博文
[转载]新“文”发布 | GreenChE 最新上线文章集锦
|||
01 Review
From biomass to wealth: biomass-derived carbon dots for green synthesis, photoluminescence mechanisms, and multifunctional applications
Fu Qin, Lili Ren*

❖ We summarized the fluorescence mechanism of biomass-derived carbon dots (BCDs).
❖ A framework linking biomass types to properties and the application of BCDs.
❖ The classification criteria for synthesis methods of BCDs were reconstructed.

https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gce.2025.10.004
02 Article
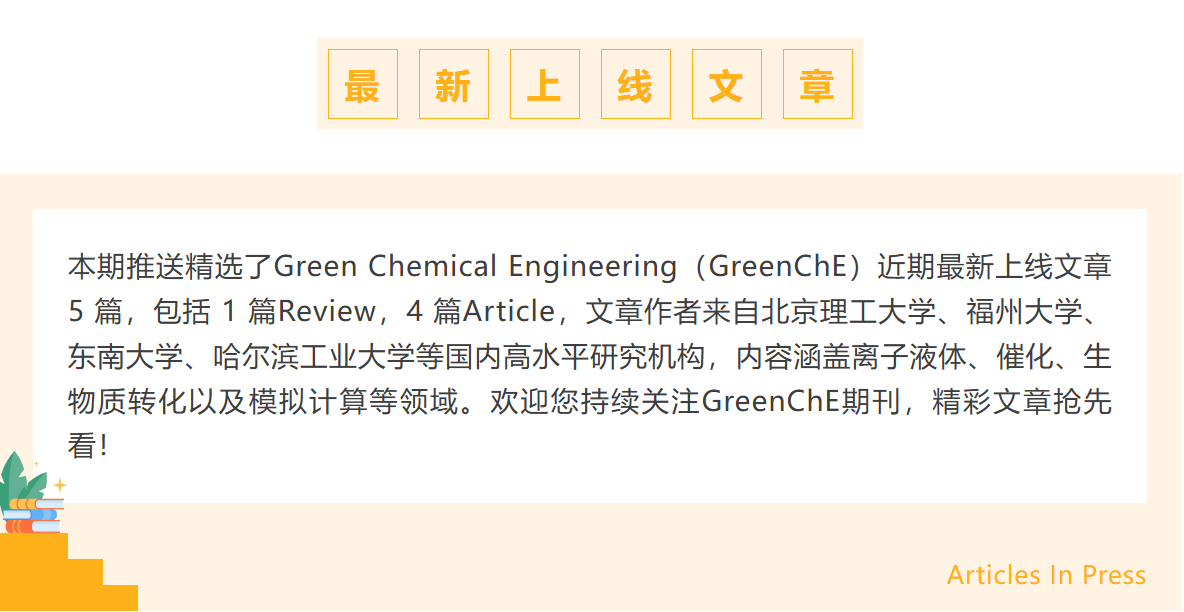
Size-controlled flexible ionic polymer catalysts with enhanced mass transfer for sustainable ethyl methyl carbonate production
Rongkai Cui, Miaomiao Cui, Fuying Zhang, Xiaoyan Chen, Ting Qiu*, Jie Chen*
❖ A directly shaped flexible ionic polymer (PVD-x) was developed for EMC synthesis.
❖ Shaped PVD-x could be directly applied in industrial continuous catalytic units.
❖ PVD-x provided recyclable, sustainable alternative to sodium methoxide in industry.
❖ PVD-x delivered excellent performance with EMC 50.83% yield, 96.25% selectivity.
❖ PVD-x maintained stability for over 2400 h in continuous fixed-bed operation.
❖ DFT revealed the mechanism by which adsorption enhances catalytic activity.

