博文
室内空气甲醛污染健康危害及控制
||
摘要:以某高层新装修住宅室内空气甲醛污染为研究对象,采用现场实测与数值模拟方法,分析了甲醛污染对成人的健康安全危害及自然通风控制措施。结果表明:不开启门窗时甲醛浓度都超过了我国室内空气质量标准,对成人的致癌风险较高,自然通风可以降低甲醛危害,尤其在安装有衣柜或书柜的房间要加强开窗开门通风;进风口的位置和数量对室内气流分布影响很大,导致不同房间甲醛浓度差异较大;相较于密闭房间,开窗开门通风可使甲醛浓度降低70%左右,仅开门通风可降低甲醛浓度45%左右。研究结果可为降低室内空气甲醛污染的健康安全危害提供一定参考。
Abstract: Taking indoor formaldehyde (HCHO) pollution of a newly renovated high-rise residential building as the research object, the health and safety hazards on adults and natural ventilation control measures of HCHO pollution were analysed with on-site measurement and numerical simulation methods. The results show that the HCHO level exceeds the indoor air quality standards of China when doors and windows are not opened, which poses a high risk of cancer for adults. Natural ventilation can reduce the harm of HCHO, especially in rooms with wardrobes or bookcases, it is necessary to strengthen ventilation by opening window and door. The position and number of air intakes have a significant impact on the indoor airflow distribution, resulting in significant differences in HCHO level among different rooms. Compared to enclosed rooms, opening windows and doors for ventilation can reduce HCHO level by about 70%, while only opening doors for ventilation can reduce HCHO level by about 45%. The research results can provide some reference for reducing the health and safety hazards of indoor HCHO pollution.
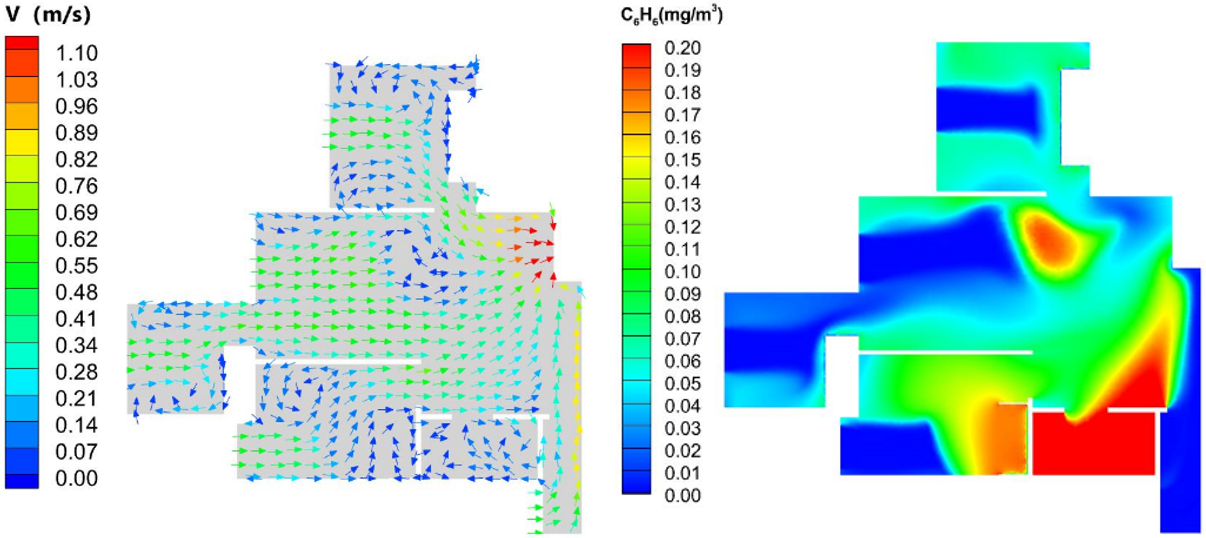
室内风速矢量与甲醛浓度分布图
结论:通过现场实测与CFD模拟分析,研究了住宅室内空气甲醛污染的自然通风控制及健康安全风险,得出以下结论:
1)实测表明某新装修高层住宅室内空气甲醛浓度均值达到0.119mg/m3,是我国室内空气质量标准限值的1.5倍,对室内成人已经构成致癌性健康安全风险。
2)对比密闭状态,自然通风对室内甲醛污染的净化控制效果明显,开窗开门通风效果最好,其次是开窗通风,环保不达标的书柜与衣柜等新家具是室内甲醛的主要来源,放置有新家具的房间应加强自然通风,降低甲醛危害。
3)书房中由于书柜的甲醛释放面积大,且书柜位于角落,在书柜处形成气流涡流,阻碍了部分甲醛污染及时排出,可通过改变门窗开启角度与加强自然通风时间来控制污染。
参考文献:
潘扬松,杞昊,杜炤江,等.住宅室内甲醛污染健康危害及通风控制[J].工业安全与环保,2024,50(11):78-82.
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-200545-1516862.html
上一篇:腾冲科学家论坛-腾冲科学大奖-腾冲青年科学家奖