博文
拓扑绝缘体中的奇偶校验异常  精选
精选
||
拓扑绝缘体中的奇偶校验异常
诸平
据德国维尔茨堡大学(University of Würzburg / Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg, Am Hubland, Würzburg, Germany)2024年3月26日提供的消息,该校的研究人员与来自德国维尔茨堡拓扑绝缘体研究所(Institute for Topological Insulators, Am Hubland, Würzburg, Germany)的实验和理论物理学家合作,观察到碲化汞(mercury telluride)器件中的可重入量子霍尔效应(re-entrant quantum Hall effect),并将其识别为奇偶异常的标志(Parity Anomaly Demonstrated in a Topological Insulator)。
拓扑绝缘体(Topological insulators)是一种可以导电的材料,但只能在其表面或边缘导电,里面没有电流。它们是世界范围内深入研究的主题,因为它们具有独特的电子特性,例如,对于提高量子计算机的效率以及加密和数据安全传输等其他技术很感兴趣。相关研究结果于2024年3月13日已经在《先进科学》(Advanced Science)杂志网站发表——Li-Xian Wang, Wouter Beugeling, Fabian Schmitt, Lukas Lunczer, Julian-Benedikt Mayer, Hartmut Buhmann, Ewelina M. Hankiewicz, Laurens W. Molenkamp. Spectral Asymmetry Induces a Re-Entrant Quantum Hall Effect in a Topological Insulator. Advanced Science, 2024. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202307447. First published: 13 March 2024.
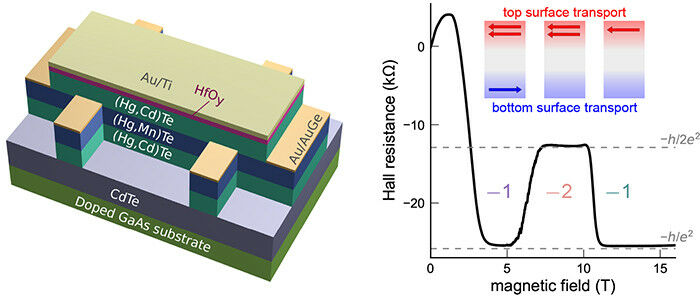
来自维尔茨堡大学(Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg简称JMU)的拓扑绝缘体研究所和理论物理与天文学研究所(Institute for Theoretical Physics and Astronomy)的研究人员,现在展示了一种不寻常的量子霍尔效应(quantum Hall effect),这种效应是在由拓扑绝缘体材料碲化汞(HgTe)制成的微观装置上观察到的。
清晰的实验观察(Clear Experimental Observation)
在碲化汞装置中,顶部和底部表面的电子表现为相对论性狄拉克粒子(relativistic Dirac particles)。正如预测的那样,狄拉克粒子应该受到所谓的宇称异常(parity anomaly)的影响,但没有得到粒子物理学的实验验证。在固态实验中,宇称异常会导致一种称为光谱不对称(spectral asymmetry)的效应,这种效应可以通过电阻的异常变化来测量。
“自20世纪80年代以来,人们就预测固态材料中会出现宇称异常。一个著名的理论建议是2016年诺贝尔物理学奖(The Nobel Prize in Physics 2016)得主邓肯·霍尔丹(F. Duncan M. Haldane)提出的模型。我们已经确定了宇称异常的另一个结果,这是第一个通过实验验证的结果,”埃维莉娜·汉凯威克兹(Ewelina Hankiewicz)教授说。
影响并不仅仅局限于碲化汞(Effect is not Specific to Just Mercury Telluride)
JMU的物理学家已经在三维拓扑绝缘体的单个表面上实现了二维狄拉克物理(two-dimensional Dirac physics)。“我们观察到一种非常规的可重入量子霍尔效应,它与单一拓扑表面状态下光谱不对称的发生直接相关。这种效应对任何拓扑绝缘体都是通用的,而不仅仅局限于碲化汞。结果的普遍性使其如此令人兴奋,”沃特·贝格林博士(Dr. Wouter Beugeling)说。
这些新发现必须克服两个挑战。首先,必须在测量电阻的其他特征中识别光谱不对称的特征。其次,该装置必须以这样一种方式控制,即来自两个表面的影响不会相互抵消。
高水平的控制允许进一步的探索(High Level of Control Allows Further Explorations)
劳伦斯·莫伦坎普教授(Professor Laurens Molenkamp)说:“这一观察表明,在这种设备中,我们拥有的高水平控制使我们能够探索拓扑绝缘体物理中比以前更有趣的方面。”
达到实验精度要求的一个关键因素是高质量的HgTe材料,它是在维尔兹堡物理研究所(Würzburg Institute of Physics)的分子束外延(molecular beam epitaxy简称MBE)设施中生产的。MBE是一种生产具有定制电子、光学和磁性质的晶圆薄层材料的技术。利用MBE,可以一个原子层一个原子层地精确地构建层结构。
ct.qmat卓越集群(Cluster of Excellence ct.qmat)
上述论文的合著者有来自德国量子物质的复杂性和拓扑结构(Complexity and Topology in Quantum Matter简称ct.qmat)卓越集群(Cluster of Excellence ct.qmat)的研究人员。自2019年以来,量子物质的复杂性和拓扑结构(ct.qmat)由维尔兹堡大学和德累斯顿工业大学{Technische Universität (TU) Dresden}联合运行。ct.qmat是由德国联邦和州政府的卓越战略(German Excellence Strategy of the Federal and State Governments)资助的。
本研究得到了德国研究基金会{Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft(DFG, German Research Foundation) through the Leibniz Program and through the projects SFB 1170 (Project ID 258499086) and SPP 1666 (Project ID 220179758)}、欧洲研究理事会{ EU ERC-AdG program (Project 4-TOPS)}、维尔兹堡-德累斯顿量子物质的复杂性和拓扑结构卓越集群{Würzburg-Dresden Cluster of Excellence on Complexity and Topology in Quantum Matter (EXC 2147, Project ID 39085490)}、德国巴伐利亚自由州拓扑绝缘体研究所(Free State of Bavaria for the Institute for Topological Insulators)的资助或支持。
上述介绍,仅供参考。欲了解更多信息,敬请注意浏览原文或者相关报道。
The band inversion of topological materials in three spatial dimensions is intimately connected to the parity anomaly of 2D massless Dirac fermions, known from quantum field theory. At finite magnetic fields, the parity anomaly reveals itself as a non-zero spectral asymmetry, i.e., an imbalance between the number of conduction and valence band Landau levels, due to the unpaired zero Landau level. This work reports the realization of this 2D Dirac physics at a single surface of the 3D topological insulator (Hg,Mn)Te. An unconventional re-entrant sequence of quantized Hall plateaus in the measured Hall resistance can be directly related to the occurrence of spectral asymmetry in a single topological surface state. The effect should be observable in any topological insulator where the transport is dominated by a single Dirac surface state.
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-212210-1427158.html
上一篇:超越血糖控制:治疗糖尿病的新目标揭晓
下一篇:新型拓扑超材料可成倍放大声波