博文
[转载]hLife collection | Drugs & Antibody
||
1. De novo design of covalent bonding peptides for target protein
hLife | 周小红/王奇慧等合作开发两步法从头设计的共价键合肽抑制剂
通讯作者:周小红、王奇慧、Lip Ket Chin
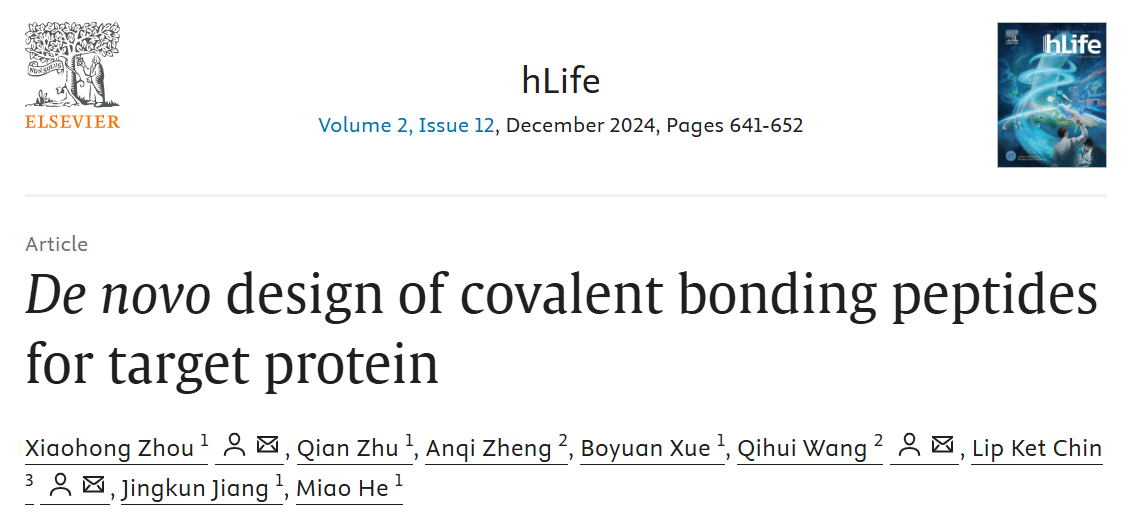
本研究展示了共价抑制剂在抗病毒药物研发中的潜力,并且将计算设计和实验验证相结合,加速了新药物的开发,此外,通过引入非天然氨基酸并同时改进分子动力学预测力场,也为蛋白质工程和药物设计提供了新的策略。
引用:
Zhou X, Zhu Q, Zheng A, et al. De novo design of covalent bonding peptides for target protein. hLife 2024; 2: 641–652.
hLife | 深圳大学张素平研究团队获得一种靶向新冠病毒关键表位的中和抗体
通讯作者:王岚峰、林正红、张素平

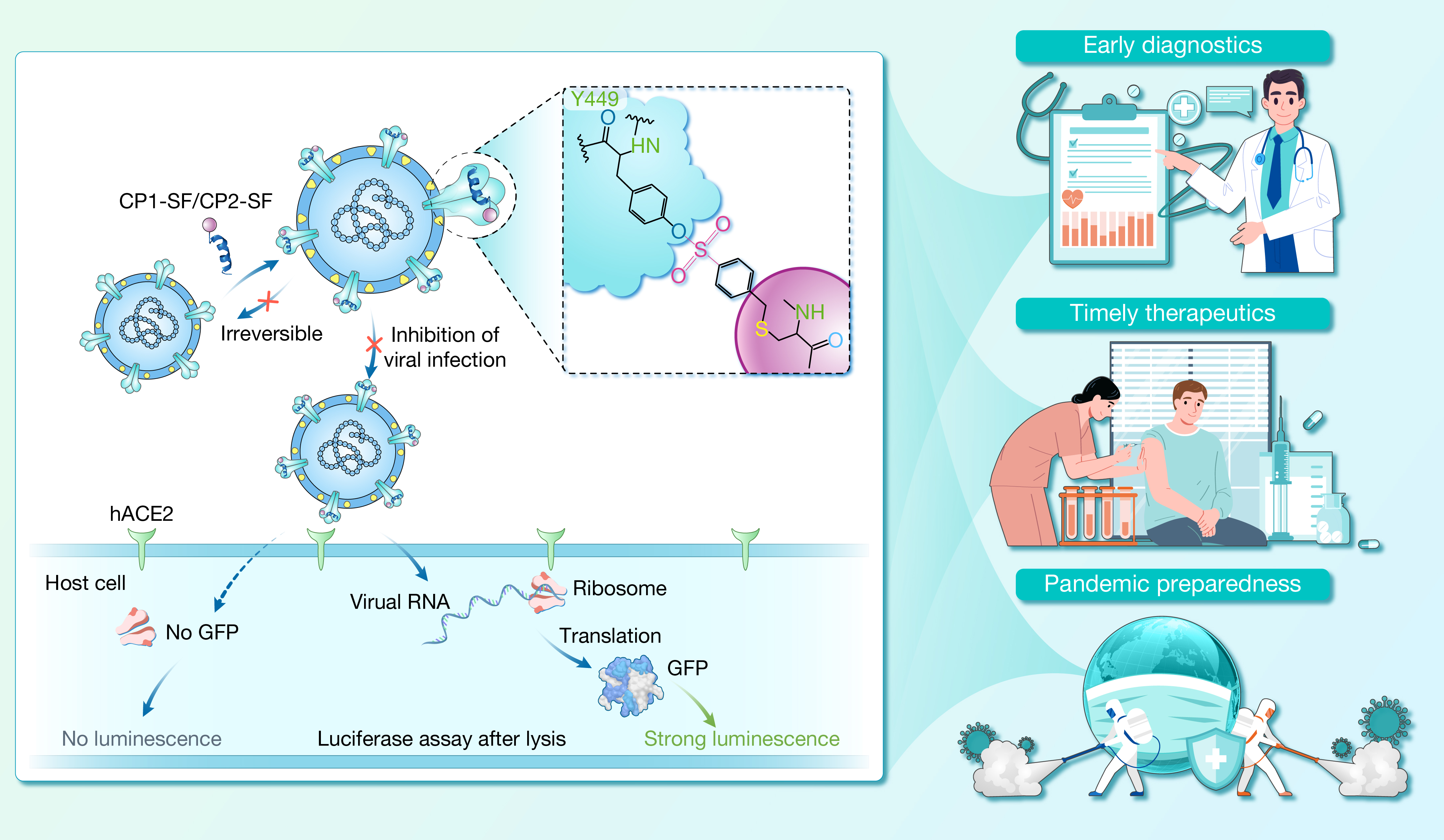
本研究揭示了SARS-CoV-2 S2亚基HR2基序的上游保守区域潜在的利用价值,有利于针对冠状病毒开发广谱的中和抗体及疫苗。
引用:
Su H, Zhang J, Yi Z, et al. A human monoclonal antibody neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants by targeting the upstream region of spike protein HR2 motif. hLife 2024; 2: 126–140.
