博文
发现可能治疗ER+乳腺癌的候选药物
||
发现可能治疗ER+乳腺癌的候选药物
诸平
据澳大利亚莫纳什大学(Monash University)2023年12月20日提供的消息,该校研究人员发现了可能治疗雌激素受体(Estrogen Receptor简称ER)阳性乳腺癌(ER-positive breast cancer简称ER+breast cancer)的候选药物(Discovery of drug candidate to potentially tackle ER-positive breast cancer)。
全球每年约有230万人被诊断患有乳腺癌(Breast cancer)。2020年,乳腺癌在全球造成68.5万人死亡。大约一半的乳腺癌发生在除了性别和年龄之外没有其他特定风险因素的女性身上。乳腺癌在世界各国都有发生。但是,也有大约0.5%的乳腺癌发生在男性身上。在一些ER+乳腺癌患者中发现了一种叫做KAT6A的酶的失调,导致了不良的患者预后。然而,靶向KAT6A的药物的发现仍然是一个挑战。CTx-648的发现为靶向KAT6A治疗ER+乳腺癌提供了新的机会。
由辉瑞公司(Pfizer)领导的一个国际研究小组,与莫纳什大学和澳大利亚癌症治疗合作研究中心(Australian-based Cancer Therapeutics Cooperative Research Centre简称Cancer Therapeutics CRC)合作,发现了一种临床前候选药物,在ER+乳腺癌模型中显示出抗肿瘤活性。相关研究结果于2023年8月8日已经在《细胞化学生物学》(Cell Chemical Biology)杂志网站发表,2023年10月19日同样在《细胞化学生物学》(Cell Chemical Biology)杂志网站发表了一篇美国作者撰写的评论详见:
Shikhar Sharma, Chi-Yeh Chung, Sean Uryu, Jelena Petrovic, Joan Cao, Amanda Rickard, Nataliya Nady, Samantha Greasley, Eric Johnson, Oleg Brodsky, Showkhin Khan, Hui Wang, Zhenxiong Wang, Yong Zhang, Konstantinos Tsaparikos, Lei Chen, Anthony Mazurek, John Lapek, Pei-Pei Kung, Scott Sutton, Paul F Richardson, Eric C Greenwald, Shinji Yamazaki, Rhys Jones, Karen A Maegley, Patrick Bingham, Hieu Lam, Alexandra E Stupple, Aileen Kamal, Anderly Chueh, Anthony Cuzzupe, Benjamin J Morrow, Bin Ren, Catalina Carrasco-Pozo, Chin Wee Tan, Dharmesh D Bhuva, Elizabeth Allan, Elliot Surgenor, François Vaillant, Havva Pehlivanoglu, Hendrik Falk, James R Whittle, Janet Newman, Joseph Cursons, Judy P Doherty, Karen L White, Laura MacPherson, Mark Devlin, Matthew L Dennis, Meghan K Hattarki, Melanie De Silva, Michelle A Camerino, Miriam S Butler, Olan Dolezal, Patricia Pilling, Richard Foitzik, Paul A Stupple, H Rachel Lagiakos, Scott R Walker, Soroor Hediyeh-Zadeh, Stewart Nuttall, Sukhdeep K Spall, Susan A Charman, Theresa Connor, Thomas S Peat, Vicky M Avery, Ylva E Bozikis, Yuqing Yang, Ming Zhang, Brendon J Monahan, Anne K Voss, Tim Thomas, Ian P Street, Sarah-Jane Dawson, Mark A Dawson, Geoffrey J Lindeman, Melissa J Davis, Jane E Visvader, Thomas A Paul. Discovery of a highly potent, selective, orally bioavailable inhibitor of KAT6A/B histone acetyltransferases with efficacy against KAT6A-high ER+ breast cancer. Cell Chemical Biology, 2023 Oct 19; 30(10): 1191-1210. e20. DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.07.005. Epub 2023 Aug 8.
