博文
刊·见 | 与Wood Material Science and Engineering一起探索木材科学的前沿技术  精选
精选
||
木材科学是一个重要的学术研究领域,应用前景广阔。随着环保和可持续发展理念的逐渐深入,木材科学未来的研究方向更重视材料是否可再生以及对于环境是否友好,推动木材产业可持续发展的创新技术是科研人员当前关注的热点。
本期刊·见栏目,为您介绍材料科学:木材科学领域期刊Wood Material Science and Engineering,除了对期刊详尽的介绍外,还向您介绍刊内近三年内作者高被引文章,以及近一年内高阅读量文章:
l 综述:人造板中超低甲醛释放胶粘剂系统和甲醛清除剂的最新进展
l 综述:关于影响木材建筑中实木产品胶合质量的因素的部分前人研究成果及可能的发展
l 二氧化碳激光切割后榉木的解剖和形态特征
l 大跨度受压表皮木地板的动态试验

Wood Material Science and Engineering 是一本跨学科国际期刊,旨在为木材科学和技术领域的前沿提供服务,发表基础研究和应用研究,主题涵盖:
l 木材材料科学,重点聚焦于:水木关系、木材耐久性、木材改性、木材力学、木材复合材料、工程木制品、能源转换和高效节能的木质产品。
l 木材工程学,即把木材材料科学应用于林产品的设计、加工和制造,以及对于这些产品的机器和工艺使用。聚焦生物燃料、锯材和精炼的产品,如结构元件、室内配件和家具。在这方面侧重木材材料的性质与终端木制品的特性及其对环境的影响之间的联系。
此外,Wood Material Science and Engineering还接受高水平的综述。
该期刊已被Scopus, CAB Abstracts, AgBiotechNet, Review of Agricultural Entomology等数据库收录。

2022影响因子:2.2
2022 5年影响因子:2.3
影响因子最佳分区:Q2
2022 CiteScore: 4.4
2022 CiteScore最佳分区: Q2
年下载量:7.4万次
稿件接受率:44%
JCR排名
根据JCR显示,Wood Material Science and Engineering 在材料科学、造纸和木材领域排名6/21。
CiteScore
根据Scopus显示, Wood Material Science and Engineering的
· CiteScore(2022)为4.4
· CiteScoreTracker(2023)为3.5
Wood Material Science and Engineering在材料科学领域排名203/453
中国科学院文献情报中心期刊分区表
根据2023年12月27日发布的中国科学院期刊分区表(升级版)显示:
大类及分区:农林科学3区
小类及分区:材料科学-纸与木材2区
编辑团队
Wood Material Science and Engineering主编是Dick Sandberg教授(瑞典吕勒奥理工大学)。副主编由Charles Frihart博士(美国农业部森林产品实验室)、Magnus Wålinder教授(瑞典 KTH 建筑材料学院)、Andreja Kutnar教授(斯洛文尼亚 InnoRenew CoE研究所 和Primorska 大学)、George Mantanis教授(希腊塞萨利大学)共同担任。此外,编委团队由多国学者组成。其中,来自中国的是北京林业大学曹金珍教授。
主编介绍

Dick Sandberg教授任职于瑞典吕勒奥理工大学,他的研究方向为木材科学与工程。
副主编介绍

Charles R. Frihart博士任职于美国农业部森林产品实验室,致力于在应用研究与基础研究、工业界与学术界、纳米级工艺与宏观性能、化学结构与聚合物性能之间架起美国与外国研究人员之间的桥梁。他主要的研究方向为粘合剂,他认为化学品与木材的相互作用也具有重要价值。

Magnus Wålinder教授任职于瑞典KTH建筑材料学院,他的研究方向聚焦支持未来由可再生资源制成的生物基建筑材料的开发。

Andreja Kutnar教授任职于斯洛文尼亚科佩尔普利莫斯卡大学,她也是InnoRenew CoE 研究所的负责人。她的研究方向包括木材复合材料、木材的热-水-机械处理以及粘合。