hLife | HSV-1 gB-中和抗体复合物结构揭示疱疹病毒潜在广谱中和结构域
通讯作者:孙聪、刘铮、曾木圣

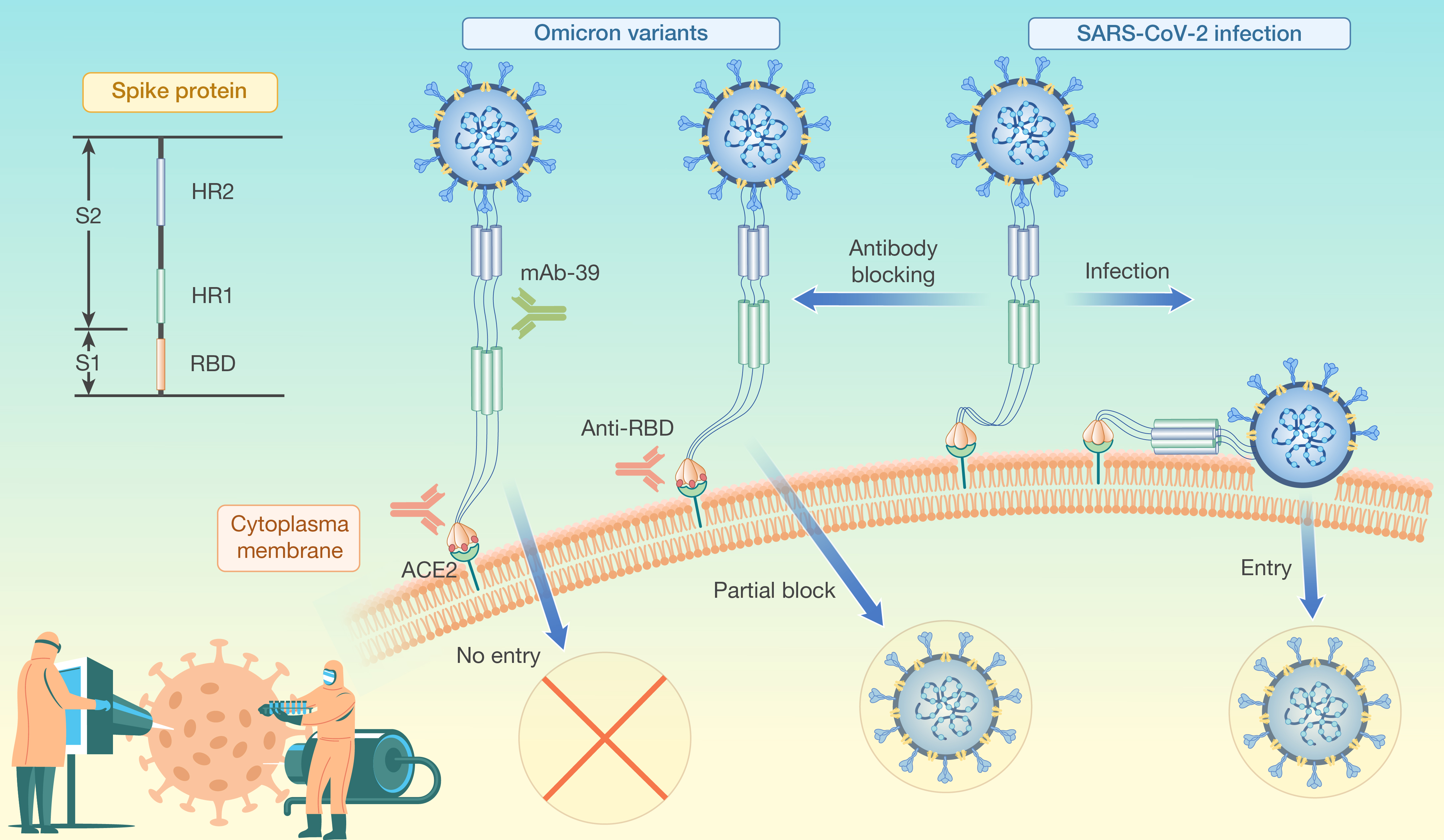
本研究通过解析HSV-1中和抗体结构复合物,创新地提出了疱疹病毒家族gB DII结构域是一个广谱保守的中和表位结构域并在融合前-融合后构象中均暴露抗原表位,将为泛疱疹病毒广谱药物和疫苗开发提供重要参考。
引用:
Sun C, Yang JW, Xie C, et al. The structure of HSV-1 gB bound to a potent neutralizing antibody reveals a conservative antigenic domain across herpesviruses. hLife 2024; 2: 141–146.
