博文
【论文推荐】多执行器协同鲁棒平行驱动
||
编辑荐语
本期将给大家分享"多执行器协同鲁棒平行驱动(Cooperative robust parallel operation of multiple actuators)". 如您对本期相关内容有好的理解与建议, 欢迎评论区留言.
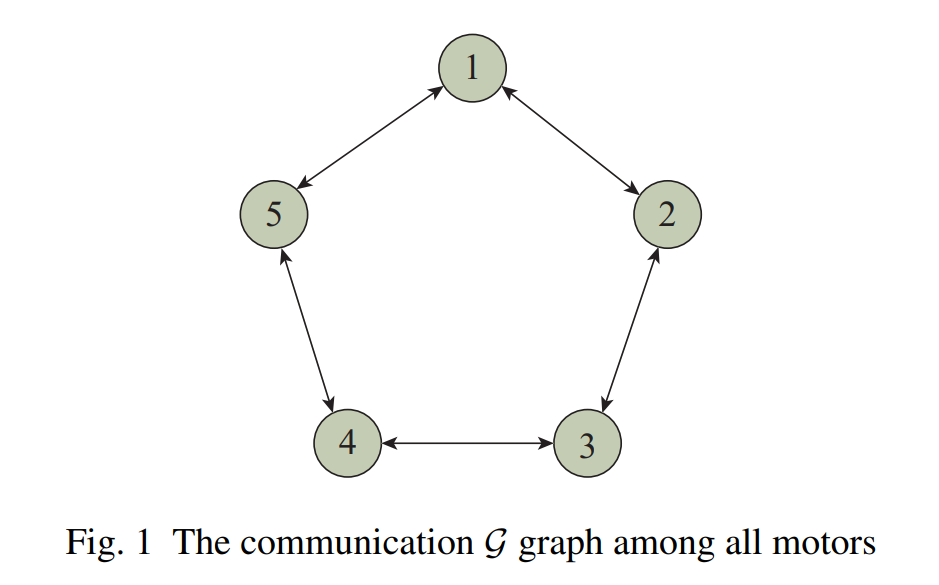
本文针对实际工程中单执行器输出功率有限而需多执行器并行驱动的普遍需求, 从系统控制理论层面, 对具有不确定性的线性系统在无向通信网络下的协同鲁棒平行驱动问题进行了系统性研究. 文章提出了一种基于内模原理的分布式动态输出反馈控制律, 创新性地在统一框架下同步实现了闭环系统的鲁棒输出调节与系统输入在多执行器间的精确共享两大核心目标. 该研究突破了现有下垂控制需在均流精度与调节性能间权衡、以及主从控制存在单点故障风险的局限, 为电机组、微电网、电力电子变换器等广泛领域的多执行器协同系统提供了普适性更强的鲁棒控制方案. 文中以五台电机协同驱动不确定转轴为例的数值仿真, 验证了所提控制律在存在外部干扰时的有效性. 本工作不仅推进了多智能体协同控制理论在平行驱动这一重要工程问题中的应用深度, 也为构建高可靠、高精度、可扩展的并行驱动系统奠定了坚实的理论基础.
本研究从一般化的线性系统模型出发, 将鲁棒控制、输出调节与分布式协同有机结合, 理论框架严谨, 针对工程中普遍存在的不确定性问题提出了系统性的解决方案. 所提出的控制策略兼具鲁棒性、可靠性及分布式优势, 具有重要的理论创新性与工程应用前景. 推荐给从事协同控制、鲁棒控制、电力电子系统、多电机驱动及相关领域研究的学者与工程师阅读参考.
论文介绍
多执行器协同鲁棒平行驱动
Cooperative robust parallel operation of multiple actuators
徐亮, 徐翔, 刘涛†
机构: 南方科技大学 深圳市控制理论与智能系统重点实验室
引用: 徐亮, 徐翔, 刘涛. 多执行器协同鲁棒平行驱动. 控制理论与应用, 2026, 43(1): 3 – 11
DOI: 10.7641/CTA.2025.40561
全文链接:
http://jcta.alljournals.ac.cn/cta_cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=CCTA240561&flag=1
摘要
本文研究了多执行器在无向通信网络下的协同鲁棒平行驱动. 考虑一个具有不确定性的线性系统, 且所有执行器具有相同的线性动力学. 基于内模原理, 本文提出了一种分布式动态输出反馈控制律, 同步实现了闭环系统的鲁棒输出调节与系统输入在执行器之间的共享. 最后, 在外部负载扭矩作用下, 五台电机协同驱动不确定转轴的数值仿真验证了所提控制律的有效性.
Introduction
When confronted with the constraint of limited output power from a single actuator, employing parallel operation of multiple actuators emerges as an effective strategy for driving plants that require substantial power. Compared to single actuator operation, parallel operation of multiple actuators offers superior flexibility, reliability, and scalability. This straightforward approach has been widely applied to various practical systems, including motor-driven systems, direct current (DC) microgrids, and DC–DC converters.
A systematic classification of paralleling schemes for DC–DC converters was described in [1], which also discussed the associated control methods such as droop control and master-slave control. Droop control is simple to achieve current sharing without the need for communication among converters. However, a trade-off must be made between the accuracy of current sharing and that of output voltage regulation [2]. Master-slave control requires a communication link between the master and slaves, where one converter is dedicated to be the master whose output current becomes the reference for the remaining slave converters. Master-slave control can provide current sharing, but does not achieve redundancy, since a single point of failure happens to the master disables the entire system [3]. To address this issue, reference [4] developed a cooperative control framework for DC–DC converters over a communication graph. Some other related results can be found in, e.g., [5–7].
