博文
减肥突破:科学家发现抑制食欲的天然化合物  精选
精选
||
减肥突破:科学家发现抑制食欲的天然化合物
诸平
据美国贝勒医学院(Baylor College of Medicine)2024年11月15日提供的消息,减肥突破:科学家发现抑制食欲的天然化合物(Weight Loss Breakthrough: Scientists Discover Natural Compound That Suppresses Appetite)。
BHB-Phe是一种新发现的化合物,通过激活特定的大脑神经元来降低食欲和体重。
来自贝勒医学院和斯坦福大学医学院(Stanford University School of Medicine)的研究人员及其合作者发现了一种名为BHB-Phe的新型化合物,这种化合物是由人体自然产生的。他们的研究表明BHB-Phe通过与大脑中的神经元相互作用来调节食欲和体重。相关结果于2024年11月7日已经在《细胞》(Cell)杂志网站发表——Maria Dolores Moya-Garzon, Mengjie Wang, Veronica L. Li, Xuchao Lyu, Wei Wei, Alan Sheng-Hwa Tung, Steffen H. Raun, Meng Zhao, Laetitia Coassolo, Hashim Islam, Barbara Oliveira, Yuqin Dai, Jan Spaas, Antonio Delgado-Gonzalez, Kenyi Donoso, Aurora Alvarez-Buylla, Francisco Franco-Montalban, Anudari Letian, Catherine P. Ward, Lichao Liu, Katrin J. Svensson, Emily L. Goldberg, Christopher D. Gardner, Jonathan P. Little, Steven M. Banik, Yong Xu, Jonathan Z. Long. A β-hydroxybutyrate shunt pathway generates anti-obesity ketone metabolites. Cell, 2024 Nov 7: S0092-8674(24)01214-5. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.10.032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2024.10.032
参与此项研究的有美国斯坦福大学(Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA)、美国休斯顿的贝勒医学院(Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX, USA)、丹麦哥本哈根大学(University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark)、加拿大不列颠哥伦比亚大学(University of British Columbia, Kelowna, BC, Canada)、西班牙格拉纳达大学(Universidad de Granada, Campus de Cartuja sn, Granada, Spain)以及美国加州大学旧金山分校(University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA)的研究人员。
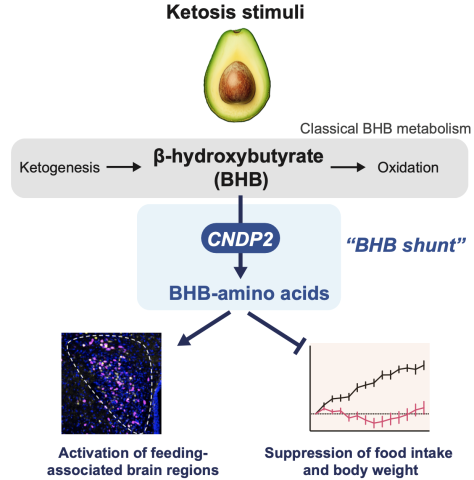
到目前为止,β-羟基丁酸酯{β-Hydroxybutyrate(BHB)}一直被认为是肝脏产生的一种用作燃料的化合物。然而,近年来,科学家们发现,在禁食或运动后,BHB在体内的含量会增加,这激发了人们对研究BHB在肥胖和糖尿病方面的潜在有益应用的兴趣。
BHB-Phe及其在代谢中的作用(BHB-Phe and Its Role in Metabolism)
在上述的研究论文中,由共同通讯作者、病理学副教授Jonathan Z. Long博士领导的斯坦福大学研究小组发现BHB还参与另一种代谢途径。在这种情况下,一种叫做CNDP2的酶将BHB与氨基酸连接起来。此外,最丰富的BHB-氨基酸(BHB-amino acid),BHB-Phe,可以影响动物模型的体重和代谢。
贝勒医学院的研究小组由共同通讯作者、美国农业部农业研究局儿童营养研究中心(USDA/ARS Children’s Nutrition Research Center)儿科营养学教授、基础科学副主任徐勇博士(Dr. Yong Xu音译)领导,他们的任务是调查BHB-Phe如何影响老鼠的摄食行为和体重。
徐勇说:“我们知道大脑中的神经元群调节着进食行为,所以我们绘制了整个大脑之图,以确定哪些区域被BHB-Phe激活。我们发现BHB-Phe激活了下丘脑和脑干的神经群,这抑制了进食,减轻了体重。相比之下,转基因小鼠不产生CNDP2,因此缺乏BHB-Phe,吃得更多,体重增加。”
