博文
Green Carbon│意大利佩鲁贾大学Castellani副教授:置换法实现天然气水合物开发协同二氧化碳海底封存
||

英文原题:Interdisciplinary results of an Italian research project on methane recovery and carbon dioxide storage in natural gas hydrate reservoirs
作者:Beatrice Castellani*, Rita Giovannetti, Umberta Tinivella, Salvatore F. Cannone, Roberto Fazioli, Fabio Trippetta, Michele Ciulla, Valentino Canale, Pietro Di Profio, Alberto Maria Gambelli, Andrea Nicolini, Giorgio Minelli, Massimiliano Barchi, Marco Zannotti, Andrea Rossi, Michela Giustiniani, Andrea Lanzini, Massimo Santarelli, Federico Rossi
01 论文信息
论文信息
Castellani B, Giovannetti R, Tinivella U, et al. Interdisciplinary results of an Italian research project on methane recovery and carbon dioxide storage in natural gas hydrate reservoirs[J]. Green Carbon, 2024 2 (4) 351-365.
论文关键词
Natural gas hydrates; CO₂–CH₄ replacement; Membranes; Carbon storage; Clathrate hydrates
论文网址
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.greenca.2024.09.001
论文下载
中文解读原链接
Green Carbon文章│意大利佩鲁贾大学Castellani副教授:置换法实现天然气水合物开发协同二氧化碳海底封存
02 背景简介
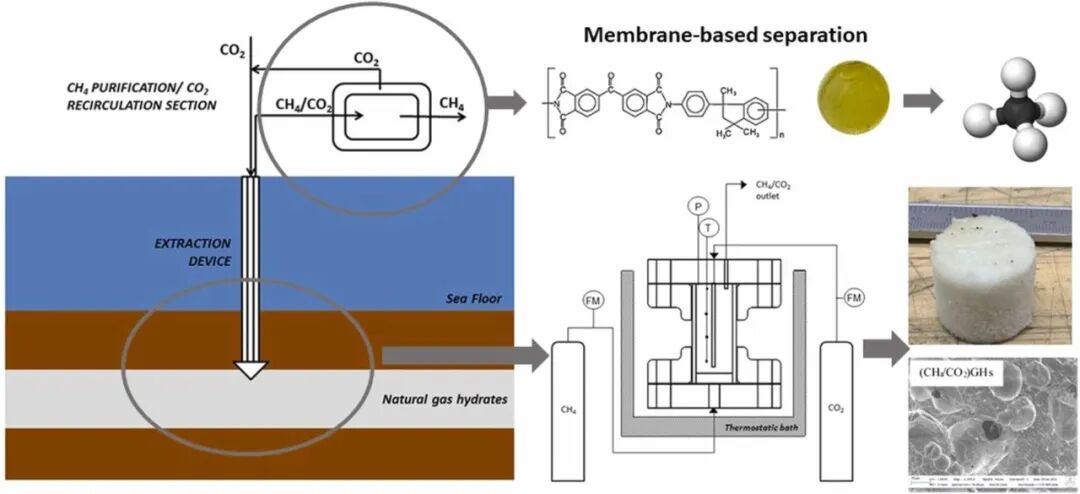
天然气水合物(Natural gas hydrates, NGH)是天然气分子(主要组分为CH₄)和水分子在高压、低温条件下形成的非化学计量的笼型结晶化合物,水分子通过分子间的氢键作用形成笼形框架,天然气分子通过分子间作用力存储于笼型框架内。NGH主要存在于大陆和岛屿斜坡的海洋沉积物、内陆湖泊和海洋的深水沉积物以及大陆和大陆架的极地沉积物中。
