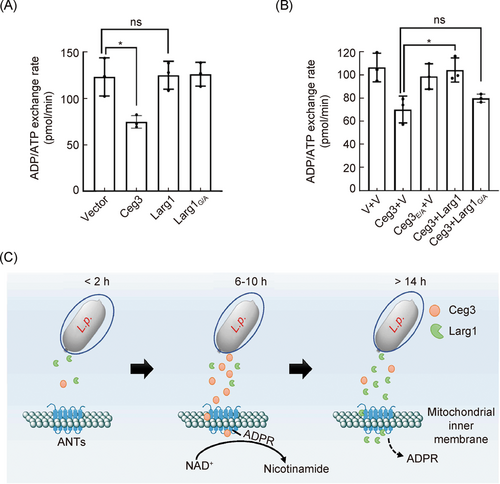
之前的研究发现,Legionella pneumophila的效应蛋白Ceg3通过对ADP/ATP转运酶进行腺苷二磷酸核糖基化修饰(ADP-ribosylation)来抑制宿主能量代谢。该文章揭示了这种抑制在受另一效应蛋白Larg1调节,它通过去ADPR修饰在感染后期使底物恢复活性。

Fu J, Li P, Guan H, Huang D, Song L,Ouyang S, et al. Legionella pneumophila temporally regulates the activity of ADP/ATP translocases by reversible ADP‐ ibosylation. mLife. 2022; 1: 51–65.
https://doi.org/10.1002/mlf2.12014
A forkhead transcription factor contributes to the regulatory differences of pathogenicity in closely related fungal pathogens
Weixin Ke, Yuyan Xie, Yue Hu, Hao Ding, Xin Fan, Jingjing Huang, Xiuyun Tian, Baokun Zhang, Yingchun Xu, Xiao Liu, Ying Yang, Linqi Wang
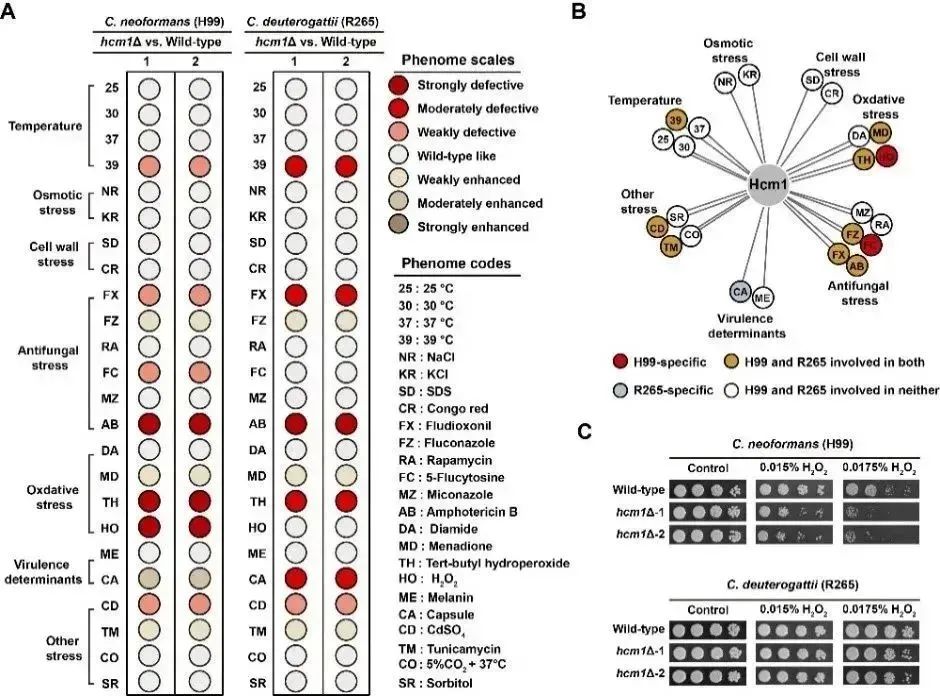
新生隐球菌和格特隐球菌是重要的侵袭性人类病原真菌,二者亲缘关系紧密但临床特征有别。该研究对决定它们致病性差异的分子进化基础进行了系统性揭示,确定了Hcm1-Srx1抗氧化通路在其中的关键贡献。