hLife | COVID-19相关非药物干预措施对急性腹泻和人畜共患沙门菌的影响
通讯作者:乐敏

本研究对比了浙江省杭州市急性腹泻疾病的发病情况,并通过生物信息学方法解析了NTS的基因组数据。研究发现,与COVID-19相关的非药物干预措施有效降低了急性腹泻的发病率,但NTS的感染情况出现了意外的增加。总体上,NTS的耐药性、耐消毒能力和毒力能力有所降低,人畜共患传播的规模也减小,这暗示着NTS可能通过其他潜在途径感染人类。尽管多项非药物干预措施主要用于应对新冠大流行,但它对其他传染病和非传染病的研究仍值得进一步关注。
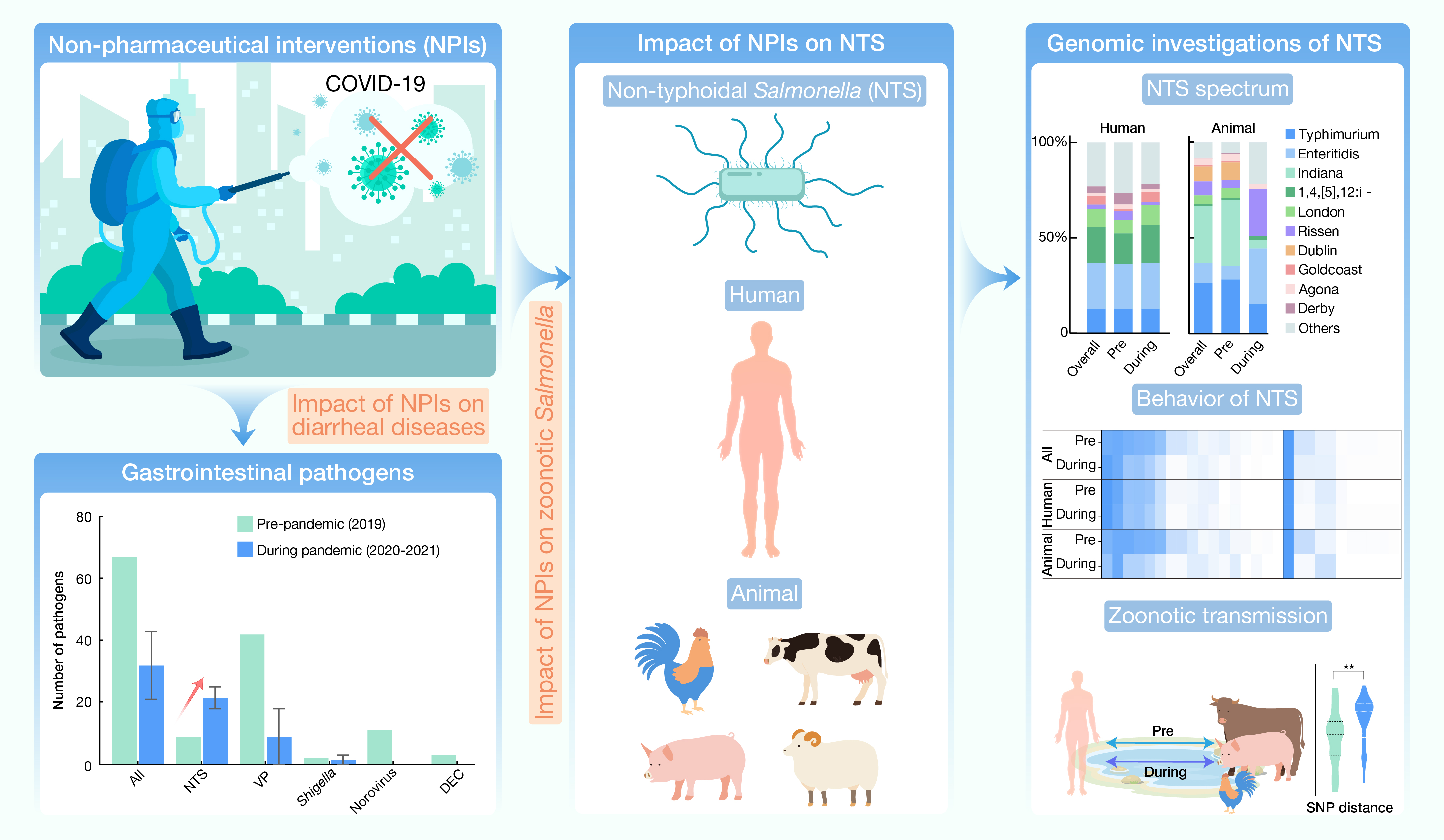
引用:
Huang L, Zhou H, Chen J, et al. Impact of COVID-19-related nonpharmaceutical interventions on diarrheal diseases and zoonotic Salmonella. hLife 2024; 2: 246–256.
5. Structural insights into the distinct protective mechanisms of human antibodies targeting ZIKV NS1
hLife | 揭秘寨卡病毒NS1抗体的不同保护机制:表位差异如何影响防御
通讯作者:赵卫、庾蕾、胡红丽
本研究结合结构和生化实验揭示了两组靶向寨卡病毒(ZIKV)NS1蛋白不同表位抗体的差异保护机制。
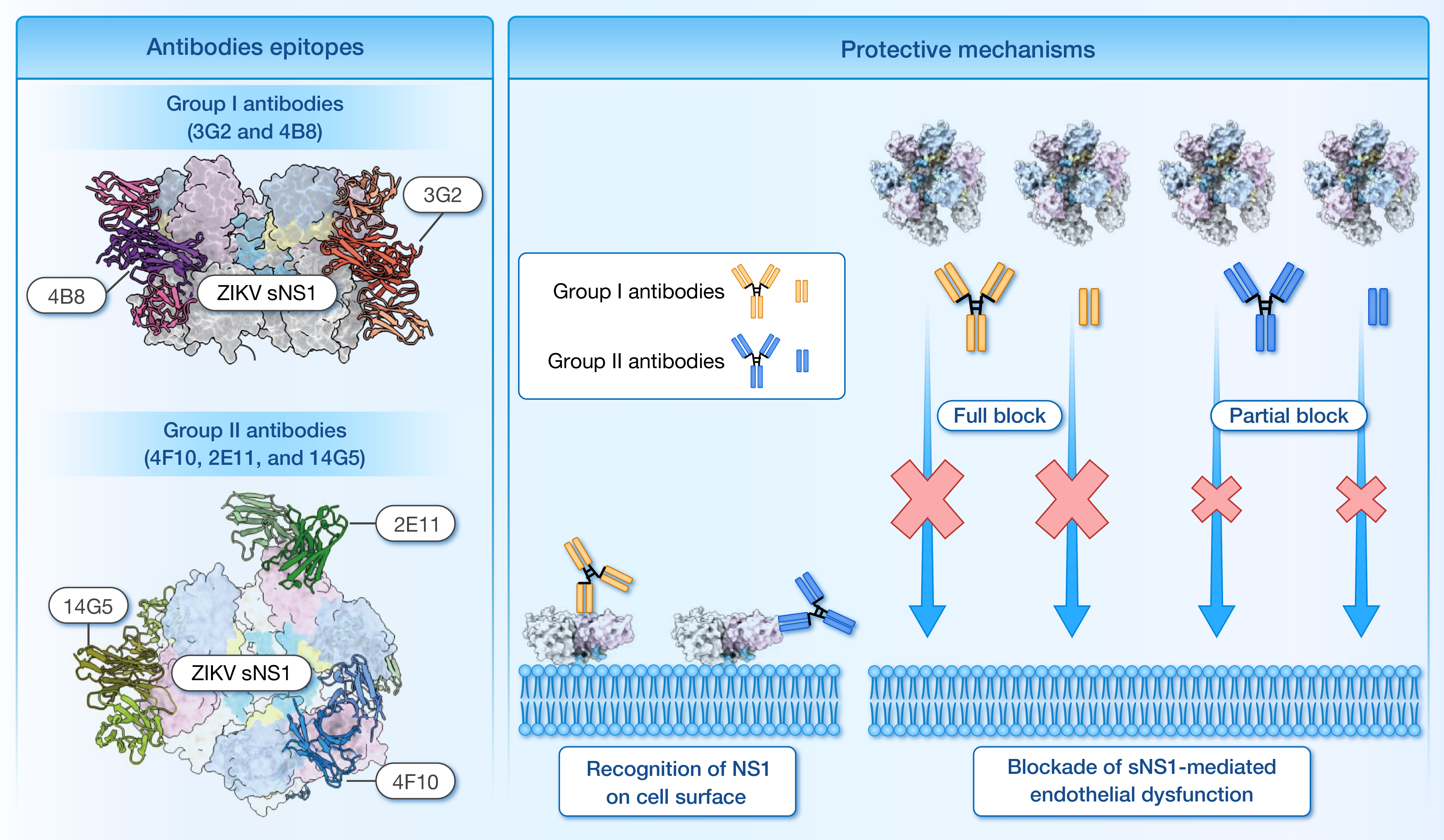
引用:
Pan Q, Xing X, Yu J, et al. Structural insights into the distinct protective mechanisms of human antibodies targeting ZIKV NS1. hLife 2024; 2: 527–541.
