博文
Gut:郝继辉/刘静团队揭示KRAS突变驱动CLDN18.2 O-GlcNAc糖基化修饰调控胰腺癌进展及耐药的新机制
|
近日,天津医科大学肿瘤医院郝继辉教授团队与复旦大学附属肿瘤医院刘静教授团队合作,在消化系统领域顶刊Gut上发表了题为“KRAS mutation-driven O-GlcNAcylation of CLDN18.2 enhances the progression of pancreatic cancer and reduces the efficacy of CLDN18.2-targeted therapy”的研究论文 。天津医科大学肿瘤医院郝继辉教授为论文通讯作者;复旦大学附属肿瘤医院刘静教授为论文第一作者及共同通讯作者。天津医科大学肿瘤医院解永杰教授、黄崇标教授为共同通讯作者;博士研究生侯绪鹏、博士后白伟伟及周天兴副研究员为共同第一作者。
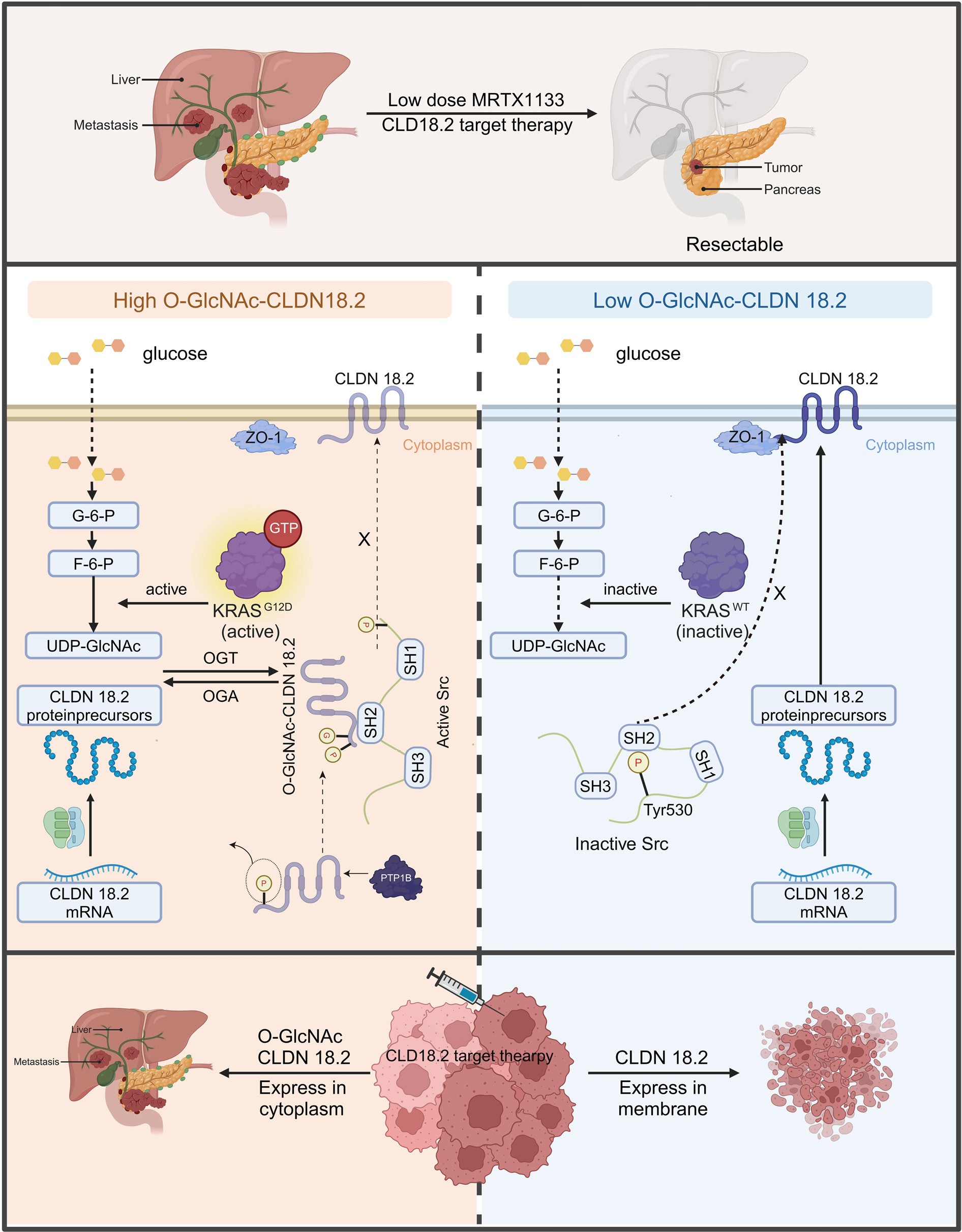
该研究首次系统阐明了KRAS突变如何通过调控CLDN18.2蛋白的O-GlcNAc糖基化修饰,导致其亚细胞定位由细胞膜向胞质转变,进而驱动胰腺癌恶性进展并诱导靶向治疗耐药。同时,研究提出了一种利用低剂量KRAS抑制剂逆转耐药的创新联合治疗策略 。
研究背景
CLDN18.2作为一种在多种消化系统肿瘤中特异性高表达的膜蛋白,已成为胃癌及胃食管结合部肿瘤临床治疗的热门靶点 。然而,在胰腺导管腺癌(PDAC)中,靶向CLDN18.2的疗法效果却差强人意 。由于90%以上的胰腺癌存在KRAS基因突变,研究团队聚焦于探讨KRAS突变引发的代谢重构是否影响了CLDN18.2的功能及其作为药物靶点的有效性 。
核心发现:糖基化修饰导致“靶点错位”
通过代谢组学、转录组学及单细胞测序等多组学分析,研究团队发现:
修饰位点的确立:在高血糖和KRAS突变的共同驱动下,CLDN18.2蛋白的C末端T204位点会发生异常的O-GlcNAc修饰。
亚细胞定位改变:这种修饰破坏了CLDN18.2与支架蛋白ZO-1的结合,导致原本应定位于细胞膜的CLDN18.2异常累积在细胞质内。
功能转变:胞质滞留的O-GlcNAc-CLDN18.2不仅使细胞失去了靶向药物的“攻击点”,更转变为驱动肿瘤迁移、侵袭和转移的“帮凶” 。
机制揭示:激活Src信号通路
机制研究显示,O-GlcNAc化的CLDN18.2与磷酸酶PTP1B的结合能力减弱,导致其自身酪氨酸磷酸化水平升高 。随后,它通过SH2结构域招募并激活Src激酶,从而增强胰腺癌细胞的恶性生物学行为 。
临床转化与逆转策略
预后判断与AI模型:临床数据显示,胞质CLDN18.2(cyto-CLDN18.2)是胰腺癌独立的强不良预后因子 。为此,团队建立了AI辅助的CLDN18.2病理判读模型,以更精准地预测药物敏感性 。
联合用药方案:研究证实,使用低剂量的KRASG12D抑制剂(如MRTX1133)可显著抑制CLDN18.2的糖基化修饰,促使其重返细胞膜,从而显著增强胰腺癌对CLDN18.2靶向疗法的敏感性。这一发现为胰腺癌患者提供了潜在的个体化联合治疗方案 。
原文摘要 Abstract
Background CLDN18.2 has emerged as a promising therapeutic target in gastric and gastro-oesophageal junction cancers. However, its clinical efficacy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) has been modest, suggesting the presence of regulatory mechanisms impairing its efficacy.
Objective We aim to investigate how O-linked N-acetylglucosaminylation (O-GlcNAcylation) affects CLDN18.2 subcellular localisation, tumour progression and therapeutic resistance in PDAC, while exploring strategies to restore treatment sensitivity.
