博文
刊·见 | 从采矿废料到关键金属,矿物加工与冶金工程领域期刊探讨如何“变废为宝”  精选
精选
||
在矿物加工与冶金工程领域,随着全球经济的快速发展,对金属资源的需求持续攀升。然而,优质矿产资源不断减少,低品位、复杂难处理矿石逐渐成为开发重点。同时,环境保护意识的增强,也对资源高效利用与绿色生产提出更高要求。如何在复杂条件下实现资源的高效提取,降低能耗与污染,成为行业亟待解决的关键问题,推动着矿物加工与提取冶金研究向更深层次迈进。
本期【刊•见】将介绍矿物加工与冶金处理领域的国际期刊—Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review。除了对期刊进行详尽解读外,还向您推荐近一年的高阅读量文章:
影响因子根据JCR显示,Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review
在冶金学与冶金工程排名 17/97
在矿业与矿物加工排名 6/33
根据Scopus显示, Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review
在地球与行星科学:经济地质学领域排名 2/47
在地球与行星科学:岩土工程与工程地质学领域排名 10/239
在工程学:机械工程学领域排名 35/720
在化学:普通化学领域排名 44/404
根据2025年3月20日发布的中国科学院期刊分区表显示:
大类及分区:
工程技术3区
小类及分区:
冶金工程2区
矿业与矿物加工3区
审稿周期
从提交稿件到获取初审意见,平均需要1天
获取首个同行评审决定,平均需要27天
稿件一旦接受后,在线出版平均需要17天
Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review 为混合开放获取期刊,支持作者以开放获取的模式发表文章,提升研究影响力。

Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review 期刊由来自美国密歇根理工大学的 S. Komar Kawatra教授担任,编辑团队由来自中国、美国、澳大利亚等地的行业翘楚组成。
主编S. Komar Kawatra
S. Komar Kawatra,美国密歇根理工大学荣誉教授,曾任化学工程系主任。主要研究领域是化学工程,专注于用于化学和颗粒过程工厂的监测和控制的仪器及在线分析以及化学和工业废物的处理与修复。
中国编委陶东平
陶东平,山东理工大学资源与环境工程学院院长,担任美国肯塔基大学终身教授、中国矿业大学特聘教授20余年。长期从事资源与环境领域颗粒分离分选理论和技术的研究和教学。
杜浩
杜浩,中国科学院过程工程研究所研究员、博士生导师,主要从事表面化学、清洁工艺、绿色过程与工程废弃物资源化利用的基础研究与应用工作。
作者分布根据JCR显示,近三年在Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review 发文的国家/地区中,发文较为活跃的是:
中国
澳大利亚
印度
全球高校和科研机构中,近三年在Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review 发文比较活跃的是:
澳大利亚联邦科学与工业研究组织
韩国国立木浦大学
东北大学(中国)
通讯作者:Hani Ababneh, Aiping Chen & Bassam Dally
文章摘要:
This study systematically evaluates steam calcination as a method for producing magnesium oxide (MgO) from magnesite (MgCO₃), by testing actual industry samples under varying conditions. While the potential benefits of steam calcination were previously acknowledged, this work provides the first comprehensive quantification of its advantages over conventional methods such as flue gas and flue gas with steam calcination. The results demonstrate that steam calcination significantly lowers the decomposition temperature of MgCO₃, achieving near-complete decomposition within 20 min at 600°C while also accelerating the decomposition of dolomite and calcite present in magnesite ores. Steam calcination enhances the specific surface area of MgO to 49.61 m2/g, optimizes structural properties such as pore volume, and improves reactivity, with reaction times as short as 45 s. Environmentally, steam calcination reduces total energy consumption by approximately 15%, and simplifies CO₂ capture by separating it from condensed steam, enabling a potential carbon emissions reduction of 1.09 kg CO₂-e per kilogram of MgO produced. Furthermore, its compatibility with renewable energy sources aligns with sustainable industrial goals, establishing steam calcination as a highly efficient and environmentally friendly alternative for industrial MgO production.

Figure 1. (a) Experimental setup flow diagram used in the study, (b) Horizontal and vertical furnaces assembly used in the study, (c) Reaction bed used to calcine the samples.