CO₂-CH₄置换是一种具有巨大潜力的天然气水合物开发手段。该技术不仅能够从水合物储层中有效提取甲烷,而且还能实现二氧化碳的有效封存。基于此项技术的可行性研究,天然气水合物(NGH)有望成为地球上最大的碳氢化合物资源库之一,并作为可持续能源的重要储备形式存在。这意味着将天然气水合物开采与碳捕获技术相结合,在构建更加环保、高效的能源体系方面展现出显著优势,符合未来绿色发展的战略方向。然而,尽管前景广阔,但当前该技术领域仍面临着诸多挑战性问题亟待解决,包括但不限于:水溶液特性对水合物形成及置换过程的影响机制尚不明确;沉积物本身的物理化学性质如何作用于整个反应体系仍需进一步探讨;此外,置换操作完成后储层结构稳定性的变化规律以及适用于此类复杂条件下的高精度数值模拟模型开发等也是当前研究的重点难点所在。
针对上述问题,来自意大利佩鲁贾大学的Beatrice Castellani于Green Carbon上发表标题为“Interdisciplinary results of an Italian research project on methane recovery and carbon dioxide storage in natural gas hydrate reservoirs”的研究文章,创新性地提出了一种将CO₂-CH₄置换工艺、CH₄提纯工艺及CO₂再循环工艺相结合的新型工艺,通过实验验证、模型优化、能耗及经济性的全面分析,为NGH中CH₄回收及CO₂处理提供了新思路。
03 文章简介
水合物实验
水合物生成实验表明:含盐量对CO₂-CH₄置换过程有积极影响,这是由于氯化钠对CO₂和CH₄水合物具有不同的热力学抑制作用,引起两种平衡曲线之间的距离增大(图1),进而导致盐水体系中被置换的CH₄有所增加。同时,研究发现沉积物自身性质对水合物生成具有一定的影响:在小粒径沉积物中,CH₄水合物形成速度更快、体积更大,而在较大粒径的沉积物中,CO₂替代量和捕集率则更高。此外,实验证明水合物的成核方式不仅与沉积物的存在与否严格相关,同时还受气体组成影响。研究人员对多种条件下的水合物进行拉曼光谱研究,结果表明:含沙体系CO₂水合物中水表现出无序结构,而CH₄/CO₂混合水合物中的水则表现出最为有序的结构,同时其中CO₂含量也最高。
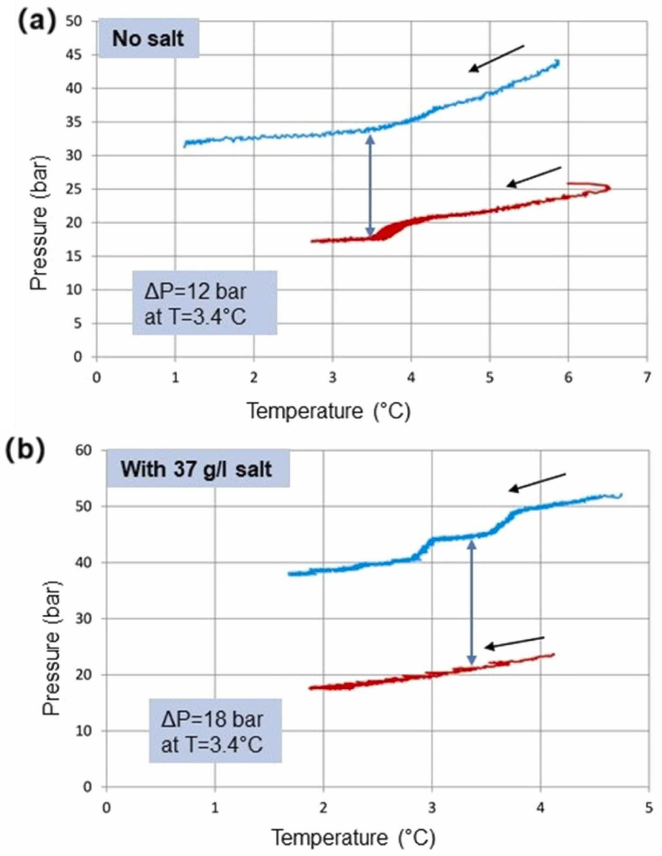
图1. (a)不含盐体系下CH₄/CO₂水合物温压图;(b)含盐体系下CH₄/CO₂水合物温压图
力学性能分析及模拟计算
在力学性能分析过程中,研究人员对沉积物施加轴向P波和S波。结果表明,当CO₂存在于天然沉积物中时,P波速度和Ed明显增加,而对于合成砂,这种增加要低得多。两种沉积物之间最重要的差异是颗粒形状、粒度和筛选标准,这是沉积物力学行为的重要特征。因此,置换过程必然会影响水合物的力学性质,但这些变化的数量可能与储层基质的岩性特征密切相关。
模拟计算过程中,将NGH力学分析结果应用于模型,以组分的弹性特性和体系泊松比作为输入参数,估计样品的水合物浓度(sh),增加理论公式中的sh,直到理论泊松比与实际泊松比拟合,结果表明,玻璃微珠模拟沉积物与自然沉积物的水合物浓度相同(图2),样品部分水合物饱和。
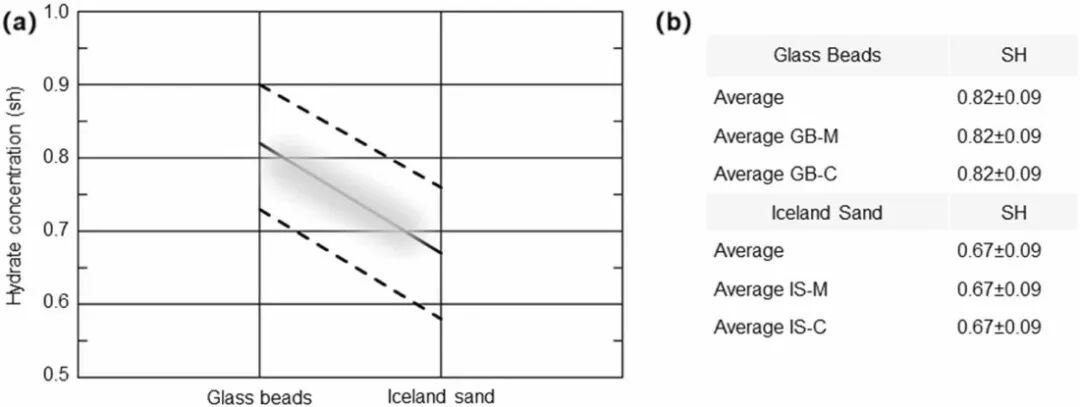
