博文
科学家在遥远的岛屿上发现了“令人不安”的塑料岩石
||
科学家在遥远的岛屿上发现了“令人不安”的塑料岩石
诸平


之前关于塑料方面的博文曾经写过几篇,如
今天介绍物理学家组织网(phys.org)2023年3月21日报道,科学家在遥远的岛屿上发现了“令人不安”的塑料岩石(Scientists make 'disturbing' find on remote island: plastic rocks)。
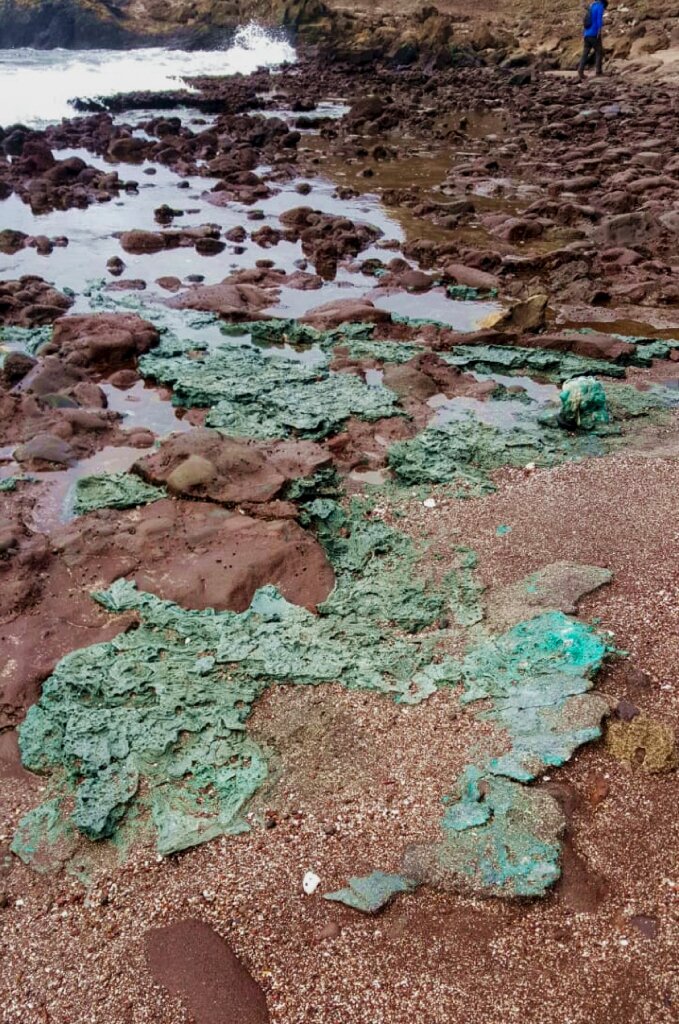
地球上很少有地方像特林达德岛(Trindade island)这样与世隔绝,它是一个火山露头处,距离巴西海岸只有三到四天的航程。因此,地质学家费尔南达·阿瓦尔·桑托斯(Fernanda Avelar Santos)在此惊讶地发现了一个令人不安的迹象,即人类对这片原本未受影响的土地产生了影响:海洋中漂浮的大量塑料污染在这里形成了岩石。
费尔南达·阿瓦尔·桑托斯第一次发现塑料岩石是在2019年,当时她前往该岛研究她的博士论文(doctoral thesis),这是一个完全不同的主题,滑坡、侵蚀和其他“地质风险”。
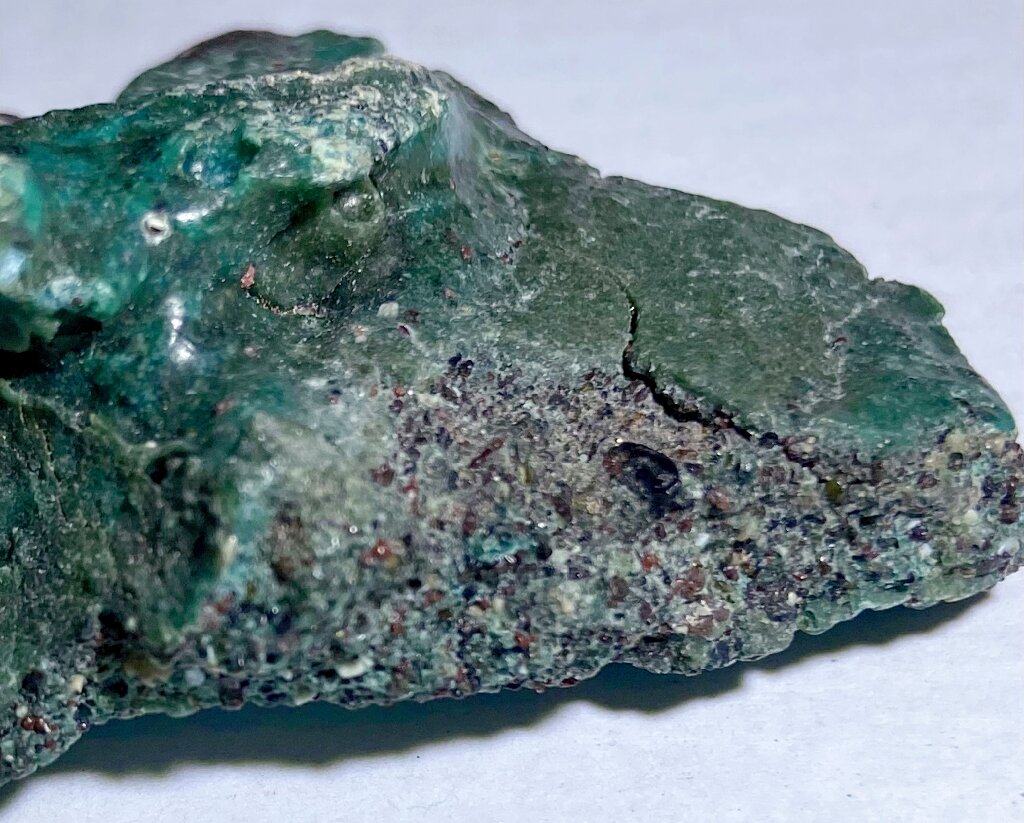
她在一个被称为海龟海滩(Turtle Beach)的受保护自然保护区附近工作,那里是世界上最大的濒危绿海龟(green turtle)繁殖地,当时她偶然发现了一大片外观奇特的蓝绿色岩石。出于好奇,她在为期两个月的探险后将一些蓝绿色岩石带了回实验室。
通过分析,她和她的团队将这些标本确定为一种新的地质构造,将地球数十亿年来用来形成岩石的材料和过程与一种新成分——塑料垃圾(plastic trash)融合在一起。
她对新闻媒体(AFP)说:“我们得出的结论是,人类现在扮演着地质代理人的角色,影响着以前完全自然的过程,比如岩石形成(rock formation)。它符合人类世(Anthropocene)的概念,科学家们最近经常谈论人类世:人类影响地球自然过程的地质时代。这种类似岩石的塑料(rock-like plastic)将被保存在地质记录中,并标志着人类世。”
岛屿天堂蓝(Island paradise)
费尔南达·阿瓦尔·桑托斯是巴西南部巴拉那联邦大学(Federal University of Parana, in southern Brazil)的教授,她说,这一发现让她感到“焦虑”和“不安”。