Ke, W, Xie, Y, Hu, Y, Ding, H, Fan, X, Huang, J, et al. A forkhead transcription factor contributes to the regulatory differences of pathogenicity in closely related fungal pathogens. mLife. 2022; 1: 79–91.
https://doi.org/10.1002/mlf2.12011
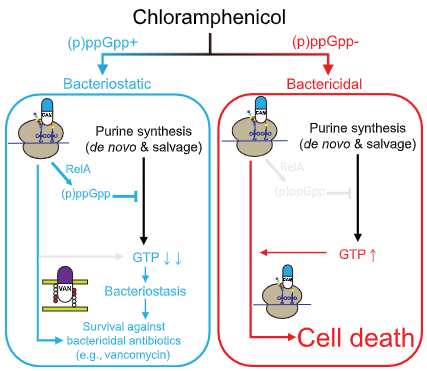
Bacillus subtilis produces (p)ppGpp in response to the bacteriostatic antibiotic chloramphenicol to prevent its potential bactericidal effect
Jin Yang, Jessica T. Barra, Danny K. Fung, Jue D. Wang
该研究团队发现革兰氏阳性菌对于抑菌性抗生素需要产生严谨反应(stringent response)才可以存活,并且揭示了严谨反应核苷酸信号(p)ppGpp介导的抗生素杀菌(bactericidal)—抑菌作用(bacteriostatic)转变的机理, 从而有助于开发针对细菌核苷酸信号的抗菌疗法。

Yang J, Barra JT, Fung DK, Wang JD. Bacillus subtilis produces (p)ppGpp in response to the bacteriostatic antibiotic chloramphenicol to prevent its potential bactericidal effect. mLife. 2022; 1: 101–113.
Maternal and neonatal viromes indicate the risk of offspring's gastrointestinal tract exposure to pathogenic viruses of vaginal origin during delivery
Jinfeng Wang, Liwen Xiao, Baichuan Xiao, Bing Zhang, Zhenqiang Zuo, Peifeng Ji, Jiayong Zheng, Xiaoqing Li, Fangqing Zhao
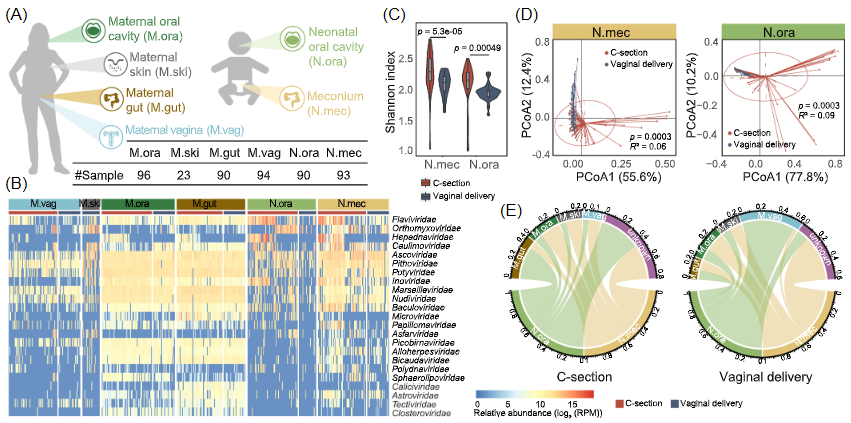
该研究团队基于对99对母婴6个身体部位486个样本的宏基因组测序和病毒组分析,绘制了高分辨率的代际病毒组图谱,发现顺产分娩新生儿的口腔和肠道中检测到的多数病毒来源都可以追溯到母体阴道。

Wang J, Xiao L, Xiao B, Zhang B, Zuo Z, Ji P, et al. Maternal and neonatal viromes indicate the risk of offspring's gastrointestinal tract exposure to pathogenic viruses of vaginal origin during delivery. mLife. 2022; 1: 303–310.
https://doi.org/10.1002/mlf2.12034
DANMEL: a manually curated reference database for analyzing mobile genetic elements associated with bacterial drug resistance
Peng Wang, Xiaoyuan Jiang, Kai Mu, Ying Jing, Zhe Yin, Yujun Cui, Cuidan Li, Xinhua Luo, Fangzhou Chen, Ting Yu, Zhichen Zhu, Yansong Sun, Fei Chen, Dongsheng Zhou

该研究基于对耐药移动元件纯手工精细注释,完成包括整合子、转座子、质粒等大量参考/原型耐药移动元件的精细注释,并以此构建耐药移动元件的参考数据库,为耐药移动元件研究提供准确、精细、全面的参考数据。

