博文
生物医学工程--血管中的流固耦合
|||
[简介]本模型研究了血管系统的一部分,特别是大动脉的上部(图 4-1)。大动脉及其分支血管被包裹于肌肉组织中,特别是心肌组织中。流动血液产生的压力作用于动脉内表面以及它的分支,从而使组织肌肉发生变形。该分析有两个耦合的物理过程:首先,流体动力学分析了速度场以及血液中的压力分布情况(为时间和空间的变量);其次,组织和动脉的变形力学分析。在该模型中,血管外壁形状的任何改变并不影响流场,即该模型只是流体-结构单方向的耦合。但是,在COMSOL Multiphysics中,使用ALE(移动网格技术)可以使得仿真双向耦合成为可能。
[Introduction]This model studies a portion of the vascular system, in particular the upper part of the aorta (Figure 4-1). The aorta and its ramified blood vessels are embedded in biological tissue, specifically the cardiac muscle. The flowing blood applies pressure to the artery’s internal surfaces and its branches, thereby deforming the tissue. The analysis consists of two distinct but coupled procedures: first, a fluid-dynamics analysis including a calculation of the velocity field and pressure distribution in the blood (variable in time and in space); second, a mechanical analysis of the deformation of the tissue and artery. In this model, any change in the shape of the vessel walls does not influence the fluid domain, which implies that there is only a 1-way fluid-structural coupling. However, in COMSOL Multiphysics it is possible to simulate a 2-way coupling using the ALE (arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian) method.
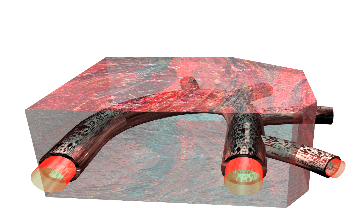
图 4-1: 模型求解域由部分大动脉,分支,以及其周围的肌肉组织组成
Figure 4-1: The model domain consists of part of the aorta, its branches, and the surrounding tissue
[模型定义]
图 4-2 表示求解域的两种不同显示形态,一个包含了心肌组织,另一个没有包含心肌组织。模型的力学分析必须考虑心肌组织,因为它在动脉血管由于流体压力发生变形的过程中,充当了阻尼力的作用。
Figure 4-2 shows two views of the problem domain, one with and one without the cardiac muscle. The model’s mechanical analysis must consider the cardiac muscle because it presents a stiffness that resists artery deformation due to the applied pressure.

Figure 4-2: A view of the aorta and its ramification (branching vessels) with blood contained, shown both with (left) and without (right) the cardiac muscle
1)流体动力学分析
2)力学分析
该模型由于大变形假设以及材料的本构关系(和橡胶材料相似的描述大动脉以及心肌组织行为准则的超弹性模型)表现为高度非线性特性。只有和生物组织相关的求解域在该分析中被激活。模型包含了在流体动力学分析中全部应力分布所产生的载荷。
