博文
[转载]氨基己糖合成途径通过免疫检查点翻译延伸驱动肿瘤免疫逃逸新机制
||
葡萄糖、脂质和氨基酸的代谢重编程,多年来一直被公认为是识别恶性肿瘤的标志。不仅在肿瘤发生发展过程中广泛存在,还与细胞恶性转化、肿瘤增殖和转移等密切相关。近年来,代谢重编程所介导的免疫抑制微环境已成为研究免疫逃逸的关键热点,然而其分子机制一直不甚明确。
近日,复旦大学糖复合物重点实验室团队在Cell Reports上联合发表题为The hexosamine biosynthetic pathway drives tumor immune evasion via translational control of PD-L1 at the elongation level 的研究论文。该论文通讯作者为复旦大学基础医学院糖复合物重点实验室阮元元、复旦大学附属肿瘤医院刘凤林、国家蛋白质科学中心徐平、复旦大学生物医学研究院陆豪杰与张莹。
该研究揭示了氨基己糖合成途径(HBP)通过信号肽介导的翻译延伸,驱动免疫检查点PD-L1的表达,进而影响抗肿瘤免疫监视的分子机制。研究团队将HBP代谢重编程与免疫检查点的翻译延伸相联系,拓展了对代谢重编程和异常糖基化修饰塑造肿瘤免疫抑制微环境的理解,也为靶向HBP这一代谢关键点和改善现有免疫治疗疗效提供了理论依据,对肿瘤免疫的病因学探索与个性化治疗的临床实践具有重要意义。
在众多失调代谢途径中, 己糖胺生物合成途径(HBP)作为营养传感器和关键代谢节点,整合了葡萄糖分解、谷氨酰胺吸收、脂肪酸氧化以及核苷酸合成等多个代谢流。该通路产生的尿苷二磷酸N-乙酰葡萄糖胺(UDP-GlcNAc)作为糖基供体,广泛参与蛋白质翻译后糖基化修饰,影响蛋白表达、亚细胞定位及功能。 通过自发性结直肠癌小鼠模型,研究团队发现敲除HBP关键限速酶GFAT1以阻断该通路,可显著抑制肿瘤生长并激发抗肿瘤免疫监视。除此之外,HBP还可在翻译延伸水平调控免疫检查点PD-L1的表达。
进一步机制研究表明,HBP通过促进整合素α2/α3亚基的N-糖基化修饰及蛋白上调,激活下游FAK信号,进而驱动翻译延伸因子eEF1A2的转录与表达,促进PD-L1蛋白水平上调并激活免疫逃逸。
该发现首次在结直肠癌中建立了代谢紊乱与免疫逃逸之间的分子联系,为提升靶向治疗策略的有效性提供了新思路。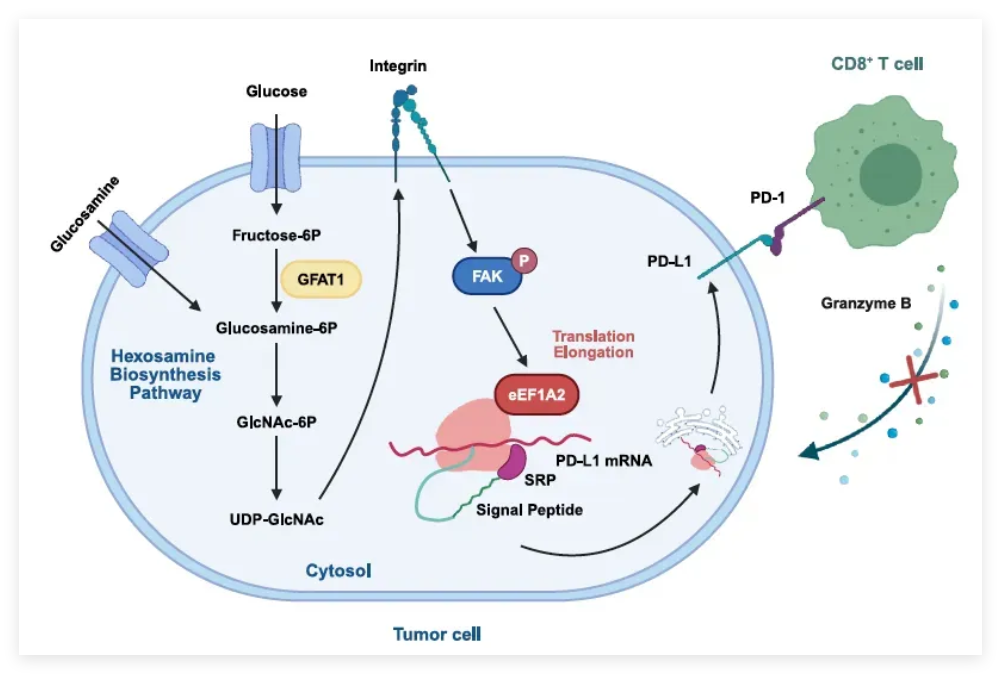
机制假说图
亮点 Highlights
•HBP induces an immunosuppressive microenvironment via PD-L1 in colorectal carcinoma
•HBP upregulates eEF1A2 to enhance PD-L1 expression through translation elongation
•HBP enhances N-glycosylation of integrin subunits to activate FAK/MZF1 signaling
•HBP is associated with colorectal tumor immune evasion and poor outcome of patients
摘要 Summary
Cancer cells reprogram cellular energetics to drive tumorigenesis and escape immunosurveillance. Nevertheless, how this is molecularly connected remains largely undefined. The hexosamine biosynthetic pathway (HBP) serves as a critical metabolic node in cancer cells that provides the basis for protein glycosylation. Herein, we show that HBP flux inhibition by knocking out its rate-limiting enzyme GFAT1 suppressed tumor growth and stimulated cytotoxic CD8+ T lymphocyte infiltration in a colorectal cancer model. GFAT1 induced the expression of the immune checkpoint PD-L1 at the translational level by bypassing signal peptide-mediated translation elongation arrest. Proteomic and glycoproteomic screening indicated that GFAT1 facilitated the N-linked glycosylation and protein expression of integrin α2/α3 subunits, leading to FAK activation and elongation factor eEF1A2 upregulation. Pharmacological inhibition of HBP noticeably enhanced the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade in vivo. Together, these findings unravel how immune checkpoint proteins are manipulated by metabolic dysregulation, which can be exploited as metabolic vulnerability for improving immunotherapies.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2025.116249
原文链接:https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(25)01020-4
参考文献: Liu, Bo et al. The hexosamine biosynthetic pathway drives tumor immune evasion via translational control of PD-L1 at the elongation level. Cell Reports, 2025 Volume 44, Issue 9, 116249
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-446272-1505548.html
上一篇:[转载]Dev Cell: 王佳谊/唐道林/于永春/周谦君团队揭示O-GlcNAc修饰型TR11B驱动肺癌恶性增殖的机制
下一篇:Gut :重庆医科大学发现克服MASH相关肝癌免疫治疗耐药的新策略