https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gce.2025.11.001
03 Article
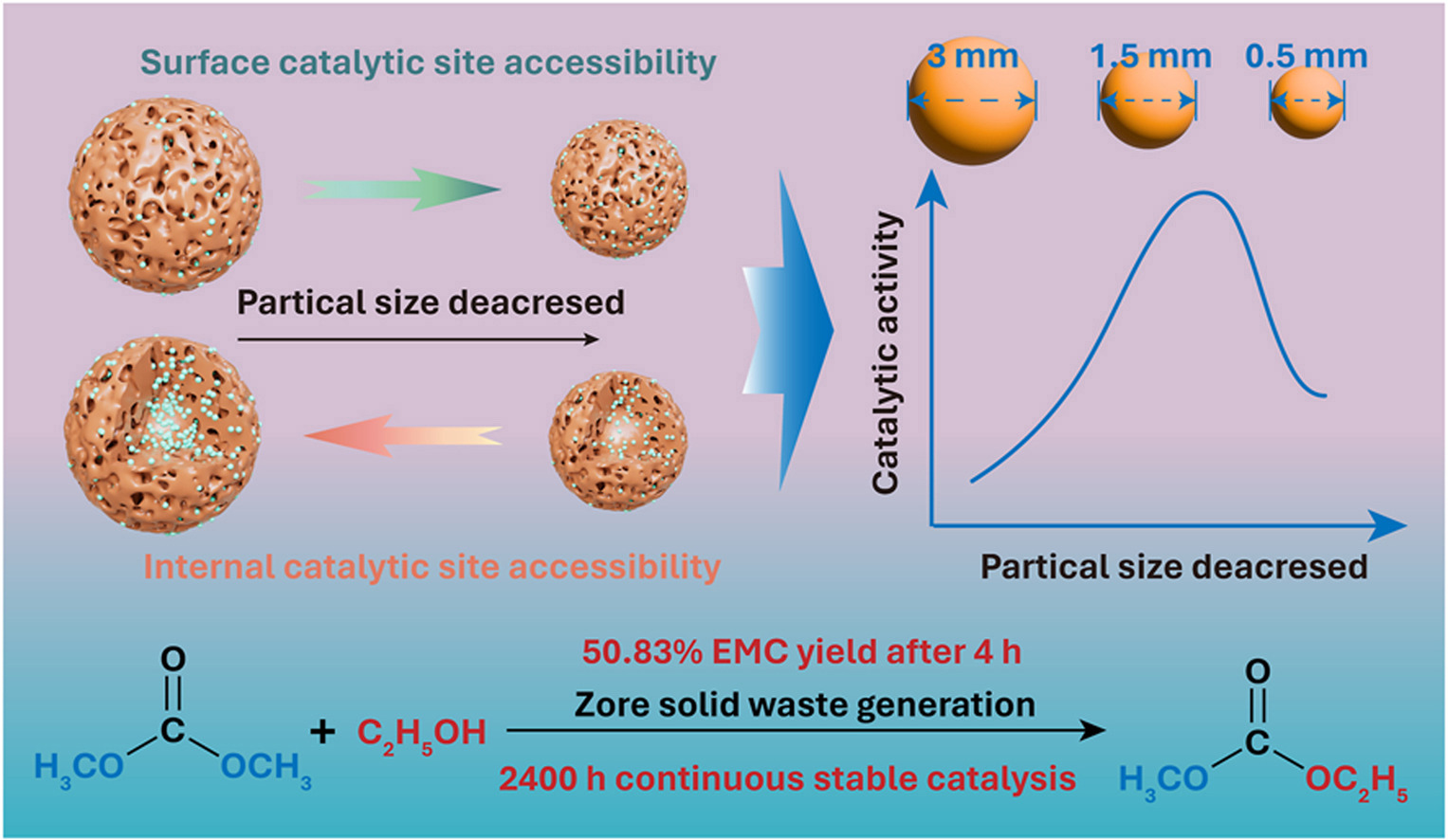
External intensifications for ionic liquids-based biorefinery in highly viscous systems
Yichen Liu, Weidong Zhao*, Jian Sun*
❖ Strong IL-biomass interactions result in high viscosity and hinder mass/heat transfer.
❖ External intensifications enhance transfer efficiency without altering IL chemical structures.
❖ Co-solvents lower viscosity, facilitating improved heat and mass transfer in IL systems.
❖ Microwave enhances heat transfer via dipole relaxation and ionic polarization in ILs.
❖ Ultrasound boosts mass transfer mainly through cavitation and microjet formation.