6. Nasal mucosal secretory immunoglobulin A but not serum antibodies is resistant to Omicron evasionhLife | 鼻黏膜 sIgA 抗体具更强广谱中和能力,且更不容易被奥密克戎变异株逃逸
通讯作者:李锋、陈凌

本研究发现鼻黏膜 sIgA 比血清抗体具有更强且更广谱的中和活性,凸显了上呼吸道黏膜 sIgA 在预防新冠病毒感染方面的重要作用,也为设计能有效诱导上呼吸道产生sIgA的鼻喷疫苗提供了依据。
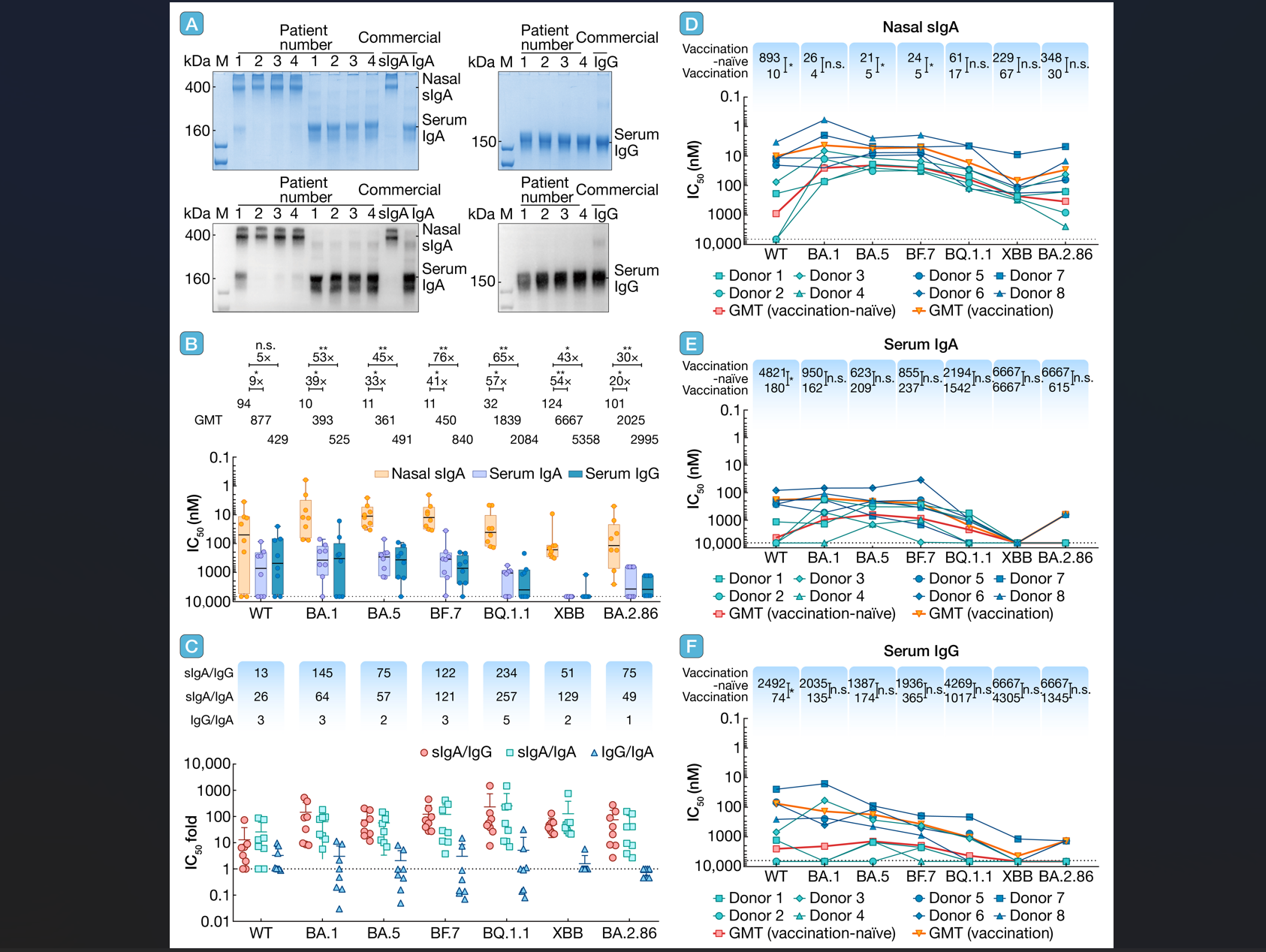
引用:
Chen S, Zhang Z, Wang Q, et al. Nasal mucosal secretory immunoglobulin A but not serum antibodies is resistant to Omicron evasion. hLife 2024; 2: 488–491.
7. Lycorine derivative effectively inhibits the replication of coronaviruses both in vitro and in vivo
通讯作者:殷利眷、杨扬、王春花

Highlights
Lycorine derivatives, including Ly-8, were designed and synthesized to reduce cytotoxicity in anti-coronavirus experiments.
Ly-8 inhibits various coronaviruses, including severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, in vitro.
Ly-8 did not result in any drug-resistant mutant viruses during long-term in vitro passages.

引用:
Shen L, Zhao J, Xia Y, et al. Lycorine derivative effectively inhibits the replication of coronaviruses both in vitro and in vivo. hLife 2024; 2: 75–87.