她把特林达德(Trindade)形容为“天堂”("like paradise"):一个美丽的热带岛屿,它的偏远使其成为各种物种——海鸟,只有那里才有的鱼,几乎灭绝的蟹类(crabs),绿海龟(green turtle)——的避难所。这个南大西洋岛屿(South Atlantic island)上唯一的人类存在是一个小型巴西军事基地(Brazilian military base)和一个科学研究中心。
2022年9月,在巴西圣埃斯皮里图州的特林达德岛(Trindade Island, Espirito Santo state, Brazil)发现了“塑料岩石”('Plastic rocks')——由漂浮在海洋中的大量塑料污染形成的岩石(见上述图所示)。
费尔南达·阿瓦尔·桑托斯说:“太令人惊讶了!在生态最重要的海滩之一发现这样的东西,就更加可怕了。”
2022年年底,她回到岛上,收集更多的标本,并深入研究这一现象。继续她的研究,她发现自2014年以来,美国夏威夷、英国、意大利和日本等地曾报道过类似的岩石状塑料结构。但特林达德岛是迄今为止发现它们的地球上最偏远的地方。费尔南达·阿瓦尔·桑托斯担心,随着岩石的侵蚀,它们将把微塑料浸到环境中,进一步污染岛上的食物链。
“范式转移”('Paradigm shift')
费尔南达·阿瓦尔·桑托斯和她的团队的研究发表在2022年9月份的《海洋污染公报》(Marine Pollution Bulletin)杂志上,详见:Fernanda Avelar Santos, Giovana Rebelo Diório, Carlos Conforti Ferreira Guedes, Gerson Fernandino, Paulo C. F. Giannini, Rodolfo José Angulo, Maria Cristina de Souza, Maria Aparecida Ferreira César-Oliveira, Angelo Roberto dos Santos Oliveira. Plastic debris forms: Rock analogues emerging from marine pollution. Marine Pollution Bulletin, September 2022, Volume 182, 114031. DOI: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.114031.