https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gce.2025.10.003
04 Article
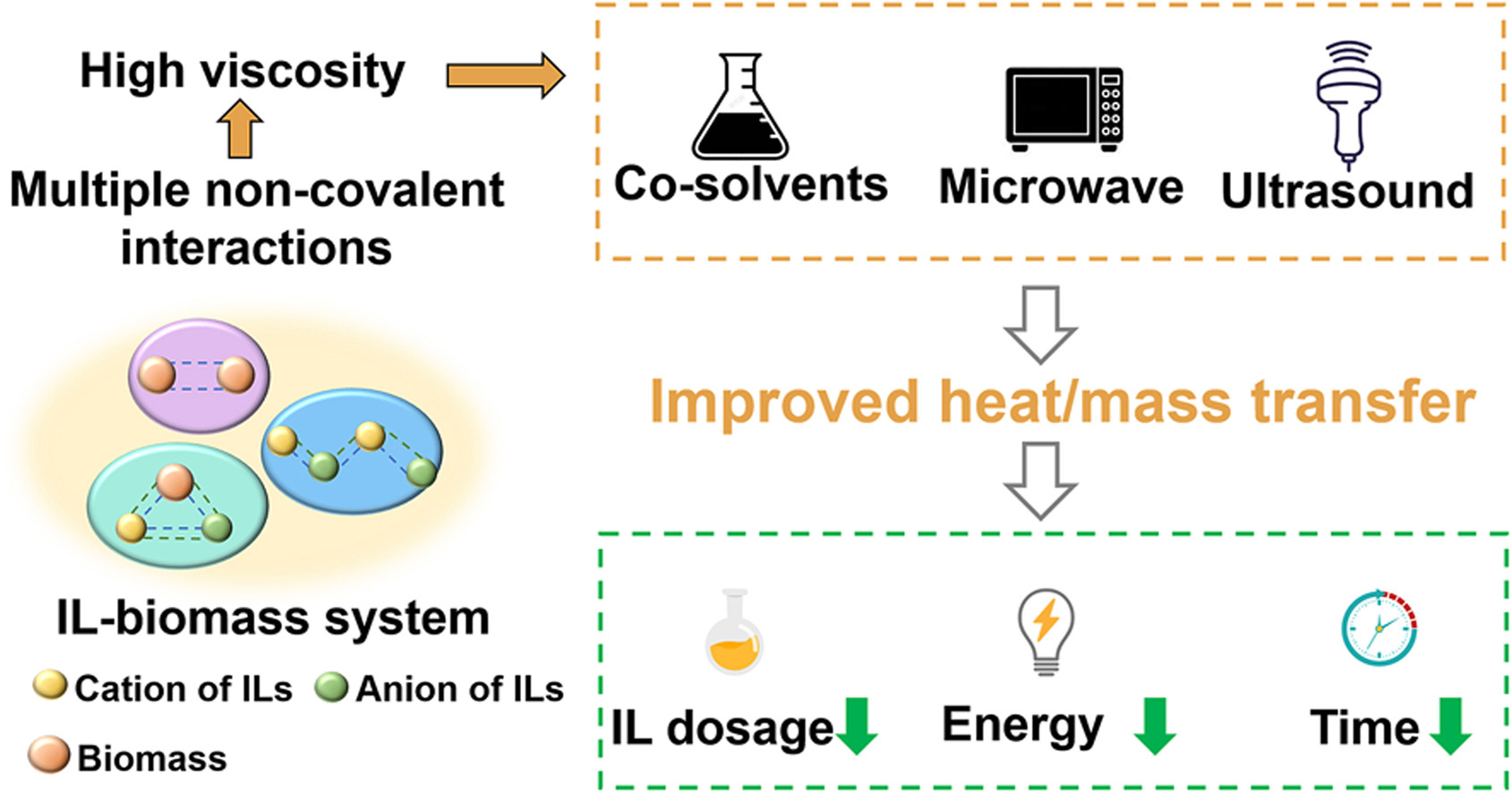
Study on core-shell ionic liquid@metal-organic framework composites for direct oxidative carboxylation of CO2 and olefins under cocatalyst and solvent- free conditions
Huidong Wang, Jiaxing Wen, Jianmin Sun*
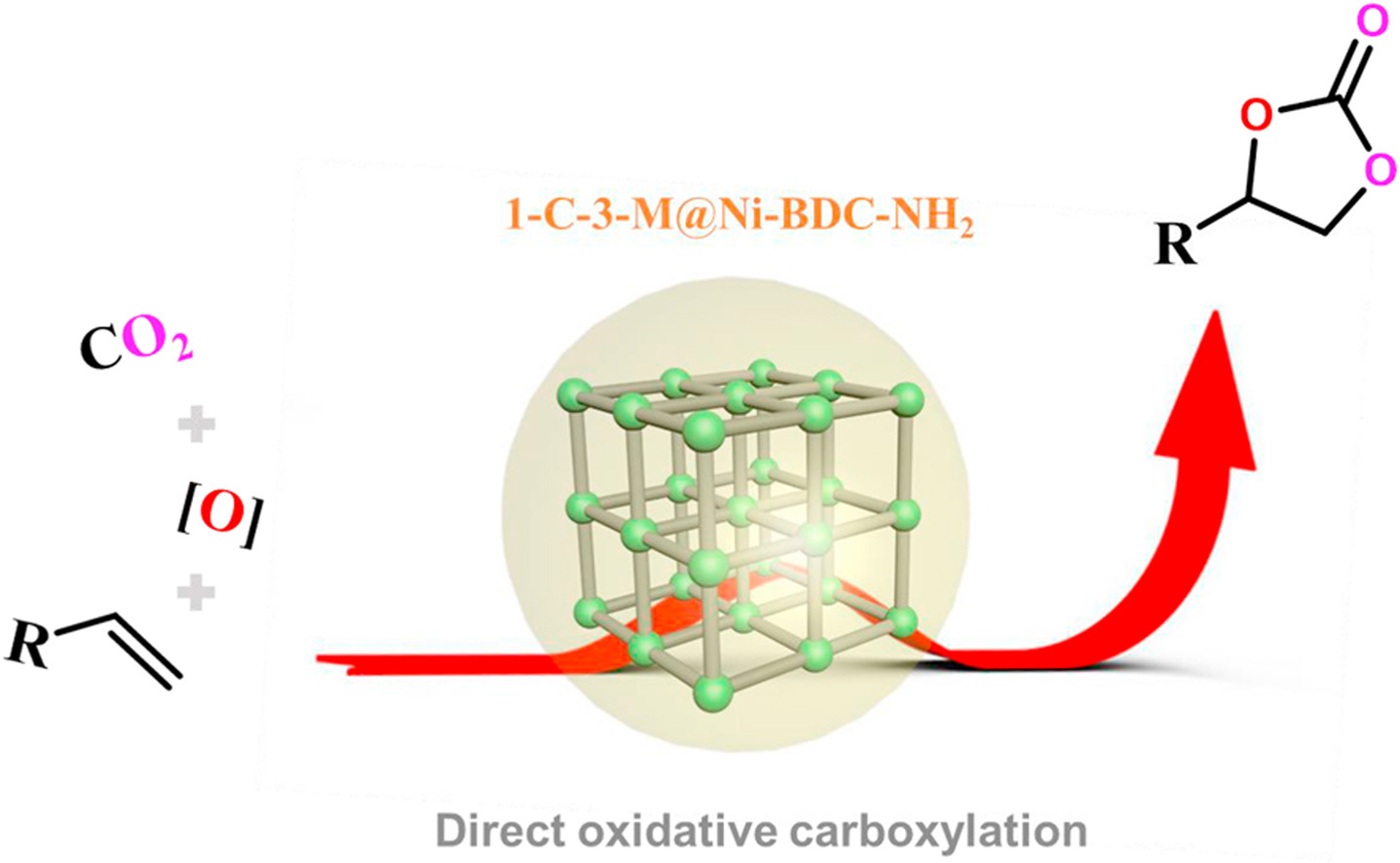
❖ A core-shell structured composite catalyst (1-C-3-M@Ni-BDC-NH2) with multiple active sites comprising metal-organic framework and ionic liquid was designed and synthesized.
❖ Ionic liquid shell of 1-C-3-M@Ni-BDC-NH2 exhibited good affinity for both CO2 and ST.
❖ Due to synergistic effects of multiple active sites, 1-C-3-M@Ni-BDC-NH2 demonstrated excellent catalytic activity for direct oxidative carboxylation of CO2 and styrene under mild reaction conditions.
❖ As a heterogeneous catalyst, 1-C-3-M@Ni-BDC-NH2 is easy to separate from the product and has good thermal stability and cycle stability.