通讯作者:王奇慧
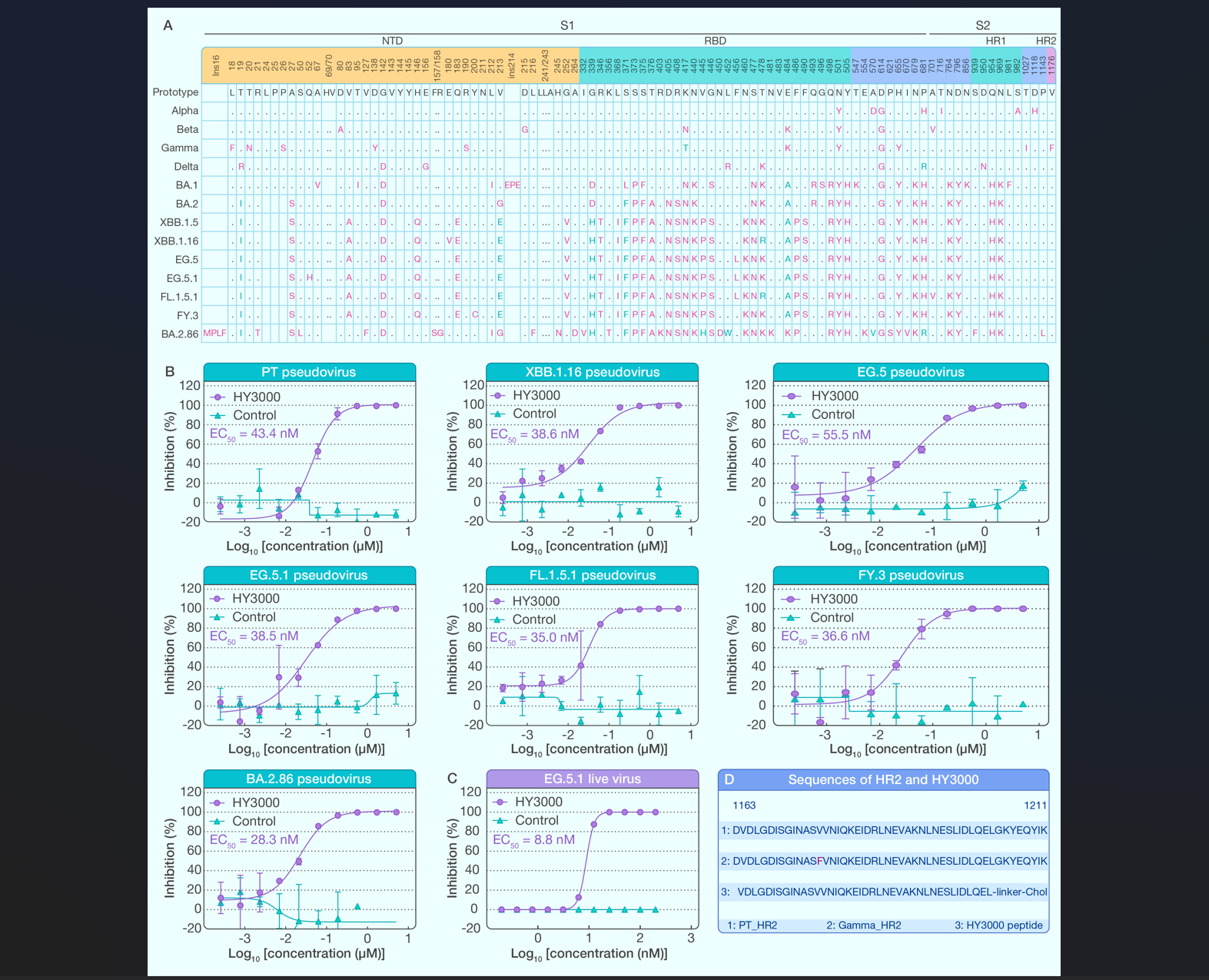
HY3000, which has shown significant inhibitory activities against SARS-CoV-2 and all tested variants, including XBB.1.5/XBB.1.9.1/XBB.1.9.2, and has completed Phase II clinical trials in China. HY3000 peptide exhibited comparable inhibitory potencies against EG.5 and EG.5.1, with half-maximal effective concentration (EC50) values of ~50 nM, and also displayed similar inhibitory activities against XBB.1.16, FL.1.5.1, and FY.3 strains. Notably, HY3000 showed slightly higher inhibitory activity against BA.2.86, with anEC50 value of 28.3 nM. HY3000 also potently inhibited live EG.5.1 strain, with an EC50 of 8.8 nM. These results suggest that the HY3000 peptide fusion inhibitor has a potential broad-spectrum antiviral effect against current and future SARS-CoV-2 variants and sub-variants.
引用:
Wu L, Zheng A, Tang Y, et al. Efficient inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 emerging EG.5, EG.5.1 and BA.2.86 variants by fusion inhibitor HY3000 peptide. hLife 2024; 2: 43–46.
