博文
2025年09月嘲风作品集(一)
||

▲ Vol 08 Issue 05 | September , 2025
Artificial Intelligence-Driven Innovations in Hydrogen Storage Technology
Yusong Ding, Lele Tong, Xiaolin Liu, Ying Liu, Yan Zhao
In the global transition towards sustainable energy sources, hydrogen energy has emerged as an indispensable pillar in reshaping the energy landscape, owing to its environmental sustainability, zero emissions, and high efficiency. Nevertheless, the large-scale deployment of hydrogen energy is confronted with substantial technical barriers in storage and transportation. Although contemporary research has shifted focus to the development of highly efficient hydrogen storage materials, conventional material design concepts remain predominantly empirical, typically relying on trial-and-error methodologies. Importantly, the widespread application of artificial intelligence technologies in accelerating materials discovery and optimization has attracted considerable attention. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements in hydrogen storage technologies, with an emphasis on the synergistic application of high-throughput screening and machine learning in solid-state hydrogen storage materials. These approaches demonstrate exceptional potential in accurately predicting hydrogen storage properties, optimizing material performance, and accelerating the development of innovative hydrogen storage materials. Specifically, we discuss in detail the essential role of artificial intelligence in developing hydrogen storage materials such as metal hydrides, alloys, carbon materials, metal–organic frameworks, and zeolites. Moreover, underground hydrogen storage is further explored as a scalable renewable energy storage solution, particularly in terms of optimizing storage parameters and performance prediction. By systematically analyzing the limitations of existing hydrogen storage approaches and the transformative potential of artificial intelligence-driven methods, this review offers insights into the discovery and optimization of high-performance hydrogen storage materials, contributing to sustainable global energy development and technological innovation.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/eem2.70041

▲ September 03, 2025
Safety Science and Technology创刊号
Safety Science and Technology《安全科学与技术》英文期刊是由Wiley与中国化学品安全协会联合创办的开放获取国产学术期刊,由中国化学品安全协会常务副理事长路念明担任荣誉主编,澳大利亚斯威本科技大学王浩教授担任创刊主编,昆士兰大学Maureen Hassall教授、英国萨里大学温晓玲教授、西安科技大学邓军教授、中国科技大学胡隆华教授、大连理工大学高伟教授、华北科技学院徐景德教授、青岛科技大学王磊教授担任副主编。期刊致力于解决传统和新兴行业中的关键安全问题,助力构建更安全、更具韧性的社会与技术体系。期刊旨在为学术界、工业界和政策制定者搭建高水准的交流平台,推动安全科学理论突破与技术创新,促进全球安全标准的提升与可持续发展。该期刊聚焦全球安全科学领域的创新研究与实践,涵盖化学品安全(Chemical Safety)、工业过程安全(Industrial Process Safety)、矿业安全(Mine Safety)、火安全(Fire Safety)、能源存储与运输安全(Energy Storage and Transportation Safety)、环境风险评估(Environmental Risk Assessment)、职业健康与安全(Occupational Health and Safety)、应急管理(Emergency Management)及先进安全技术(Advanced Safety Technologies)等跨学科主题。
Safety Science and Technology《安全科学与技术》国产英文期刊创刊
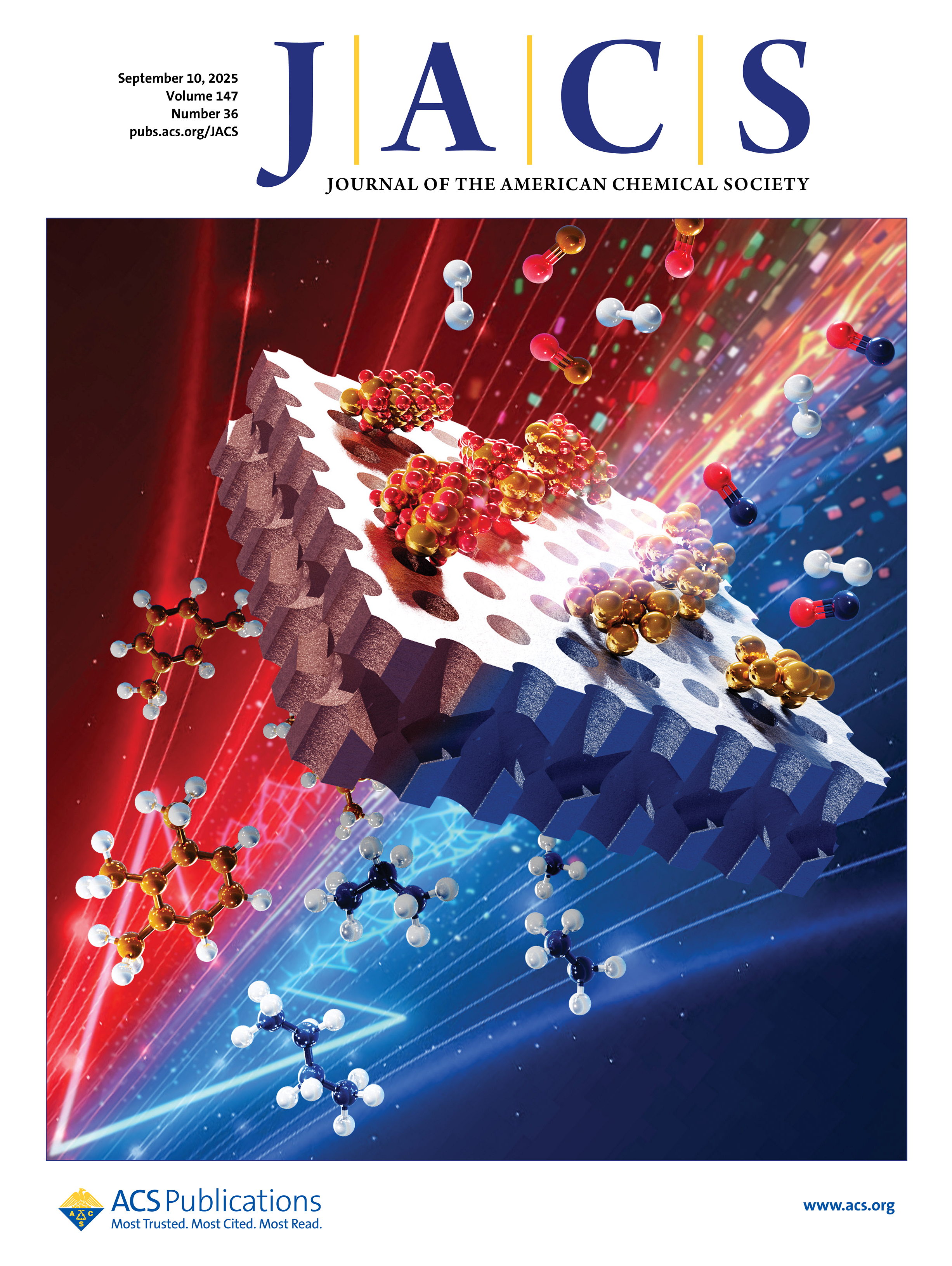
▲ Vol 147 Issue 36 | September 10 , 2025
Determination of Mn Valence States in Nanocatalysts During Sustainable Syngas Conversion
Zhiping Li, Duohua Liao, Guo Tian, Xiaoyu Fan, Xu Chai, Wenxi Chang, Yuan Gao, Bo Yuan, Zonglong L, Fei Wei, Chenxi Zhang
Constructing structure–activity relationships (SAR) between nanocatalysts under reactive atmospheres makes them indispensable for chemical synthesis, energy transformation, and environmental remediation. However, this structure sensitivity remains ambiguous for metals/metal oxides due to dynamic changes in metal valences under a reductive atmosphere. Herein, this study delves into the complexities of Mn-based nanocatalysts, focusing on the impact of the Mn valence state in a test reaction converting sustainable syngas to aromatics-a process highly sensitive to the catalyst’s redox environment and active site characteristics. We conducted a thorough SAR analysis and discovered a direct correlation between the Sabatier effect, CO adsorption, and the space-time yields of aromatics. Notably, Mn in the +2-oxidation state emerged as the optimal valence for achieving the highest catalytic performance, with a maximum yield of 1.6 mmol·h–1·gcat–1. Our findings provide critical insights into the role of the catalyst’s intrinsic properties in dictating the selectivity and efficiency of CO hydrogenation for the rational design of nanocatalysts that can sustainably transform small molecules into valuable chemicals and fuels.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.5c06550