George Mantanis教授任职于希腊塞萨利大学,他的研究领域为木材结构与性能。
中国编委介绍

曹金珍教授任职于北京林业大学,她主要的研究方向为木材功能性改良,包括木材防腐防霉、防水及尺寸稳定化、耐光老化性能改良和新型木基功能化材料的研究。
作者分布
根据JCR显示,近三年在Wood Material Science and Engineering 发文的国家中,发文排名前三位的国家有:
· 中国
· 瑞典
· 德国
近三年,在Wood Material Science and Engineering 发文的全球高校和科研机构中,发文数量排名前三位的是:
· 南京大学
· 吕勒奥理工大学
· 哥廷根大学
近三年内高被引文章

综述:人造板中超低甲醛释放胶粘剂系统和甲醛清除剂的最新进展
摘要:
Traditional wood-based panels are produced with synthetic, formaldehyde-based adhesives, commonly made from fossil-derived constituents, such as urea, phenol, melamine, etc. Along with their numerous advantages, such as chemical versatility, high reactivity and excellent adhesive performance, these adhesives are characterized by certain problems, connected with the hazardous volatile organic compounds (VOCs), mostly free formaldehyde in the adhesives and the formaldehyde emission from the finished wood composites, which is carcinogenic to humans and harmful to the environment. The growing environmental concerns and stringent legislative requirements to the formaldehyde emission from wood-based panels have posed new challenges to researchers and industrial practice, related to the development of sustainable, eco-friendly wood-based panels with close-to-zero formaldehyde emission. The most common methods to reduce the formaldehyde emission from wood-based panels have been to decrease the free formaldehyde in the adhesive by modifying the adhesive (like lowering the molar ratio of formaldehyde to urea in UF resin) or by using formaldehyde scavengers, one group of scavengers being for adhesives by mixing or reacting and the second one scavengers for wood-based panels as post-treatments. Another way is to use alternative bio-based adhesives, however, there are still substantial challenges for the complete replacement of formaldehyde-based adhesives with bio-based adhesives, mainly because of their relatively low bonding strength, poor water resistance, etc. This article presents a review and analysis of the current state of research in the field of low formaldehyde emission wood adhesives and formaldehyde scavengers for manufacturing low-toxic, eco-friendly wood composites.

综述:关于影响木材建筑中实木产品胶合质量的因素的部分前人研究成果及可能的发展
摘要:
Various factors affect the bonding quality of elements used for timber construction. This review includes literature studies and personal experiences related to relevant technological variables defining glue bond performance in glue-laminated timber elements during their service life. The gluing of hardwood species receives special focus as it is considered by the industry to be the most challenging process for implementation. In particular, the effects of wood species, type of adhesive, glued-wood surface quality, physical and/or chemical modification of the wood, technological solutions for gluing, and varying climatic conditions during the use phase (relative humidity, temperature, air circulation, etc.) are considered. In addition, overlapping of individual influencing factors often leads to problems with bonding, thus requiring strongly integrating measurement methods (e.g. NIR spectroscopy). The causes of variations in the results when glued wood is tested using different standardized methods are discussed. A list of open research questions is provided, and problem solutions are recommended based on systematized cutting-edge knowledge. The aim of the work is to systematize the state of knowledge of wood gluing to create a basis for controlled and stable manufacturing processes. The progress of the work will be reported in further publications.
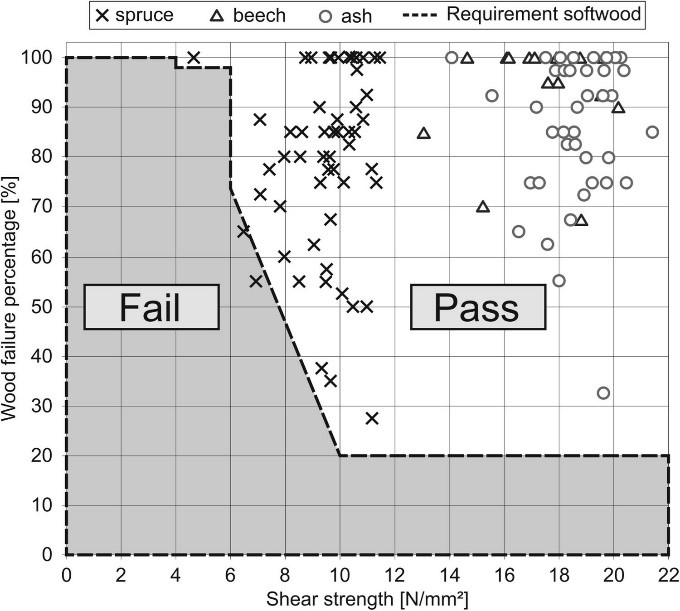
Shear strength and wood failure percentages of glue laminated timber made of beech and ash compared to spruce.
Note: an unacceptable performance limits for individual glue lines in softwood engineered products are marked as gray. (Arnold et al. Citation2019).
近一年内高阅读量文章