9. Tip optofluidic immunoassay: Evaluating COVID-19 antibody protection with 1 μL fingertip blood
通讯作者:谭骁天、柴语鹃、郑海荣、范旭东、谢良志、曹云龙、杨慧

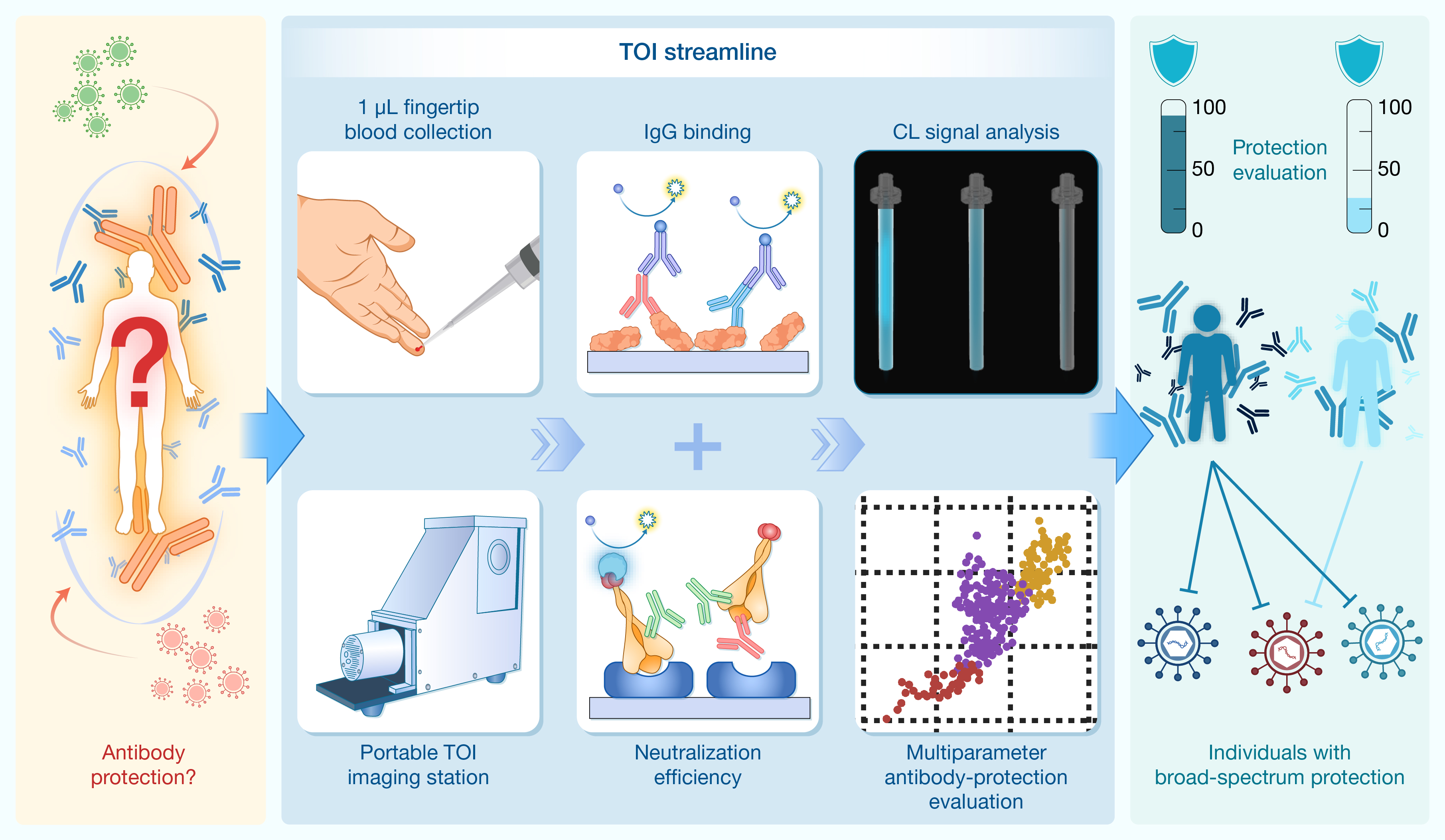
本研究团队成功研发出一种便携式微流控化学发光免疫分析平台(Tip Optofluidic Immunoassay,简称TOI)。只需1微升指尖血,研究人员就能利用TOI平台在40分钟内完成抗体结合能力和中和能力等多维度免疫指标的快速定量评估,为传染病防控与免疫防护能力监测提供了先进技术手段。
引用:
Tan X, Chai Y, Li R, et al. Tip optofluidic immunoassay: Evaluating COVID-19 antibody protection with 1 μL fingertip blood. hLife 2025; 3: 338–356.
hLife | 中国科学院高福院士团队开发BAADesign:赋能埃特司韦单抗破解新冠Omicron
通讯作者:杨梦苏、高福

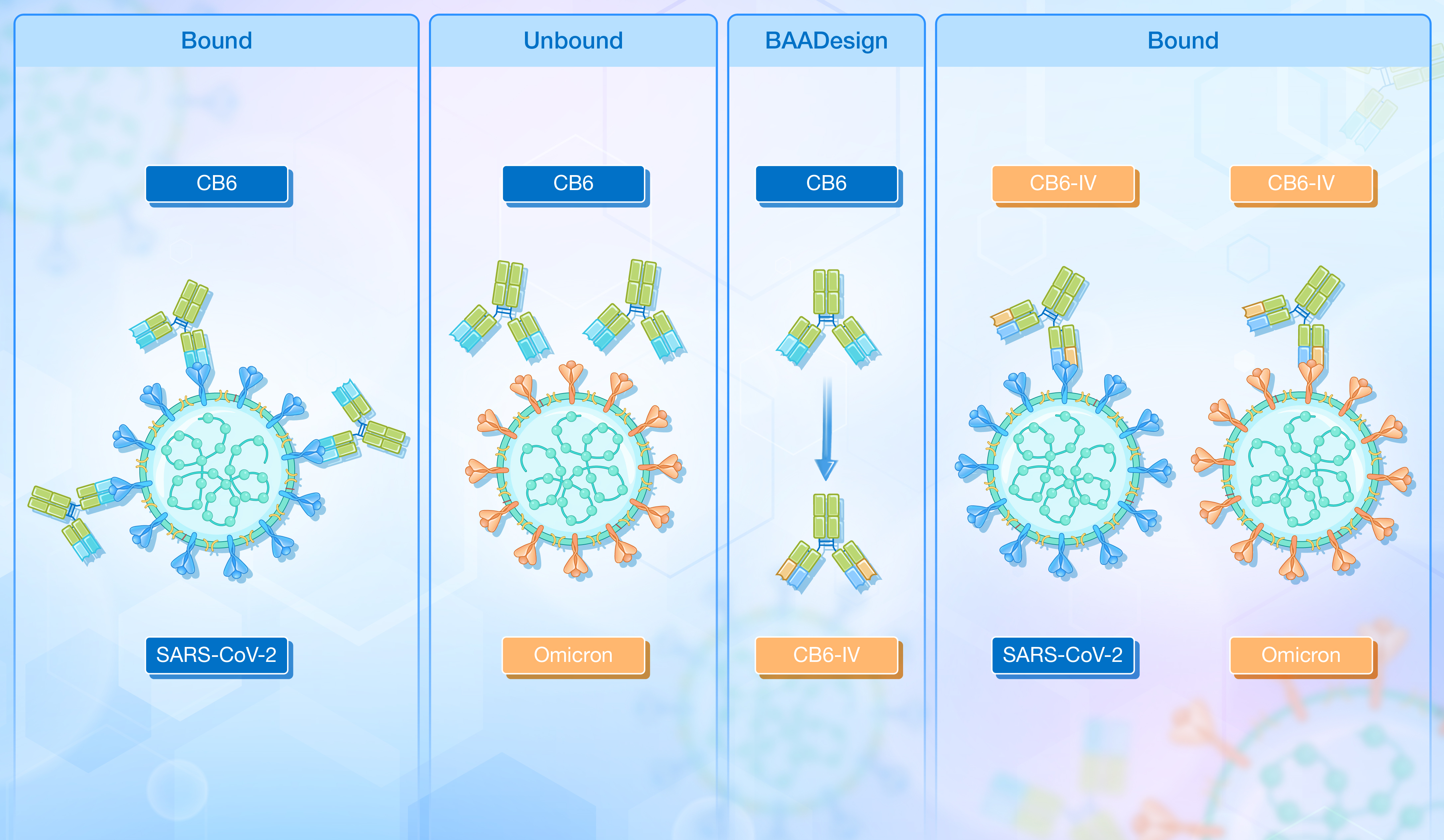
本研究提出了一种基于骨架和序列设计的广谱亲和力成熟抗体开发策略,称为 BAADesign。BAADesign为恢复失效抗体活性提供了全新的思路。通过骨架与序列设计相结合,这一策略赋能了埃特司韦单抗,使其重新获得对Omicron子代变异株的中和能力,也为其他抗体药物的改造提供了范例。未来,这一方法有望为应对新冠病毒及其他快速变异的病原体提供强有力的技术支持。
引用:
Su C, He J, Xie Y, et al. Enabling the immune escaped etesevimab fully-armed against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants including KP.2. hLife 2025; 3: 132–145.
