博文
高效生产H2O2和生物质提升的电催化剂突破
||
高效生产H2O2和生物质提升的电催化剂突破
诸平
Fig. 1 New Approach Developed for Electrocatalytic H2O2 Production and Biomass Upgrading. Credit: Hui Xu
据《科技日报》(SciTechDaily)网站2023年12月21日报道中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院(Hefei Institutes Of Physical Science, Chinese Academy Of Sciences)提供的消息,高效生产H2O2和生物质提升的电催化剂有了突破性进展(Electrocatalyst Breakthrough for Efficient H2O2 Production and Biomass Upgrading)。相关研究结果于2023年11月9日已经在《应用化学国际版》(Angewandte Chemie International Edition)杂志网站发表——Hui Xu, Dr. Shengbo Zhang, Xinyuan Zhang, Min Xu, Dr. Miaomiao Han, Prof. Li Rong Zheng, Prof. Yunxia Zhang, Prof. Guozhong Wang, Prof. Haimin Zhang, Prof. Huijun Zhao. Atomically Dispersed Iron Regulating Electronic Structure of Iron Atom Clusters for Electrocatalytic H2O2 Production and Biomass Upgrading., Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 09 November 2023. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202314414. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202314414
中国科学家发明了一种新型的氧配位铁原子电催化剂,显著提高了H2O2的产量和生物质的升级。这种催化剂标志着可持续化学合成的重要一步。
中国科学院合肥物理科学研究院(Hefei Institutes of Physical Science简称HFIPS)的科学家合成了一种氧配位铁单原子和原子团簇催化剂,在H2O2生产和生物质升级方面表现出优异的电催化性能。
H2O2与电催化的意义(The Significance of H2O2 and Electrocatalysis)
过氧化氢(H2O2)是一种广泛使用的化学品,在环境、能源和医疗保健等各个领域都有应用。电催化合成是一种使用水和氧气的更环保、更高效的方法,而传统的制造方法是通过能源密集型工艺进行的。然而,这种方法需要先进的电催化剂来实现高收率和选择性的H2O2生产,并且需要进一步关注所产生的H2O2的利用,特别是在电化学有机氧化过程中。这为环境修复以外的增值应用提供了巨大的潜力。
创新催化剂开发流程(Innovative Catalyst Development Process)
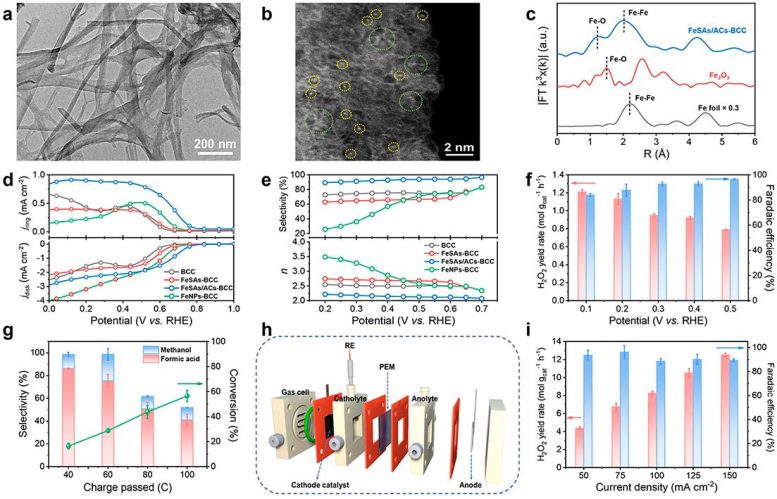
在这项研究中,科学家们利用细菌纤维素作为吸附调节剂和碳源,结合湿化学浸渍、热解和酸蚀等多步骤工艺,制备了一种名为FeSAs /ACs-BCC的催化剂,该催化剂由氧配位铁单原子和原子团簇组成。利用先进的成像技术,如像差校正扫描透射电子显微镜(aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy),证实了铁单原子和团簇的存在。利用X射线精细结构吸收光谱(X-ray fine structure absorption spectroscopy)和X射线光电子能谱(X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy)测定了Fe的原子结构。
卓越的电催化性能(Exceptional Performance in Electrocatalysis)
该催化剂在碱性条件下对2电子氧还原反应(2-electron oxygen reduction reaction简称2e-ORR)表现出优异的电催化性能和选择性。进一步的氢电池实验证实了电解液中H2O2的积累。
生物质提升的创新(Innovations in Biomass Upgrading)
研究人员以乙二醇(ethylene glycol)为反应物,酸化0.1M Na2SO4为电解液,成功地将原位生成的H2O2与电芬顿工艺(electro-Fenton process)耦合。这导致乙二醇转化率高,甲酸(formic acid)选择性高,表明电芬顿工艺具有通过氧化提升改善生物质原料的潜力。
除此之外,他们还开发了一种基于气体扩散电极的三相流动电池(three-phase flow cell),以进一步提高H2O2的产率。
来自密度泛函理论的见解(Insights from Density Functional Theory)
密度泛函理论分析表明,Fe团簇是2e-ORR过程的实际催化活性位点,Fe单原子与Fe团簇之间的电子相互作用可以显著提高2e-ORR的电催化性能。
对未来催化剂设计的启示(Implications for Future Catalyst Design)
本研究对原子级电催化剂的设计和开发具有重要意义。这些催化剂对于高效的2e-ORR制H2O2和生物质提升至关重要。
上述介绍,仅供参考。欲了解更多信息,敬请注意浏览原文或者相关报道。
The integration of highly active single atoms (SAs) and atom clusters (ACs) into an electrocatalyst is critically important for high-efficiency two-electron oxygen reduction reaction (2e− ORR) to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Here we report a tandem impregnation-pyrolysis-etching strategy to fabricate the oxygen-coordinated Fe SAs and ACs anchored on bacterial cellulose-derived carbon (BCC) (FeSAs/ACs-BCC). As the electrocatalyst, FeSAs/ACs-BCC exhibits superior electrocatalytic activity and selectivity toward 2e− ORR, affording an onset potential of 0.78 V (vs. RHE) and a high H2O2 selectivity of 96.5% in 0.1 M KOH. In a flow cell reactor, the FeSAs/ACs-BCC also achieves high-efficiency H2O2 production with a yield rate of 12.51±0.18 mol gcat−1 h−1 and a faradaic efficiency of 89.4%±1.3% at 150 mA cm−2. Additionally, the feasibility of coupling the produced H2O2 and electro-Fenton process for the valorization of ethylene glycol was explored in detail. The theoretical calculations uncover that the oxygen-coordinated Fe SAs effectively regulate the electronic structure of Fe ACs which are the 2e− ORR active sites, resulting in the optimal binding strength of *OOH intermediate for high-efficiency H2O2 production.
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-212210-1415068.html
上一篇:发现可能治疗ER+乳腺癌的候选药物
下一篇:Hindawi透露撤回8000多篇造文厂“杰作”