参与此项研究的有来自美国辉瑞公司(Pfizer, Oncology Research & Development, San Diego, CA, USA)、澳大利亚癌症治疗合作研究中心(Cancer Therapeutics CRC, Melbourne, VIC, Australia)、澳大利亚莫纳什大学(Monash University, Parkville, VIC, Australia)、澳大利亚墨尔本CANThera 发现(CANThera Discovery, Melbourne, VIC, Australia)、澳大利亚沃尔特和伊丽莎霍尔医学研究所(The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, Parkville, VIC, Australia)、合成医学化学(澳大利亚)有限公司{ SYNthesis Med Chem (Australia) Pty Ltd, Bio21 Institute, Parkville, VIC, Australia}、澳大利亚联邦科学和工业研究组织(Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation简称CSIRO, Parkville, VIC, Australia)、澳大利亚格里菲斯大学(Griffith University, Brisbane QLD, Australia)、澳大利亚墨尔本大学(University of Melbourne, Parkville, VIC, Australia)、澳大利亚彼得·麦卡勒姆癌症中心(Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, Melbourne VIC, Australia)、澳大利亚墨尔本的肿瘤学I有限公司(OncologyOne Pty Ltd, Melbourne, VIC, Australia)、澳大利亚儿童癌症研究所(Children's Cancer Institute, Randwick, NSW, Australia)、澳大利亚新南威尔士大学(University of New South Wales, Randwick, NSW, Australia)以及澳大利亚皇家墨尔本医院和彼得·麦卡勒姆癌症中心帕克维尔家族癌症中心和肿瘤内科(Parkville Familial Cancer Centre and Department of Medical Oncology, The Royal Melbourne Hospital and Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, Parkville, VIC, Australia)的研究人员。
评论文章详见:Rinath Jeselsohn, Kornelia Polyak. HATS off to KAT6A/B inhibitors: A new way to target estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer. Cell Chemical Biology, 2023, 30(10): 1183-1185. DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.08.006. Pub Date: 19 October 2023.
参与此评论的有来自美国波士顿的丹娜-法伯癌症研究所(Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA, USA)、美国波士顿的布里格姆妇女医院(Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, MA, USA)以及美国哈佛医学院(Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA)的研究人员。
上述第一篇论文描述了一种高效、选择性和口服生物可利用的KAT6A/B抑制剂CTx-648的鉴定,该抑制剂在小鼠ER+乳腺癌模型中具有很好的肿瘤生长抑制作用。
该来自辉瑞和澳大利亚的研究人员团队还发现,CTx-648治疗导致对激素治疗有抵抗力的肿瘤具有抗肿瘤活性,激素治疗是ER+乳腺癌患者的常用治疗方法。因此,CTx-648的发现为靶向KAT6A治疗ER+乳腺癌患者提供了一个令人兴奋的新机会。
莫纳什制药科学研究所(Monash Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences简称MIPS)药物化学主任和研究合著者Paul Stupple教授说:“CTx-648是一种有效的,选择性的,口服生物可利用的KAT6A抑制剂,它在ER+乳腺癌的临床前模型中显示出抗肿瘤活性,包括对激素治疗有抗性的肿瘤,这是令人难以置信的令人兴奋。KAT6A是一种有助于调节体内多种化学过程的酶。然而,KAT6A的失调已经在几种癌症中被发现,包括乳腺癌,其中KAT6A基因的扩增可能发生。”
澳大利亚癌症治疗合作研究中心(CRC)的前首席科学官,现任MIPS澳大利亚MedChem主任(Director of MedChem Australia)布伦登·蒙纳罕教授( Professor Brendon Monahan)评论说:“乳腺癌中的KAT6A扩增与总体生存率低有关,对乳腺癌患者数据集的分析表明,KAT6A扩增发生在6%~ 11%的肿瘤中。KAT6A扩增的肿瘤与较短的无进展生存期和总生存期密切相关。”
布伦登·蒙纳罕教授教授说:“激素疗法仍然是治疗ER+乳腺癌患者的主要方法,然而,对这一疗法的耐药性最终会出现,这凸显了针对这类肿瘤的新疗法的必要性。”
来自莫纳什大学莫纳什制药科学研究所候选药物优化中心(Centre for Drug Candidate Optimisation)的团队是MIPS的五个研究主体之一,由苏珊·查曼教授( Professor Susan Charman)领导,他们在分析候选化合物的物理化学、代谢和药代动力学特性方面发挥了关键作用,为化合物优化的药物化学设计策略提供了信息。
苏珊·查曼教授教授说:“与以前鉴定的KAT6抑制剂相比,CTx-648在效力、选择性和药物样特性方面有显著改善。CTx-648在临床前模型中显示出强大的靶向体内疗效,包括肿瘤消退,毒性最小,突出了这种新疗法在治疗乳腺癌患者方面的前景。”
癌症治疗合作研究中心常务董事(Managing Director of Canthera Discovery formally Cancer Therapeutics CRC )艾伦·罗伯森博士(Dr Alan Robertson)说:“这项研究是整个团队的努力,包括莫纳什大学和辉瑞在内的癌症治疗合作研究中心(Cancer Therapeutics CRC)合作伙伴的合作,是多学科团队合作如何产生不可思议影响的一个例证。”