11. Selection and engineering of broad-spectrum antiviral affibody peptides against SARS-CoV-2 variants
通讯作者:Christopher John Hipolito、齐建勋、施一
In summary, we successfully identified ZSpike:2, a broad-spectrum antiviral affibody targeting SARS-CoV-2 S protein, through mRNA display technology. To improve its neutralizing potency, ZSpike:2 was structurally optimized using three multimerization engineering strategies: a (GGGGS)3-linked homodimer, (ZSpike:2)2 fused with the Fc region of IgG1, and a self-assembled ferritin nanoparticle displaying the (ZSpike:2)2-Fc. The nanoparticle-conjugated construct, (ZSpike:2)2-Fc-ferritin, exhibited broad-spectrum neutralizing activity against all tested SARS-CoV-2 variants, indicating that it has acquired novel neutralization mechanism compared with the (ZSpike:2)2-Fc. We propose that this modification allows (ZSpike:2)2-Fc to assemble into multimeric structures, enhancing its binding avidity to the S protein. Additionally, when (ZSpike:2)2-Fc-ferritin specifically binds to the S protein, the increasing size of (ZSpike:2)2-Fc-ferritin could result in steric hindrance and further block interactions between S protein and ACE2. Moreover, the increasing size of (ZSpike:2)2-Fc-ferritin likely contributes to its broad-spectrum activity by conferring an alternative functional mechanism. This modification strategy is not only applicable to ZSpike:2 but can also be extended to other antiviral protein-binder agents, such as monobodies and nanobodies. Furthermore, the approach of conjugating different antiviral agents with nanoparticles holds promise for developing novel broad-spectrum antiviral drugs. Future studies will assess the in vivo efficacy of (ZSpike:2)2-Fc-ferritin and explore its underlying antiviral mechanisms.
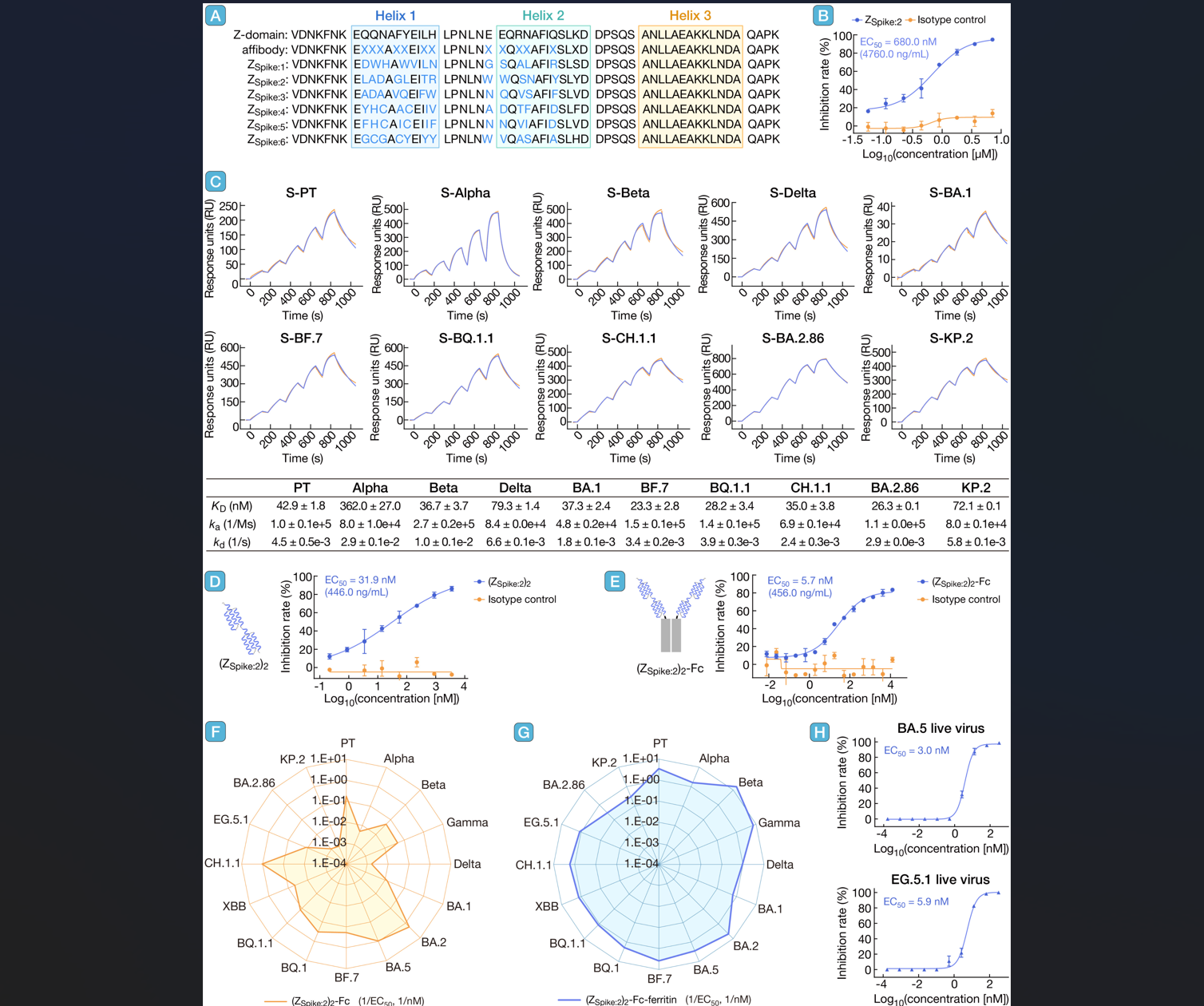
引用:
Yang J, Wang M, Chen Z, et al. Selection and engineering of broad-spectrum antiviral affibody peptides against SARS-CoV-2 variants. hLife 2025; 3: 448–451.