Dynamic tests on a long-span, stressed-skin, timber floor
大跨度受压表皮木地板的动态试验
摘要:
The design of timber floors is often governed by the fulfilment of serviceability requirements concerning human-induced vibrations. The stiffness and modal properties (eigenfrequency and damping ratio) are essential parameters for the design verification of timber floors against vibrations. In the present paper, a series of experimental tests (static tests, impact hammer modal tests, forced resonant vibrations and free vibrations) on a long-span, stressed-skin, timber floor are presented, together with predictions using a Finite Element model. Moreover, the effect of additional mass was investigated by adding extra weight in the mid-span. The modal properties obtained by different methods were in good agreement. The measured damping ratios were low, especially for the first two modes (of the order of 0.7% for the first mode and 0.8-1.0% for the second mode). The FE predictions were in good agreement with the experimental results regarding stiffness and the first two eigenfrequencies. However, the FE model overestimated the third eigenfrequency and underestimated the steady state accelerations observed under forced vibrations. A stiffness-proportional Rayleigh damping was found to describe best the energy dissipation.
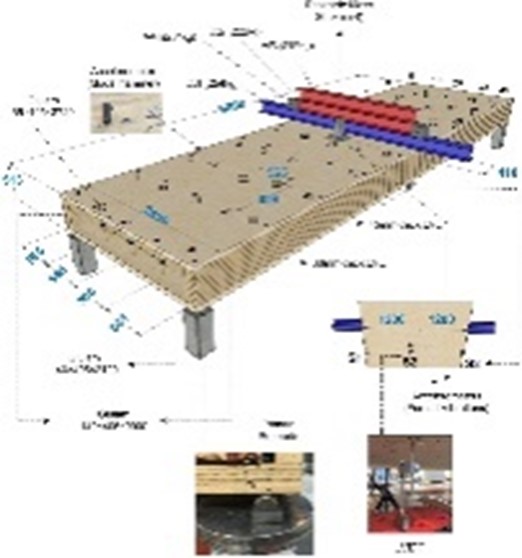
3D layout of the floor and details.
审稿周期
从提交稿件到获取初审意见,平均需要38天
获取首个同行评审决定,平均需要43天
稿件一旦接受后,在线出版平均需要14天
为帮助更多科研人员选择更加合适的期刊,Taylor & Francis推出专栏——刊·见,该专栏致力于为读者和广大科研人员带来Taylor & Francis旗下期刊的详细解读,从期刊的基本情况、编委阵容、社会影响力到审稿速度、高被引文章等实用信息,专栏将为您带来最详细的介绍,让您更加全面地了解Taylor & Francis旗下优秀的国际期刊,帮助更多中国卓越科研成果顺利在国际期刊上发表。
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-3574014-1420638.html
上一篇:刊·见 | 与 Applied Mathematics in Science and Engineering一起探索数学
下一篇:揭示生命演变的奥秘,古生物学领域优质期刊