图2. 玻璃/自然沉积物中水合物浓度及其估计误差
气体分离模型优化、能耗及经济性分析
气体分离采用一种高选择性的Matrimid膜,同时选择两级串联再循环和两台压缩机进行甲烷提纯,模型优化后(图3),输出混合物中CH₄含量达到97.1%,纯度为98.5%,达到直接注入电网使用的标准。能耗分析表明:由于压缩CO₂所需能量和膜分离所需能量均较低,回收CH₄的废能与储能之比为17%,因此该工艺显示出良好的能量平衡。经济性分析指出:从试点规模到全面工业规模的技术转型可能会带来经济效益,并产生显著的短期影响;从中长期来看,积极回报的明确证据可能并不明显。因此,研究天然气价格下降的经济和金融状况与必要投资的可持续性之间的一致性至关重要。
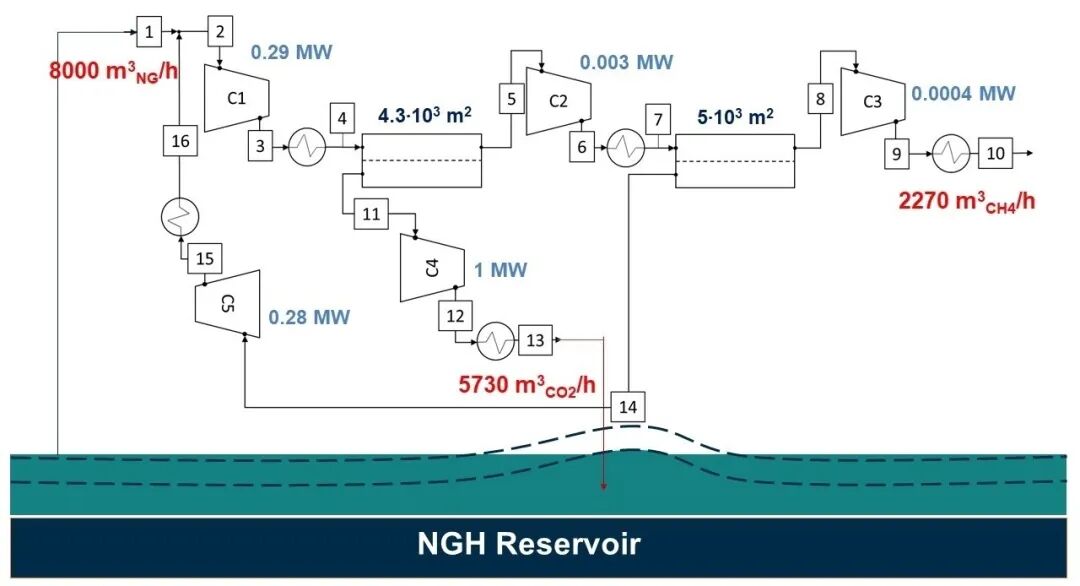
图3. 系统质能平衡优化模型
总结及展望
本文提出一种将CO₂-CH₄置换工艺、CH₄提纯工艺及CO₂再循环工艺相结合的新型工艺技术,旨在概述意大利一个跨学科的天然气水合物开发研究项目所获得的主要实验结果,并在实验结果的基础上,提出总体的能源、地球物理和经济评价。本文所述的工艺技术将NGH开采与碳捕集相结合,为集成化、绿色化的技术发展提供了新思路。
04 文章摘要

Natural gas hydrates (NGH) are found in marine sediments on continental and island slopes, deep-water sediments of inland lakes and seas, and polar sediments on continents and continental shelves. NGH constitutes the largest hydrocarbon resource on Earth, representing a reservoir of sustainable fuel owing to the possibility of a so-called CO₂–CH₄ replacement process. If CO₂ is injected into NGH sediments, CH₄ is released and CO₂ hydrate formed. The extraction of gas from NGH, combined with carbon capture, presents significant potential advantages in the energy infrastructure and various economic and political contexts, aligning with future green policies. This study contributes to the advancement of knowledge by reviewing the findings of a three-year Italian research project focused on methane recovery