hLife | 高福院士等研究团队获得一种靶向呼吸道合胞病毒保守表位的保护性单克隆抗体
通讯作者:谢正德、邬征、高福

本研究从康复儿童的体内分离到了两个针对RSV融合蛋白(F)的中和性单克隆抗体。其中1个抗体RV11显示了很高的中和活性,能中和A和B两种基因型的RSV,活性较帕利珠单抗大幅提高。小鼠攻毒试验显示,预防性注射RV11能够保护RSV对肺部的感染,其体内保护活性相较于帕利珠单抗提高了约6.3倍。晶体结构解析揭示这个抗体结合在F蛋白融合前构象的表位,横跨IV和V号位点。该表位在A和B基因型RSV中都非常保守,使得RV11不易于被病毒所逃逸,有利于临床使用。
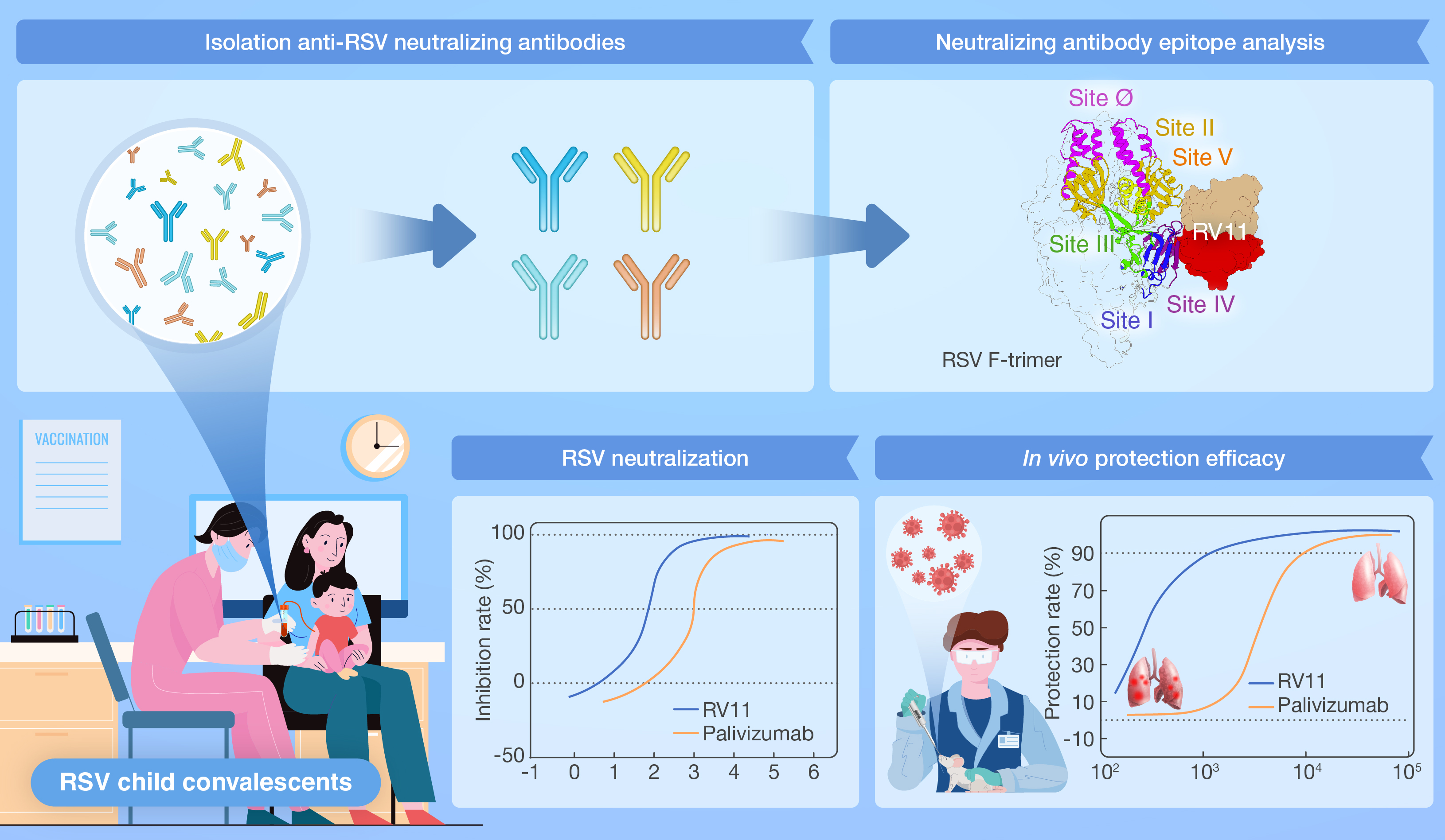
引用:
Dai L, Song J, Xu L, et al. A protective human antibody against respiratory syncytial virus by targeting a prefusion epitope across sites IV and V of the viral fusion glycoprotein. hLife 2023; 1: 12–25.
期刊简介
hLife 由高福院士、董晨院士和Jules A. Hoffmann教授(2011诺奖获得者)领衔,是中国科学院微生物研究所主办,中国生物工程学会,浙江大学陈廷骅大健康学院,西湖大学医学院,上海市免疫治疗创新研究院和广州霍夫曼免疫研究所联合支持,与国际出版商爱思唯尔合作的健康科学领域综合性英文期刊。
hLife 聚焦健康科学领域的前沿进展,旨在促进基础研究与临床应用的融合发展。期刊发表与医学相关各研究领域最新成果,学科领域包括(但不限于)病原生物学、流行病学、生理学、免疫学、结构生物学、疾病监测、肿瘤、药物、疫苗和健康政策等。
hLife是一本金色开放获取期刊,月刊出版;2022年成功入选“中国科技期刊卓越行动计划高起点新刊”;2023年11月正式创刊;2024年5月被DOAJ收录;2024年8月被Scopus收录;2024年10月入选“首都科技期刊卓越行动计划——重点英文科技期刊支持项目”;2025年6月入选北京市科委“2025年度支持高水平国际科技期刊建设-强刊提升”项目;2025年8月入选中国科学引文数据库(CSCD)核心库。
hLife实行高标准与高效率并重的同行评审机制:
投稿至给出“是否送审”决定⏰1天
投稿至给出“首轮审稿”决定⏰28天
投稿至给出“是否录用”决定⏰61天
2026年前hLife接收的稿件免收文章处理费(APC)。
https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/hlife
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-3552961-1507963.html
上一篇:[转载]hLife collection | Organoids
下一篇:[转载]高福院士:科普是一种“社会疫苗”