Design This study used samples from patients with PDAC, along with the following models: humanised patient-derived xenograft (PDX), patient-derived organoids (PDOs), orthotopic PDO xenograft, KPC mice (LSL-KrasG12D/+; LSL-Trp53R172H/+; Pdx1-Cre) and KPC-Cldn18.2 knockout (KO) mice.
Results KRAS (Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog) mutation and hyperglycaemia cooperatively drive CLDN18.2 O-GlcNAcylation at T204, promoting CLDN18.2 cytoplasmic accumulation. O-GlcNAcylated CLDN18.2 promotes pancreatic cancer migration, invasion and metastases and reduces its sensitivity to anti-CLDN18.2 based targeted therapy. Mechanistically, O-GlcNAcylated CLDN18.2 exhibits reduced binding to PTP1B, leading to enhanced tyrosine phosphorylation. O-GlcNAcylated CLDN18.2 recruits Src via SH2 domain, triggering Src activation. Genetic (T204A) or pharmacological blockade of O-GlcNAcylation restores CLDN18.2 membrane localisation and suppresses tumour progression. Therapeutically, low-dose MRTX1133 (KRASG12D inhibitor) reduces O-GlcNAcylation and synergises with CLDN18.2-targeted therapy in KRAS mutant PDAC models with minimal side effects.
Conclusions KRAS mutations and hyperglycaemia drive O-GlcNAcylation of CLDN18.2 at its C-terminal T204 site. O-GlcNAcylated CLDN18.2 promotes poor prognosis and reduces the effectiveness of CLDN18.2-targeted therapies. Low dose MRTX1133 restores CLDN18.2 membrane localisation by reducing its O-GlcNAcylation and augments CLDN18.2-targeted therapy efficacy, offering a novel combinatorial strategy for KRAS-mutant PDAC.
论文链接: https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2025-336277
参考资料:Liu J, Hou X, Li L, et al. KRAS mutation-driven O-GlcNAcylation of CLDN18.2 enhances the progression of pancreatic cancer and reduces the efficacy of CLDN18.2-targeted therapy. Gut Published Online First: 09 January 2026. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2025-336277
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-446272-1518078.html
上一篇:[转载]hLife:中国科学院钟劲团队揭示O-GlcNAc糖基化调控外泌体释放新机制