and carbon dioxide disposal in NGH. The consortium comprises seven multidisciplinary Italian partners. This study introduces a novel process wherein the CO₂–CH₄ replacement process is integrated with methane purification and CO₂ recirculation, which has been experimentally tested and represents a new advancement in gas hydrate science. Experimental tests at the microscopic and macroscopic levels showed that the efficiency of the process strongly depends on the mutual influence of the properties of water, sediment, and the involved gaseous species. Energy evaluations show that the ratio between the energy spent to complete an entire cycle of replacement and recirculation over the stored energy in the recovered methane is 17%, resulting in a beneficial energy balance, while economic analysis shows that the transition could generate—even in the short term—large high-impact cash-out.
05 作者简介

Beatrice Castellani 副教授
Beatrice Castellani,意大利佩鲁贾大学副教授,Green Carbon编委会成员。主要研究领域包括天然气水合物在甲烷回收和二氧化碳储存中的应用、气体水合物在甲烷固态储存和运输以及沼气提纯应用中的作用、建筑材料的热性能以及机械能储存。在科学期刊和会议上发表100余篇论文。
06 Green Carbon
期刊官网:Green Carbon官网
投稿网址:Green Carbon投稿
公众号:Green Carbon公众号

https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-3620330-1509697.html
上一篇:Green Carbon│中国科学院大连化物所周雍进研究员、青岛农业大学杨建明教授:合成生物学助力疫苗佐剂的全生物合成
下一篇:Green Carbon绿碳封面文章 │ 中国科学院青岛能源所田亚峻研究员:生命周期评价的历史发展与研究趋势