Wang P, Jiang X, Mu K, Jing Y, Yin Z, Cui Y, et al. DANMEL: a manually curated reference database for analyzing mobile genetic elements associated with bacterial drug resistance. mLife. 2022; 1: 460–464.
https://doi.org/10.1002/mlf2.12046
Cell division factor ZapE regulates Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation by impacting the pqs quorum sensing system
Xi Liu, Minlu Jia, Jing Wang, Hang Cheng, Zhao Cai, Zhaoxiao Yu, Yang Liu, Luyan Z. Ma, Lianhui Zhang, Yingdan Zhang, Liang Yang
该研究将转座子测序技术应用在流式生物被膜培养系统中,筛选了铜绿假单胞菌生物被膜形成的遗传调控因子,发现细胞分裂因子ZapE (PA4438)通过其ATP水解活性参与了PqsH将HHQ转化为PQS的过程,进而影响pqs 群体感应、毒性因子和生物被膜形成。

Liu X, Jia M, Wang J, Cheng H, Cai Z, Yu Z, et al. Cell division factor ZapE regulates Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation by impacting the pqs quorum sensing system. mLife. 2023; 2: 28–42.
https://doi.org/10.1002/mlf2.12059
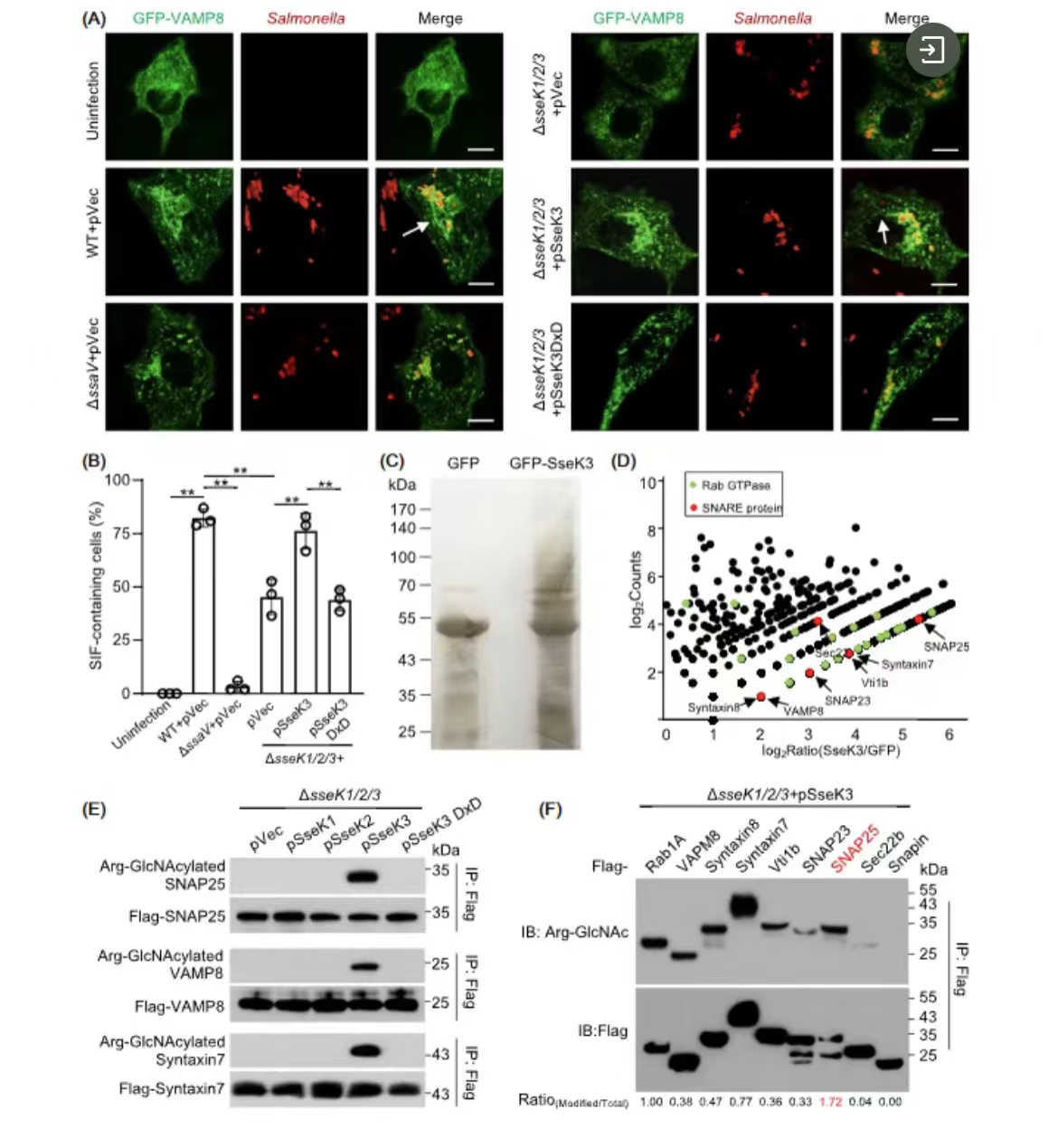
A host E3 ubiquitin ligase regulates Salmonella virulence by targeting an SPI-2 effector involved in SIF biogenesis
Kun Meng, Jin Yang, Juan Xue, Jun Lv, Ping Zhu, Liuliu Shi, Shan Li
该研究利用高分辨率生物质谱技术筛选到沙门氏菌效应蛋白SseK3的新型底物为SNARE类蛋白,发现SseK3抑制SNARE蛋白之间配对促进细菌胞内复制结构SIF的形成,同时宿主E3泛素连接酶TRIM32特异性结合并泛素化降解SseK3从而抑制病原菌侵染。