采用酒石酸与甲酸从磷酸铁锂电池中实现锂的完全提取:比较与动力学研究
通讯作者:Brenda Segura-Bailón et al.
文章摘要:
The rapid expansion of the battery market also increases the demand for raw materials, particularly metals. Recently, new technologies have been implemented to recover valuable materials from secondary resources. In this investigation, a hydrometallurgical method for lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4, LFP) battery recycling is proposed. The effectiveness of tartaric (C4H6O6) and formic (CH2O2) acids for lithium extraction was evaluated and compared. The effect of organic acid concentration, temperature, oxidant addition, and solid–liquid ratio were the parameters analyzed. This study demonstrated that both agents extract 100% of lithium. Kinetics analysis showed that lithium leaching was controlled by chemical reaction, estimated the apparent activation energies (Ea) of 42.4 kJ/mol and 38 kJ/mol for CH2O2 and C4H6O6 systems, respectively. Moreover, the effect of oxidants in preventing the co-dissolution of specific impurities like iron and phosphorus, especially in formic acid solutions, has been demonstrated. The experimental conditions, 100 g/L, 0.5 M CH2O2, 2.5 vol% H2O2, 25°C, and 250 rpm, suppressed the iron and phosphorus leaching by >90%. This work presented an alternative method that operates at room temperature and employs nontoxic substances to improve recycling techniques for LFP batteries via complete lithium extraction.
通讯作者:Yi Yang & Miao Chen
文章摘要:
Synchrotron-based technologies can provide an incomparable and unique characterization capacity over laboratory-based techniques to improve our understanding of complex mineral processing. In the last 20 years, synchrotron-based technologies, including XAS, SXPS, SXRD, PEEM, SPEM, STXM, and XCT, have been widely used in the characterization of (bio)leaching of metal sulfides in different aspects. These technologies provided an in-depth understanding of mineral-solution reaction mechanisms in mineralogy, electronic properties of sulfide minerals, surface chemistry, solution chemistry, leaching intermediate species, as well as biochemistry of bacteria and bacteria-mineral interactions. In particular, XAS and SXPS have been used to understand the properties of minerals and their stepwise dissolution by cross-evidence from spectra of S, Cu, Fe, As, etc. These studies revealed the dissolution mechanisms of a variety of metal sulfides with economic and environmental importance such pyrite, chalcopyrite, pyrrhotite, arsenopyrite, enargite. In-situ XAS and XRD have provided a unique approach to quantitatively understand the leaching mechanisms and processes in real-time. Spatially resolved technologies such as PEEM, SPEM, and STXM further elucidated the mechanisms of heterogeneous oxidation of these minerals, and microbe-mineral interaction. In addition, Synchrotron CT shows an incomparable advantage in obtaining quantitative 3D mineralogy and tomographic data, which advanced our understanding in particle void development and metal sulfide dissolution. Important directions for the use of synchrotron in sulfide (bio)leaching include using in-situ characterization to monitor the leaching process that may not be fully reflected by sampling and integrating advanced endstations and AI algorithms to better distinguish leaching intermediate and products.
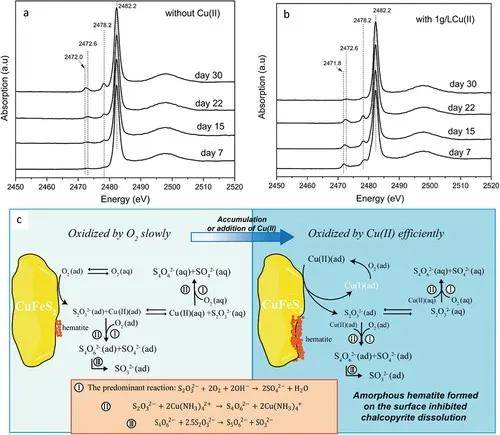
Figure 1. XANES investigation of chalcopyrite ammonia leaching.
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-3574014-1517189.html
上一篇:从城市露营到社会结构,这些文章呈现中国旅游研究的新鲜洞察(可免费阅读)
下一篇:【科研新人必读】:如何制定高效的学术发展规划?5步助您从科研小白进阶资深学者