类橡胶生物组织以及大动脉材料模型分析由于以下原因,类橡胶弹性体的分析相当的复杂:
• 材料能够承受非常大的应变(有限形变)。
• 应力-应变关系为非线性。
• 许多类橡胶材料几乎都是不可压缩的。为了获得正确的结果,你必须修改标准的以位移为基础的有限元公式(混合公式)。
• 材料能够承受非常大的应变(有限形变)。
• 应力-应变关系为非线性。
• 许多类橡胶材料几乎都是不可压缩的。为了获得正确的结果,你必须修改标准的以位移为基础的有限元公式(混合公式)。
必须特别注意定义应力应变的单位。有限的变形代表了无穷小位移假设不再有效。当具有如下条件时可考虑有限变形:
• 发生了显著的刚体转动(有限转动)。
• 应变不再是小量(大于某一个量值)。
• 体载荷依赖于变形。
• 发生了显著的刚体转动(有限转动)。
• 应变不再是小量(大于某一个量值)。
• 体载荷依赖于变形。
幸运的是,所有这些组织分析所需的超弹性材料特性模型都可以在结构力学模块中找到。
材料
本模型分析使用了如下材料特性:
• 血液
- 密度density = 1060 kg/m3
- 动力粘度dynamic viscosity = 0.005 Ns/m2
• 动脉
- 密度density = 960 kg/m3
- Neo-Hookean 超弹性行为: 弹性系数 μ=6,204,106 N/m2, 体积弹性系数为20μ,相应的泊松比ν=0.45,等价的弹性模量为1.0·107 N/m2 。
• 心肌组织
- 密度density = 1200 kg/m3
- Neo-Hookean 超弹性行为: 弹性系数 μ = 719,676 N/m2, 体积弹性系数为20μ,相应的泊松比 ν=0.45。等价的弹性模量为1.16·106 N/m2。
材料
本模型分析使用了如下材料特性:
• 血液
- 密度density = 1060 kg/m3
- 动力粘度dynamic viscosity = 0.005 Ns/m2
• 动脉
- 密度density = 960 kg/m3
- Neo-Hookean 超弹性行为: 弹性系数 μ=6,204,106 N/m2, 体积弹性系数为20μ,相应的泊松比ν=0.45,等价的弹性模量为1.0·107 N/m2 。
• 心肌组织
- 密度density = 1200 kg/m3
- Neo-Hookean 超弹性行为: 弹性系数 μ = 719,676 N/m2, 体积弹性系数为20μ,相应的泊松比 ν=0.45。等价的弹性模量为1.16·106 N/m2。
流体动力学分析
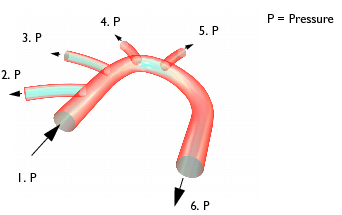
图 4-3: 流体分析的边界条件
| • |
区域 1: 11,208 Pa |
| • |
区域 2: 11,192 Pa |
| • |
区域 3: 11,148 Pa |
| • |
区域 4: 11,148 Pa |
| • |
区域 5: 11,148 Pa |
| • |
区域 6: 11,120 Pa |
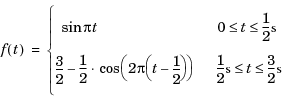 (4-1)
(4-1)首先计算稳流场以将其结果和瞬态场分析进行对比。 图 4-4 表示了速度场的切片图(单位为m/s)以及流线图(显示速度为一个方向向量)。
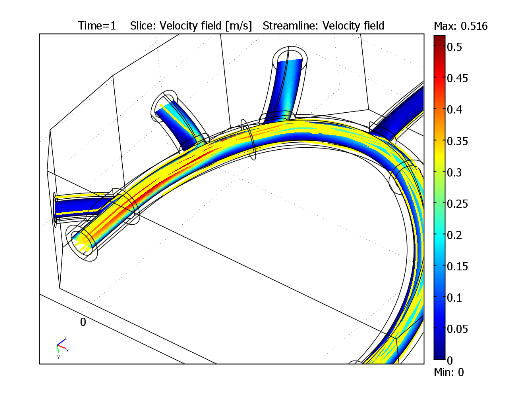
图 4-4: 速度场彩色切片以及大动脉及其分支的流线分布图
图 4-5 表示在最大载荷时的总位移量(1s后)。位移量为10μm,表明单向多物理场耦合是一种可行的近似方法。
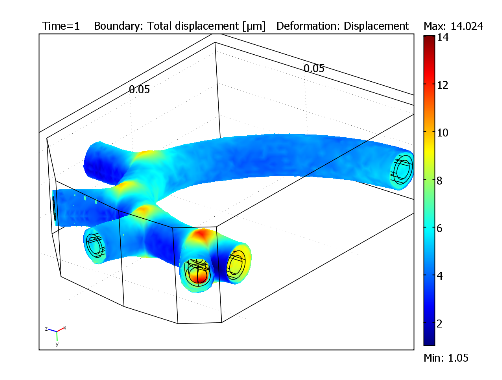
图 4-5: 采用超弹材料模型时的血管位移图
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-540512-530466.html
上一篇:用COMSOL模拟流固耦合
扫一扫,分享此博文
全部精选博文导读
相关博文
- • Discovering the Theory of Relativity: As an Infant(初学者版)
- • Discovering The Law of Gravity: As an Infant(初学者版)
- • Discovering Pythagoras\´ Theorem: As an Infant(初学者版)
- • Discovering Shannon\´s Entropy: As an Infant(初学者版)
- • Discovering the Schrödinger Equation: As an Infant(初学者版)
- • Discovering the Second Law of Thermodynamics(初学者版)