It is noted that droop control and master-slave control have also been applied to motor-driven systems and DC microgrids. Similar to what is mentioned above, regulation errors may exist in droop control while master-slave control is vulnerable to failures. To overcome these drawbacks, techniques from cooperative control of multi-agent systems were adopted and some interesting results were obtained in, for example, [8–14]. In particular, reference [8] proposed a consensus-based parallel operation scheme for multiple identical electric motors that can achieve both speed regulation and load torque sharing. An extension of [8] that further ensures a fail-safe feature was given in [9], where the overall system can continue to operate even if a single motor fails. Reference [10] reviewed a hierarchical control architecture for DC microgrids, where centralized secondary control can eliminate the errors resulting from primary droop control. Still, the issue of a single point of failure persists. Fortunately, this issue can be resolved by replacing centralized secondary control with consensus-based distributed secondary control in [11]. Further, reference [12] developed a robust cooperative distributed secondary control strategy for DC microgrids that can handle load changes and distribution line failures. Reference [13] proposed a distributed optimization and control strategy that achieves the control targets within a predefined settling time. Other consensus-based distributed secondary control schemes for DC microgrids can be found in, e.g., [14].
While parallel operation has been extensively explored in the literature, its applications have been confined to specific engineering domains such as motordriven systems and power systems. Until recently, the authors of [15] introduced an innovative and systematic formulation of the cooperative parallel operation problem where both the plant and actuators are modeled as general linear systems. By devising a distributed dynamic output feedback control law, both output regulation and plant input sharing were achieved. Nevertheless, it is noteworthy that [15] assumes precise knowledge of the plant.
Recognizing that uncertainties are inevitable in practical engineering systems, it is crucial to further investigate the cooperative robust parallel operation problem. Although some robust results have been obtained in, e.g., [6], [12], and [14], these studies focused on specific applications, such as microgrids and converters, and a robust systematic design framework is still lacking. Motivated by this, we aim to explore the cooperative robust parallel operation problem in a general setup for uncertain linear plants. Leveraging the internal model principle [16–17], we propose a distributed dynamic output feedback control law that not only ensures output regulation and plant input sharing, but also allows the plant to accommodate uncertainties to a certain degree.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 reviews the classic robust output regulation problem. Then, the cooperative robust parallel operation problem is formulated in Section 3 and the solvability of the problem is established in Section 4. Section 5 presents a numerical example and Section 6 concludes the paper.
Conclusions
In this paper, we have studied the cooperative robust parallel operation problem where a linear uncertain plant is collectively driven by multiple actuators. Assuming that the communication graph among the actuators is undirected and connected, we have proposed a distributed dynamic output control law based on the internal model principle. Our study demonstrates that, under the same standard assumptions as used in the output regulation literature, both robust output regulation of the closed-loop system and plant input sharing among the actuators can be achieved. Extensions of the current study to general digraphs and to switching graphs are underway. Additionally, investigating cooperative parallel operation involving non-identical or uncertain actuators presents an intriguing avenue for future research.
作者简介
徐 亮 从事博士后研究工作, 目前研究方向为非线性系统控制、多执行器平行驱动、事件触发控制;
徐 翔 副教授, 博士生导师, 目前研究方向为时滞系统控制与分析、无穷时滞系统控制与分析、偏微分方程的边界控制、多智能体强化学习;
刘 涛 副教授, 博士生导师, 目前研究方向为非线性控制, 输出调节、分布式控制与估计、机器人控制技术、强化学习.
期刊介绍
《控制理论与应用》(Control Theory & Applications)是经国家科学技术部批准, 教育部主管, 由华南理工大学和中国科学院数学与系统科学研究院联合主办的全国性一级学术刊物, 1984年创刊, 月刊, 国内外公开发行. 《控制理论与应用》是中国科学引文数据库首批统计源期刊之一,中文核心期刊,入选中国精品科技期刊顶尖学术论文F5000项目,中国科协自动化学科领域高质量科技期刊目录以及中国科协百篇优秀科技论文遴选计划,2021年入选广东省高质量科技期刊建设项目,2022-2024年连续获得基金委资助(科技活动专项)。


【收录】
目前被美国《工程索引》(Ei Compendex)、SCOUPS、CSCD、美国的《化学文摘》(CA)、英国《科学文摘》(Inspec)、德国《数学文摘》、俄罗斯《文摘杂志》(AJ)、《日本科学技术振兴机构中国文献数据库》等国内外检索系统收录。
官网:https://jcta.ijournals.cn/cta_cn/ch/index.aspx
知网优先发表:https://navi.cnki.net/knavi/journals/KZLY/detail
投稿:https://jcta.ijournals.cn/cta_cn/ch/author/login.aspx
微信:控制理论与应用
视频号:控制理论与应用
科学网博客:http://blog.sciencenet.cn/u/CTACTT
小红书:控制理论与应用(ID:8742781006)
Email:aukzllyy@scut.edu.cn
Tel:020-8711 1464

欢迎扫码关注控制理论与应用公众号
【2024-2026年期刊合集】
2025年第42卷第11期(“新一代智能优化理论方法与应用暨纪念郑大钟教授诞辰90周年”专刊)
2024年第41卷第7期(“秦化淑教授90寿诞—复杂系统控制理论及其应用”专刊)
2024年第41卷第6期(“数据与模型融合的智能调度优化”专刊)
2024年第41卷第3期(“人工智能驱动的过程工业自动化与智能化”专刊)
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-3633987-1522066.html
上一篇:《控制理论与应用》2026年第1期目次速览
下一篇:【论文推荐】高阶交互下具有环星型结构的分数阶时滞神经网络分岔