https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gce.2025.10.002
05 Article
Precise capacity fade modeling of NCA/graphite lithium-ion batteries across a wide-temperature range using a pseudo-two-dimensional approach
Xuecheng Qian, Shiyi Wang, Xiaoyun Zhan, Jilei Ye, Lijun Fu, Lili Liu, Zhaogen Wang*, Yuhui Chen, Tao Wang*, Yuping Wu*
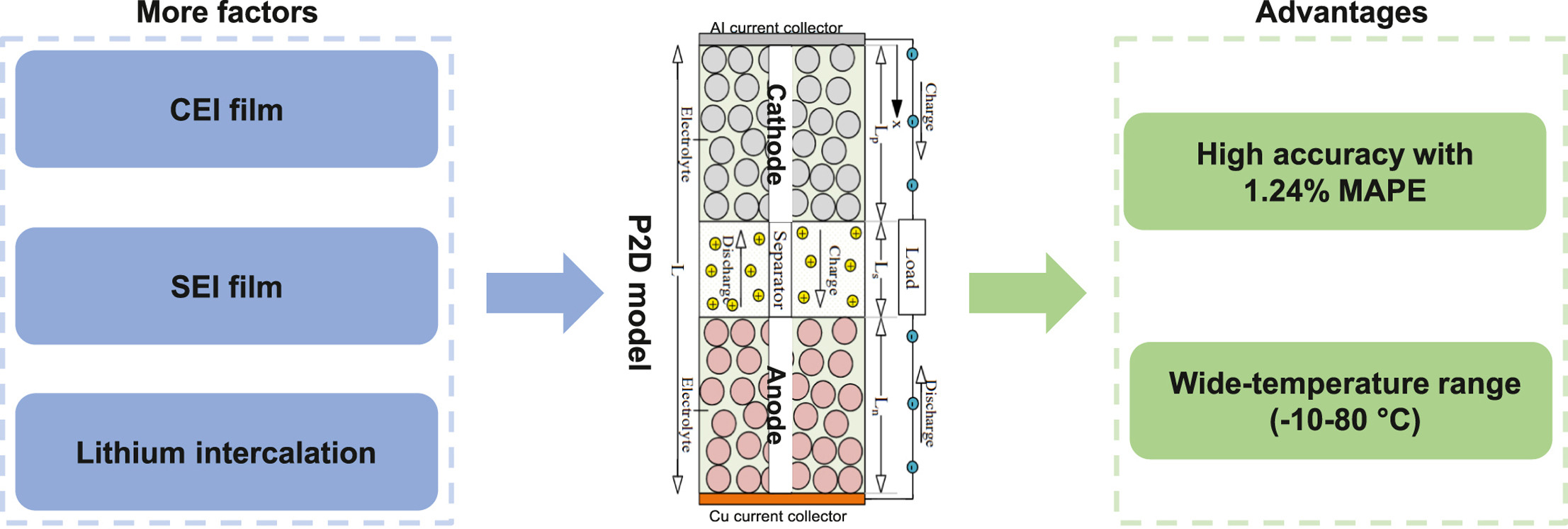
❖ The P2D model is established based on SEI, CEI, and lithium deposition over a wide-temperature rang.
❖ The MAPE of capacity fade simulation is only 1.24%.
❖ The contribution proportion of SEI film and CEI film to the side reaction film resistance is quantified.
❖ The characteristics of voltage change rate in the aging process are compared.
❖ The R2 of the charge/discharge curve is 0.94.

https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gce.2025.10.001
期刊简介
Green Chemical Engineering(GreenChE)于2019年入选“中国科技期刊卓越行动计划高起点新刊”,2020年9月正式创刊,最新影响因子7.6,位列Q1区,最新CiteScore为15.5,目前已被ESCI、EI、DOAJ、Scopus和CSCD等多个权威数据库收录。GreenChE以绿色化工为学科基础,聚焦"绿色",立足"工程" ,注重绿色化学、绿色化工及其交叉领域的前沿问题,紧紧围绕低碳化、清洁化和节能化的发展要求。目前是对读者和作者双向免费的开源期刊。
竭诚欢迎各位老师同学积极投稿!

E-mail: gce@ipe.ac.cn
Tel: 86-10-82544856
Web: http://www.keaipublishing.com/gce
微信公众号: GreenChemEng
Twitter: GreenChE
Facebook: Journal Greenche
科学网: GreenChE
关注我们,获取最新绿色化学工程资讯。

https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-3464012-1512654.html
上一篇:[转载]整期速递 | GreenChE Vol. 7 Issue 1
下一篇:[转载]「好文分享」东南大学任丽丽教授团队:从生物质走向财富—生物质衍生碳点的绿色合成、光致发光机理及多功能应用