Meng K, Yang J, Xue J, Lv J, Zhu P, Shi L, et al. A host E3 ubiquitin ligase regulates Salmonella virulence by targeting an SPI‐2 effector involved in SIF biogenesis. mLife. 2023; 2: 141–158.
https://doi.org/10.1002/mlf2.12063
The secretory Candida effector Sce1 licenses fungal virulence by masking the immunogenic β‐1,3‐glucan and promoting apoptosis of the host cells
Hongyu Wu, Li Wang, Wenjuan Wang, Zhugui Shao, Xin-Ming Jia, Hui Xiao, Jiangye Chen
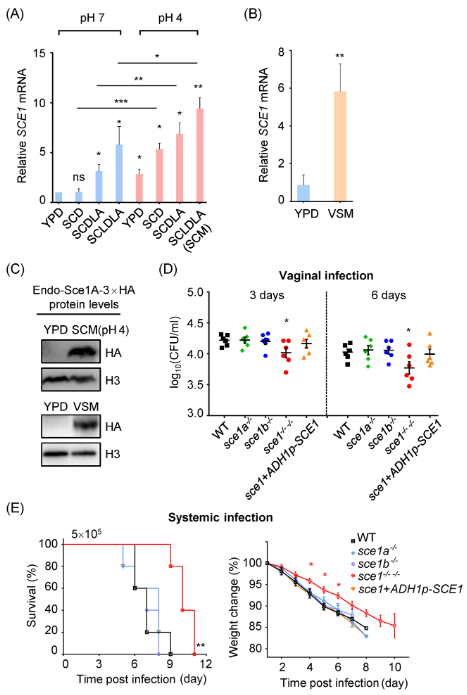
该研究团队基于真菌学和免疫学技术开展了真菌和宿主的相互作用的研究,发现了白念珠菌中一个新的分泌型效应因子Sce1,该效应因子能够在酸性、营养缺乏或厚壁孢子培养条件下高表达。在正常条件下,Sce1定位于细胞壁并能够掩盖β-(1,3)-葡聚糖的免疫激活功能。当白念珠菌被免疫细胞吞噬后,Sce1能够从细胞壁上释放并造成免疫细胞死亡,从而从两方面达到免疫逃逸的效果,该研究为理解白念珠菌和宿主相互作用机制提供了新的思路。

Wu H, Wang L, Wang W, Shao Z, Jia X‐M, Xiao H, et al. The secretory Candida effector Sce1 licenses fungal virulence by masking the immunogenic β‐1, 3‐glucan and promoting apoptosis of the host cells. mLife. 2023; 2: 159–177.
https://doi.org/10.1002/mlf2.12066
mLife
期刊简介
mLife是由中国科学院主管、中国科学院微生物研究所主办(中国微生物学会为合作单位)的我国微生物学领域第一本综合性高起点英文期刊。mLife瞄准全球微生物学领域高水平科研成果和前沿进展,报道内容覆盖微生物学各个学科。mLife的办刊目标是打造微生物学领域国际旗舰期刊。
期刊网站:
http://mlife.im.ac.cn/
https://wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/mLife
投稿网站:https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/mlife
扫码关注mLife

mLife@im.ac.cn
010 - 64807055
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-3563286-1398644.html
上一篇:mLife | 剑走偏锋——扇贝共生菌裂解二甲基巯基丙酸(DMSP)
下一篇:mLife专题分享 | 微生物代谢研究