博文
ABBS: Apolipoprotein A-I inhibits atherosclerosis
|||
Jiyang Li , Weina Wang , Lei Han , Meiqing Feng , Hui Lu , Li Yang , Xiangxiang Hu , Si Shi , Shanshan Jiang , Qian Wang , and Li Ye
Department of Biosynthesis & Key Laboratory of Smart Drug Delivery, Ministry of Education, School of Pharmacy, Fudan University, Shanghai 201203, China,
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 2017, 49: 149–158; doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmw128
Apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) is the major functional protein fraction of high-density lipoprotein. The prophylactic effect and mechanism of human apoA-I on atherosclerosis (AS) were investigated in a high-fat diet-induced AS rabbit model. The rabbits were injected with apoA-I once a week while fed high-fat diet for 20 weeks. Our results showed that apoA-I could raise the serum level of high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol and reduce those of lipid total cholesterol, triglyceride, and low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol in AS rabbits. Decreased aortic plaque area and aortic injury degree were also observed by Oil Red O staining and HE staining in apoA-I-treated high-fat diet-induced AS rabbits. Further study elucidated that apoA-I could down-regulate the expression of some inflammatory mediators including intercellular adhesion molecule type 1, vascular adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6 (IL-6), and C-reactive protein in serum and aorta of AS rabbits. In addition, real-time quantitative RT-PCR analyses showed that the apoA-I infusions decreased the mRNA levels of two pro-inflammatory molecules, i.e. nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), in aorta of AS rabbits, which was associated with a concomitant reduction in endothelial VCAM-1 and IL-6 mRNA transcription. Together, our results support the atheroprotective and prophylactic role of apoA-I in vivo, and this activity may be correlated with its anti-inflammatory effect.
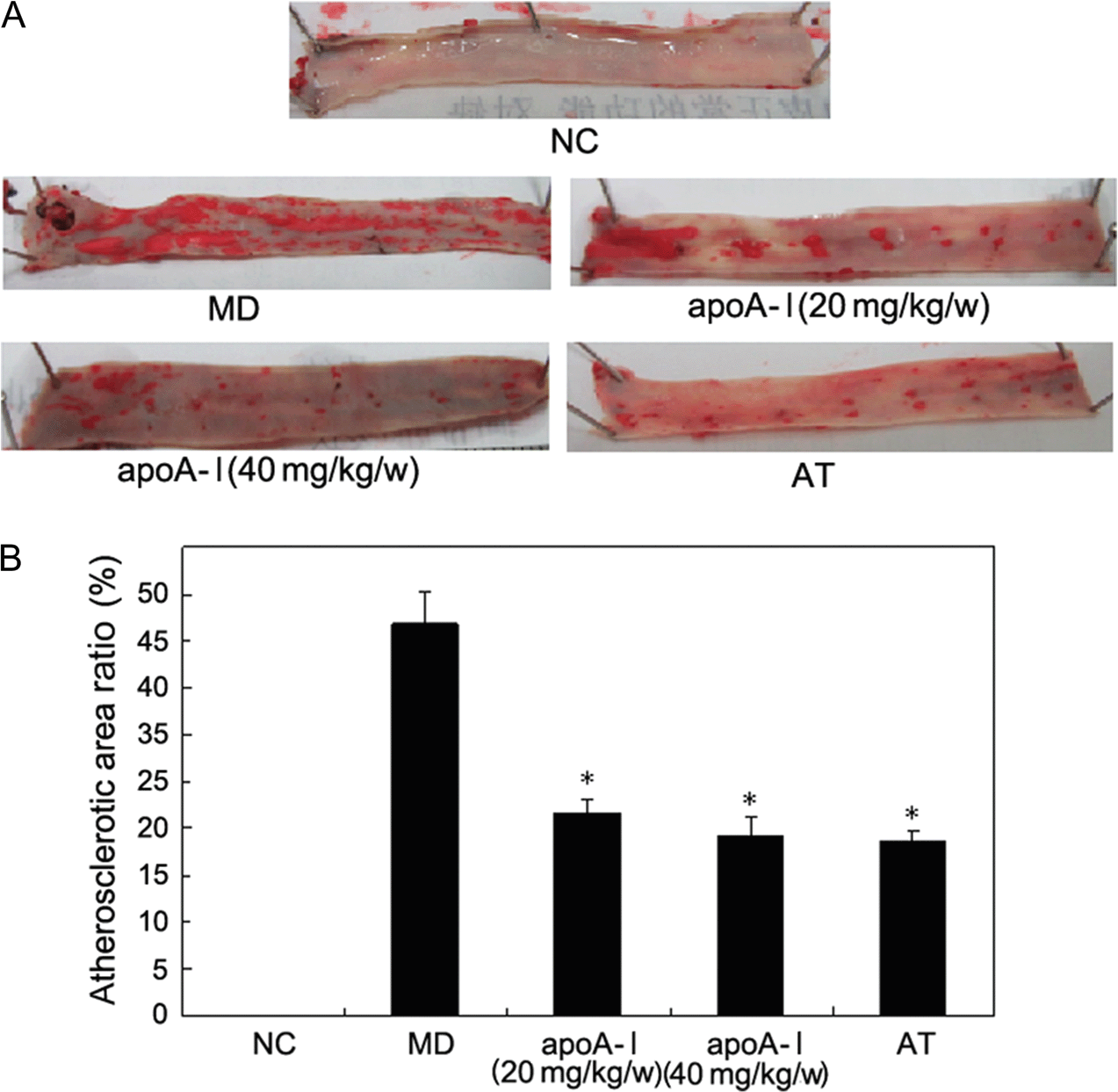
ApoA-I decreased the atherosclerotic plaque area in aorta of high-fat diet-fed rabbits
阅读全文: http://www.abbs.org.cn/arts.asp?id=4117
获取全文: abbs@sibs.ac.cn
相关论文:
1 Cholesterol, inflammation and innate immunity
2 HDL and cardiovascular disease
3 Dysfunctional HDL and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
4 Microdomains, Inflammation, and Atherosclerosis
5 HDL and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: genetic insights into complex biology
6 Perilipin2/adipophilin and ApoA-1 team up to combat atherosclerosis
7 Molecules That Mimic Apolipoprotein A-I: Potential Agents for Treating Atherosclerosis

https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-592748-1136831.html
上一篇:ABBS: Squalene epoxidase induces EMT through miR-133b
下一篇:ABBS: MiR-375 --| Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma