博文
刊·见 | 能源领域SCI期刊Energy Sources Part A,呵护地球绿色肌肤  精选
精选
||
随着全球能源需求激增,传统化石能源的过度开采不仅加剧资源枯竭,还引发严重环境污染与温室气体排放,加剧全球气候变化。能源回收与利用作为资源节约与环保的关键手段,具有显著的重要性。
本期刊·见将为您介绍能源领域SCI期刊Energy Sources Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects。除了对期刊进行详尽的介绍外,还向您介绍近期中国学者团队发表的最新研究,均以开放获取模式发文,可免费阅读、下载:
煅烧气氛对高铁赤泥校正原料中铬(Ⅵ)转化率的影响
新型建筑外墙气凝胶保温材料的最新进展综述
由重整甲醇高温质子交换膜燃料电池和吸收式制冷循环组成的组合系统的能量、放能、放经济和环境(4E)分析
 https://www.tandfonline.com/journals/ueso
https://www.tandfonline.com/journals/ueso
Print ISSN: 1556-7036
Online ISSN: 1556-7230
Energy Sources Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects旨在深入探究全球能源需求持续增长背景下,能源利用对环境和气候造成的日益严峻影响,并探索实现可持续能源转型以有效应对这些挑战的创新解决方案。
期刊对以下技术、科学及环境方面的议题感兴趣:
生物燃料和生物能源
煤炭能源
碳捕获、储存和利用
能源系统脱碳
废物能源
储能和灵活发电
能源效率
智能技术对环境的影响
能源来源的环境影响
能源转型
天然气能源
地热能
温室气体去除
核能源
油页岩能源
石油及加工业
能源应用中的智能技术
太阳能
风能
该期刊已被SCI、Scopus、 BIOSIS Previews 等数据库收录。
影响因子
根据JCR显示,Energy Sources Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects
2023年影响因子为2.3
在能源与燃料领域排名123/171
在工程:化工领域排名95/170
CiteScore
根据Scopus显示,Energy Sources Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects
2023年CiteScore为4.4
能源
核能与工程领域排名17/77
燃料技术领域排名49/128
能源工程与动力技术领域排名102/272
可再生能源、可持续性和环境领域排名134/270
作者须知
接收文章类型
Energy Sources Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects接收
Original articles
Letter to the editor
审稿周期
从提交稿件到获取初审意见,平均需要5天
获取首个同行评审决定,平均需要34天
稿件一旦接受后,在线出版平均需要15天
编辑团队
Energy Sources Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects主编由克罗地亚斯普利特大学(University of Split, Croatia)的Sandro Nižetić 教授担任,副主编团队汇聚了来自意大利、中国等地的行业翘楚。编辑顾问委员会云集了来自美国、中国、土耳其等多地的学者。
主编介绍
Sandro Nižetić 教授

Sandro Nižetić 教授任职于斯普利特大学(University of Split, Croatia)电气工程、机械工程和船舶建筑学院,他的研究领域包括能源、建筑能源效率、智能技术和可再生能源。
中国副主编介绍
张亚宁

张亚宁,哈尔滨工业大学能源科学与工程学院教授,主要从事热力学、有机固废、生物质、热泵等方面的研究。
金辉

金辉,西安交通大学能源与动力工程学院教授,长期从事煤炭超临界水气化制氢发电多联产技术(超临界水蒸煤),有机废弃物的无害化处理与资源化利用。
期刊的编辑顾问委员会中多位成员来自中国。
作者分布
根据JCR显示,近三年在Energy Sources Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects发文的国家中,发文前三的国家/地区有:
中国
印度
土耳其
近三年,在Energy Sources Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects发文的全球高校和科研机构中,发文数量排名前三位的是:
印度国立理工学院
中国矿业大学
伊斯兰阿扎德大学
中国学者团队最新发表文章精选
通讯作者:齐砚勇 西南科技大学
文章以开放获取模式发文
文章摘要:
The aim of this study was to investigate a new approach for reducing the production of harmful Cr(VI) heavy metals in the collaborative disposal of Red mud by cement enterprises. The study examined the effects of different ratios on the conversion rate of Cr(VI) in clinker under various calcination temperatures and atmospheres, and analyzed the raw material composition, clinker composition, and Cr(VI) content using XRD and XPS. The results indicate that the conversion rate of Cr(VI) is positively correlated with the concentration of oxygen, with the highest conversion rate of 93.4% achieved at 15% oxygen concentration. XPS analysis revealed that the peak intensity of Cr(VI) in clinker calcined under 4% O2 atmosphere was significantly higher than that of the sample calcined under 4000 mg/kg CO atmosphere. The study also found that the concentration of CO can reduce the conversion rate of Cr(VI) at high calcination temperatures, while at low calcination temperatures, the change in CO concentration has little effect on the conversion rate of Cr(VI). The specific objectives include examining the effects of different ratios, calcination temperatures, and atmospheres on the conversion rate of Cr(VI) in clinker. Additionally, when the ratio is the same as the calcination atmosphere, increasing the calcination temperature leads to an increase in the conversion rate of Cr(VI). The obtained results suggest a new approach for reducing the production of Cr(VI) in the collaborative disposal of Red mud by cement enterprises, which could have practical applications in engineering environmental protection.
第一作者:陆路 矿盐资源深度利用技术国家地方联合工程研究中心
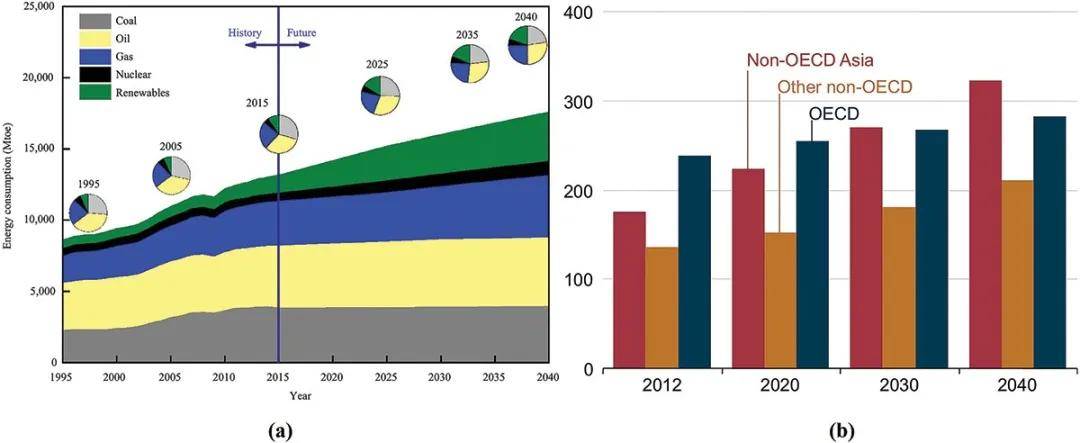
Figure 1. (a) The trends of global primary energy consumption from 1995 to 2040 and (b) consumption of energy around the world by country grouping, from 2012 to 2040 (in quadrillion btu) (Dong, Dong, and Jiang Citation2020).
文章以开放获取模式发文
文章摘要:
The unique network-like framework and nanopore structure of aerogel endow it with excellent thermal insulation performance. The thermal conductivity is as low as 0.012 W/(m·K), far lower than 0.035-0.040 W/(m·K) of traditional thermal insulation materials. Research and industrialization of nanoaerogels as building insulation have gained increasing attention in recent years. This paper discusses the application status, existing challenges, and solutions in the field of building external wall energy conservation and insulation based on nanoaerogel materials. First, it reviews the research progress of nanoaerogels and the development status of traditional building exterior wall insulation materials. The external wall using nano aerogel can reduce the heat loss by about 40%. Second, it focuses on the characteristics and research status of several types of aerogel thermal insulation products for buildings. Some products show that the energy efficiency has been improved to 50% in practical applications. Finally, it analyzes existing challenges of nanoaerogels in the application of building external wall thermal insulation and summarizes the development direction of industrialization research. Building external wall thermal insulation and the application and development of aerogels in the field of building energy conservation are facilitated by this analysis.