由来自WEHI, MIPS和癌症治疗合作研究中心的研究人员组成的团队领导的此项研究,通过他们对KAT6A和KAT6B是否可能成为治疗癌症的新方法的研究{此研究2018年发表于《自然》(The study was published in Nature in 2018)},为CTx-648的发现铺平了道路。
CTx-648随后由MIPS研究人员于2018年发明,是癌症治疗合作研究中心( Cancer Therapeutics CRC)与辉瑞公司( Pfizer )达成的数百万美元许可协议的一部分,并导致候选药物PF-07248144于2020年进入I期临床试验。
Paul Stupple教授说:“对于ER+乳腺癌,迫切需要新的安全有效的治疗方法,使我们团队感到很兴奋的是KAT6A抑制剂目前正处于I期临床试验。”
该研究由辉瑞研究员希卡尔·沙玛博士(Dr Shikhar Sharma)和辉瑞高级主管托马斯·保罗博士(Dr Thomas Paul)领导。MIPS团队包括来自药物化学和候选药物优化中心(Medicinal Chemistry and the Centre for Drug Candidate Optimisation)的药物研究人员。完整的作者名单可以在此(here)找到。
上述介绍,仅供参考。欲了解更多信息,敬请注意浏览原文或者相关报道。
Highlights(DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.07.005)
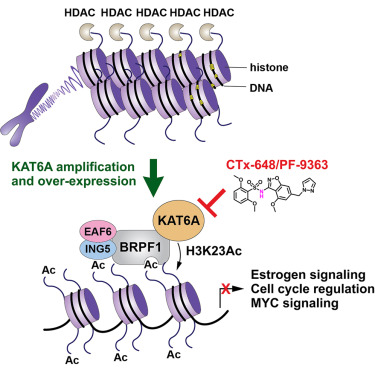
• Discovery of CTx-648/PF-9363: a potent, selective, orally bioavailable KAT6A/B inhibitor
• CTx-648/PF-9363 inhibits H3K23Ac leading to growth suppression in breast cancer models
• CTx-648/PF-9363 anti-tumor activity enriches in ER+/luminal & KAT6A high breast cancer
• In ER+ breast cancer, CTx-648/PF-9363 represses ER, cell cycle, Myc and stem cell pathways
Summary(DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.07.005)
KAT6A, and its paralog KAT6B, are histone lysine acetyltransferases (HAT) that acetylate histone H3K23 and exert an oncogenic role in several tumor types including breast cancer where KAT6A is frequently amplified/overexpressed. However, pharmacologic targeting of KAT6A to achieve therapeutic benefit has been a challenge. Here we describe identification of a highly potent, selective, and orally bioavailable KAT6A/KAT6B inhibitor CTx-648 (PF-9363), derived from a benzisoxazole series, which demonstrates anti-tumor activity in correlation with H3K23Ac inhibition in KAT6A over-expressing breast cancer. Transcriptional and epigenetic profiling studies show reduced RNA Pol II binding and downregulation of genes involved in estrogen signaling, cell cycle, Myc and stem cell pathways associated with CTx-648 anti-tumor activity in ER-positive (ER+) breast cancer. CTx-648 treatment leads to potent tumor growth inhibition in ER+ breast cancer in vivo models, including models refractory to endocrine therapy, highlighting the potential for targeting KAT6A in ER+ breast cancer.
Graphical abstract(DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.07.005)
Abstract(DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.08.006)
Inhibitors for the KAT6 family of histone acetyltransferases (HATs) have been actively pursued due to the oncogenic roles of KAT6A in human cancer. CTx-648 is a novel KAT6A/B inhibitor with excellent pharmacokinetic properties and in vivo efficacy that represents a promising new treatment strategy for estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer.
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-212210-1414835.html
上一篇:乌得勒支化学家发现了设计更可持续的分子催化剂的机制
下一篇:高效生产H2O2和生物质提升的电催化剂突破