有趣的是,产生BHB-Phe的CNDP2酶也会产生一种被称为Lac-Phe(N-lactoyl-phenylalanine)相关的化合物,这是作者2022年6月中旬发现的——Veronica L. Li, Yang He, Kévin Contrepois, Hailan Liu, Joon T. Kim, Amanda L. Wiggenhorn, Julia T. Tanzo, Alan Sheng-Hwa Tung, Xuchao Lyu, Peter-James H. Zushin, Robert S. Jansen, Basil Michael, Kang Yong Loh, Andrew C. Yang, Christian S. Carl, Christian T. Voldstedlund, Wei Wei, Stephanie M. Terrell, Benjamin C. Moeller, Rick M. Arthur, Gareth A. Wallis, Koen van de Wetering, Andreas Stahl, Bente Kiens, Erik A. Richter, Steven M. Banik, Michael P. Snyder, Yong Xu, Jonathan Z. Long. An exercise-inducible metabolite that suppresses feeding and obesity. Nature, 2022, 606: 785–790. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04828-5. Published: 15 June 2022. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-04828-5.
研究人员在《自然》(Nature)杂志上发表的论文中报告说,Lac-Phe是一种在运动过程中产生的血液化合物,可以减少老鼠的食物摄入和肥胖。但是Lac-Phe和BHB-Phe通过激活大脑中相同的神经元来调节它们的共同作用吗?值得深入研究。
BHB-Phe和Lac-Phe的不同神经通路(Distinct Neural Pathways for BHB-Phe and Lac-Phe)
徐勇说:“我们的分析表明,只有一小部分神经元被这两种化合物激活;大多数被Lac-Phe和BHB-Phe激活的神经元是不同的。这表明,尽管这两种化合物以相似的方式影响摄食行为,但它们通过不同的机制调节这种影响。”
研究结果表明,涉及BHB-Phe的新途径,也存在于人类中,可能在肥胖和其他情况下被破坏,支持进一步研究以更好地了解其机制是必要的。
另一位共同通讯作者Jonathan Z. Long说:“这项工作开辟了许多新的可能性。例如,未来人们有可能在不限制饮食中的碳水化合物的情况下,通过摄入BHB-Phe来减肥。”
上述发表在《细胞》(Cell)杂志上这项研究得到了奈特大脑恢复计划(Knight Initiative for Brain Resilience)和斯坦福大学吴仔人力绩效联盟(Stanford Wu Tsai Human Performance Alliance)敏捷性项目的研究资助,以及其他资金来源详见原文。
上述介绍,仅供参考。欲了解更多信息,敬请注意浏览原文或者相关报道。
Previously Unknown Family of Keto Metabolites Discovered
Unlocking the secrets of ketosis
Researchers discover a new metabolic compound that regulates body weightβ-Hydroxybutyrate (BHB) is an abundant ketone body. To date, all known pathways of BHB metabolism involve the interconversion of BHB and primary energy intermediates. Here, we identify a previously undescribed BHB secondary metabolic pathway via CNDP2-dependent enzymatic conjugation of BHB and free amino acids. This BHB shunt pathway generates a family of anti-obesity ketone metabolites, the BHB-amino acids. Genetic ablation of CNDP2 in mice eliminates tissue amino acid BHB-ylation activity and reduces BHB-amino acid levels. The most abundant BHB-amino acid, BHB-Phe, is a ketosis-inducible congener of Lac-Phe that activates hypothalamic and brainstem neurons and suppresses feeding. Conversely, CNDP2-KO mice exhibit increased food intake and body weight following exogenous ketone ester supplementation or a ketogenic diet. CNDP2-dependent amino acid BHB-ylation and BHB-amino acid metabolites are also conserved in humans. Therefore, enzymatic amino acid BHB-ylation defines a ketone shunt pathway and bioactive ketone metabolites linked to energy balance.
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-212210-1460436.html
上一篇:简单的日常习惯可以让你多活11年
下一篇:量子飞跃:光与声纠缠的创新突破