博文
张树鹏老师合作论文在Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering发表
||
Platanus acerifolia (Aiton) Willd. fruit-derived nitrogen-doped porous carbon as an electrode material for the capacitive deionization of brackish water
Yun Li a, Hongxiang Li a , Tiantian Zhou a,Qian Lai a , Gusunkiz Egabaierdi a, Shiwen Chen a, Haiou Song a, *, Shupeng Zhang b,* , Chenfei Shi a, Shaogui Yang a, Huan He a, Xianqiu Zhang a, *
Abstract
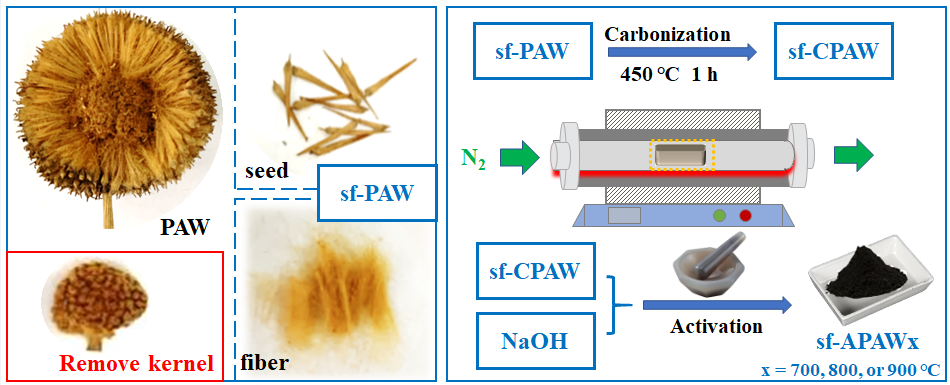
Capacitive deionization (CDI) is a new technology for the desalination of brackish water and its performance is greatly affected by the electrode materials utilized. Biomass-derived carbons have attracted significant attention as CDI materials due to their high availability, inexpensiveness, renewability and eco-friendly characteristics. In this work, Platanus acerifolia (Aiton) Willd. fruit-derived nitrogen-doped porous carbon (sf-APAWx) is prepared through carbonization at 450 °C, followed by NaOH activation at different temperatures of 700, 800 and 900 °C. The sf-CPAW activated at 800 °C possesses a large specific surface area (3846 m2 g−1), affluent pores and a hierarchical structure; and exhibits a high specific capacitance of 138.81 F g−1, a satisfactory salt adsorption capacity of 18.05 mg g−1 and the fastest salt adsorption rate of 1.01 mg g−1 min−1. These results demonstrate the potential of sf-APAW800 as an electrode material for CDI and the sustainable use of abandoned resources.
In summary, N-doped porous carbon has been successfully synthesized by a facile and effective approach using platanus fruits as precursors. The activation temperature has an important influence on the properties of the prepared carbon materials. The obtained sf-APAW800 possesses favorable characteristics, including high specific surface area (3846 m2 g−1), hierarchical pore structure and doping of N atoms, which not only provide more active sites but also improve the ion diffusion. Due to the synergistic effect, sf-APAW800 exhibits an excellent specific capacitance of 138.63 F g−1 at 10 mV s−1 and the lowest internal resistance. In the CDI tests, the highest electrosorption capacity of 18.05 mg g−1 and the fastest electrosorption rate (1.01 mg g−1 min−1) were achieved by sf-APAW800 in a 100 mg L−1 NaCl solution at 1.6 V. Furthermore, the SAC retention was 89.2% after ten cycles in the long-term experiment, illustrating the outstanding recyclability of sf-APAW800. It is believed that sf-APAW800 could be a promising candidate as an electrode material for CDI applications.
原文链接: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S221334372300653X
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-311896-1384774.html
上一篇:祝贺本科生康嘉伟、沈蓥和郭禄祺三位同学获得国家级科研训练课题资助
下一篇:祝贺曹政荣获2022年硕士研究生国家级奖学金