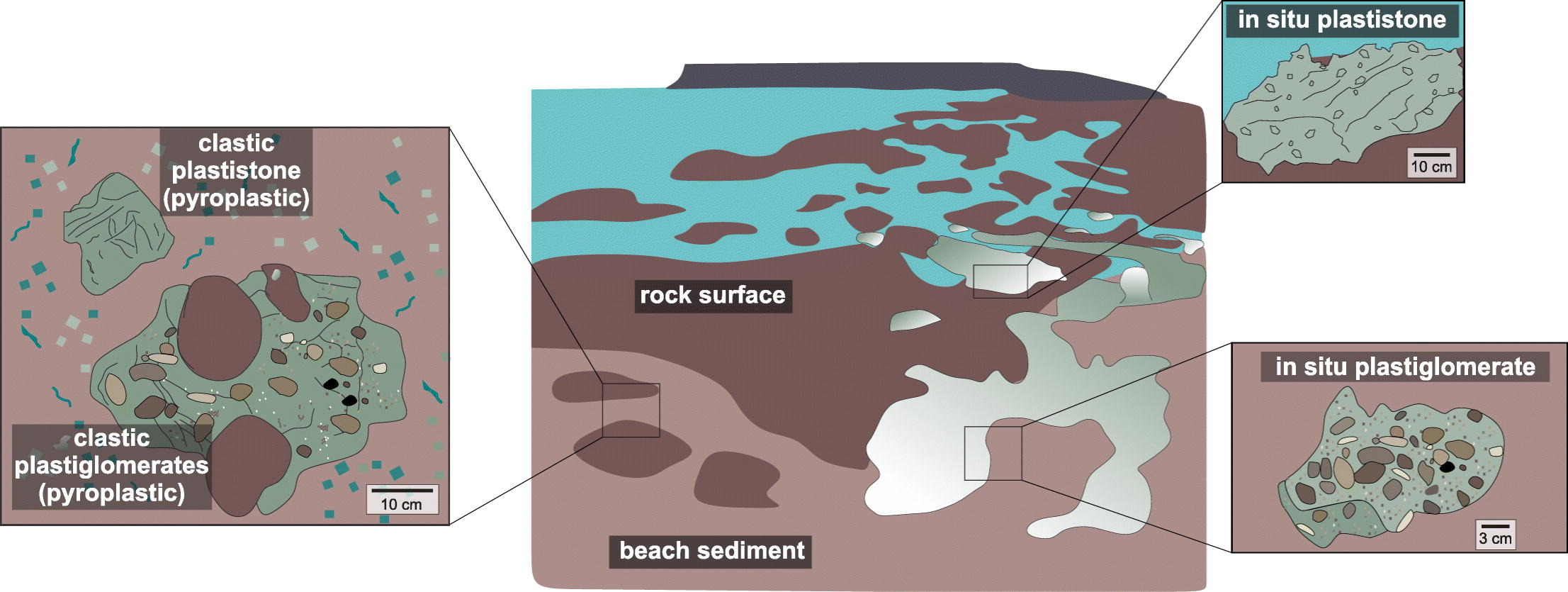
他们将世界各地发现的新型“岩石”分为几类:“塑状岩”("plastiglomerates"),类似于沉积岩(sedimentary rocks);“火塑体”("pyroplastics"),类似于碎屑岩(clastic rocks);还有一种以前未被识别的类型,“塑石”("plastistones"),类似于熔岩流(lava flow)形成的火成岩(igneous rocks)。
她的团队写道:“海洋污染正在引发岩石和沉积物(sedimentary deposit)形成概念的范式转变(paradigm shift)。人类的干预现在如此普遍,以至于人们不得不质疑什么是真正的自然。”
他们发现,费尔南达·阿瓦尔·桑托斯发现的岩石中的主要成分是渔网的残留物。但她说,洋流(ocean currents)也将大量的瓶子、家庭垃圾和其他塑料垃圾从世界各地卷到岛上。
费尔南达·阿瓦尔·桑托斯说,她计划把这个话题作为她的主要研究重点。特林达德岛“是我见过的最原始的地方,但看到污染我们海洋的垃圾是多么脆弱,就知道塑料污染这个问题在世界范围内是多么普遍。”
上述介绍,仅供参考。欲了解更多信息,敬请注意浏览原文或者相关报道。
• Marine pollution has triggered a novel situation in Earth Sciences.
• First sedimentary approach to plastic debris forms found on a single site.
• Field observations linked plastic debris forms to different substrate types.
• Plastistone is a novel plastic debris form.
• Humans became geological agents in processes considered essentially natural.
Continuous input of plastic litter in ocean and coastal environments achieved alarming levels that are exposing new settings in natural systems. While novel plastic debris pollution, with rock-like appearance, has been reported worldwide, fundamentally geological analyses are still lacking. We surveyed the first occurrence of multiple associated plastic debris on a single outcrop located in a remote site (Trindade Island, SE Atlantic Ocean). Even though all plastic debris forms consisted of polypropylene and polyethylene, through a sedimentary approach (cross section, macro, and micro analyses) distinct types were identified. We detected plastiglomerates, geogenic analogous to conglomerates, divided into in situ and clastic types, and formed over beach sediment. We identified plastistones as a new type with homogeneous composition (lacking incorporated materials), geogenic-looking igneous rocks, divided into in situ and clastic types, and formed over rock surfaces. We linked pyroplastics, geogenic analogous to clasts, to clastic plastiglomerates/plastistones, therefore representing clastic types of plastic debris forms. This association was correlated in a depositional system model, which suggests that plastic debris forms are rock synthetic equivalents in which humans act as depositional and post-depositional agents.
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-212210-1381654.html
上一篇:科学家打开了操纵量子光的大门
下一篇:《自然》:化学家合成并表征了具有立体氧原子中心的新型螺旋手性氧鎓离子