由重整甲醇高温质子交换膜燃料电池和吸收式制冷循环组成的组合系统的能量、放能、放经济和环境(4E)分析
第一作者:Zhaoda Zhong 奥尔堡大学
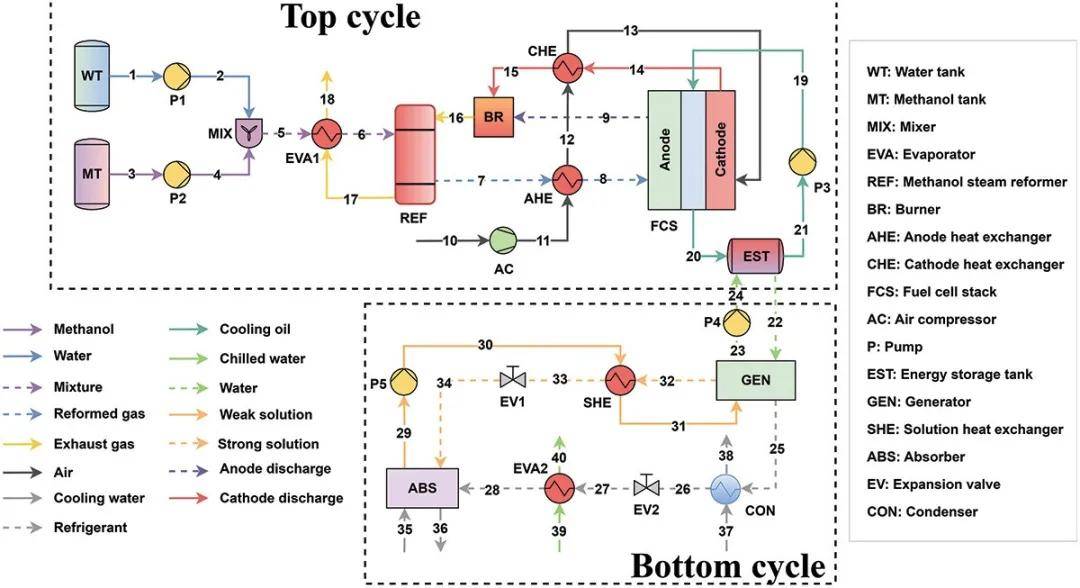
Figure 1. Proposed system combining an HT-PEMFC stack, a methanol steam reformer, and a single-effect ARC.
文章以开放获取模式发文
文章摘要:
4E (energy, exergy, exergoeconomic, and environmental) analyses of a reformed methanol high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell (RM HT-PEMFC) system identify inefficiencies, assess associated costs, and evaluate environmental impacts. However, such studies remain limited in the literature, particularly those exploring the impact of the operating parameters of the methanol steam reforming in the combined RM HT-PEMFC and single-effect absorption refrigeration cycle (ARC). This study addresses this gap by analyzing a tri-generation consisting of the RM HT-PEMFC and the single-effect ARC. Simulation results indicate a total exergy destruction of 21.65 kW, a total cost rate of 8.93 $/h, an exergoeconomic factor of 43.22%, and an exergy efficiency of 33.06% in the baseline case. Notably, the stack and burner account for the highest irreversibility, contributing 67.75% of total exergy destruction and 55.71% of the total cost rate. Parametric studies on four key variables – current density, stack temperature, reformer temperature, and steam-to-carbon ratio – reveal that higher system exergy efficiency is generally associated with lower carbon dioxide emissions. Uncertainty analysis shows that extending the HT-PEMFC’s lifespan to 40,000 h can reduce exergy cost per unit product by 16.23%, while decreasing the price of green methanol to 11.00 $/h can lower costs by 26.97%.

"Jour - Know"
为帮助更多科研人员选择更加合适的期刊,Taylor & Francis推出专栏——刊·见,该专栏致力于为读者和广大科研人员带来Taylor & Francis旗下期刊的详细解读,从期刊的基本情况、编委阵容、社会影响力到审稿速度、高被引文章等实用信息,专栏将为您带来最详细的介绍,让您更加全面地了解Taylor & Francis旗下优秀的国际期刊,帮助更多中国卓越科研成果顺利在国际期刊上发表。
以上内容可能更新,请以期刊官网主页为准。
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-3574014-1466099.html
上一篇:Routledge媒体与传播学优质期刊推荐
下一篇:北京工业大学牟伦田专访 | 人工智能与艺术的碰撞