▲ Vol 27 Issue 36 | September 12 , 2025
Pushing the Performance Boundaries of Highly Energetic Bis(1,2,4-triazoles) through Merging Dual Strategies of C-Azo Bridging and N-Nitramino Functionalization
Yangyang Long, Dongshuai Su, Hui Zhang, Yingqi Xia, Qi Lai, Ping Yin, Siping Pang
In this work, by combining the energetic -N═N-, -NO2, and N-NH2/N-NHNO2 groups with triazole, N-amino compound 3 and N-nitramino compound 4 were synthesized. Compound 3 has a unique crystal structure, exhibiting enhanced energetic properties (V = 8996 m s–1, and P = 34.0 GPa) and stability (Td = 202 °C, IS = 21 J, and FS = 216 N) comparable to that of hexogen (RDX). Compound 4 exhibits a high density (1.91 g cm–3) and excellent detonation performance (V = 9627 m s–1, and P = 41.0 GPa), and hydroxylammonium salt 5b exhibits exceedingly excellent detonation performance (V = 9677 m s–1, and P = 41.3 GPa).
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.orglett.5c03115
<静远嘲风-南京>设计制作

购书链接:
☆科学的颜值:学术期刊封面故事及图像设计
https://item.jd.com/12802188.html
☆科技绘图/科研论文图/论文配图设计与创作自学手册:CorelDRAW篇
https://item.jd.com/13504674.html
☆科技绘图/科研论文图/论文配图设计与创作自学手册:Maya+PSP篇
https://item.jd.com/13504686.html
☆科技绘图/科研论文图/论文配图设计与创作自学手册:科研动画篇
https://item.jd.com/13048467.html#crumb-wrap
☆SCI图像语法-科技论文配图设计使用技巧
https://item.jd.com/10073529532924.html?bbtf=1

静远嘲风(MY Scimage) 成立于2007年,嘲风取自中国传统文化中龙生九子,子子不同的传说,嘲风为守护屋脊之瑞兽,喜登高望远;静远取自成语“宁静致远”,登高莫忘初心,远观而不可务远。

学习更多绘图教程关注:


https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-519111-1508272.html
上一篇:低成本便携“管中实验室”助力结核病快速诊断
下一篇:2025年09月嘲风作品集(二)