博文
Communications Biology:枸杞基因组
||
Wolfberry genomes and the evolution of Lycium (Solanaceae)
第一作者:You-Long Cao
第一单位:宁夏农林科学院
通讯作者:Zhong-Jian Liu
Abstract
背景回顾:Wolfberry Lycium, an economically important genus of the Solanaceae family, contains approximately 80 species and shows a fragmented distribution pattern among the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. 提出问题:Although several herbaceous species of Solanaceae have been subjected to genome sequencing, thus far, no genome sequences of woody representatives have been available. 主要研究:Here, we sequenced the genomes of 13 perennial woody species of Lycium, with a focus on Lycium barbarum. 结果1-基本分析:全基因组加倍事件:Integration with other genomes provides clear evidence supporting a whole-genome triplication (WGT) event shared by all hitherto sequenced solanaceous plants, which occurred shortly after the divergence of Solanaceae and Convolvulaceae. 结果2-基本分析:基因家族收缩与扩张:We identified new gene families and gene family expansions and contractions that first appeared in Solanaceae. 结果3-生物学:自交不亲和:Based on the identification of self-incompatibility related-gene families, we inferred that hybridization hotspots are enriched for genes that might be functioning in gametophytic self-incompatibility pathways in wolfberry. 结果4-基因表达比较分析:Extremely low expression of LOCULE NUBER (LC) and COLORLESS NON-RIPENING (CNR) orthologous genes during Lycium fruit development and ripening processes suggests functional diversification of these two genes between Lycium and tomato. 结果5-生物学:多年开花相关:The existence of additional flowering locus C-like MADS-box genes might correlate with the perennial flowering cycle of Lycium. 结果6-生物学:木本与草本:Differential gene expression involved in the lignin biosynthetic pathway between Lycium and tomato likely illustrates woody and herbaceous differentiation. 结果7-生物学:群体演化之地理扩张轨迹:We also provide evidence that Lycium migrated from Africa into Asia, and subsequently from Asia into North America. 结论:Our results provide functional insights into Solanaceae origins, evolution and diversification. 摘 要 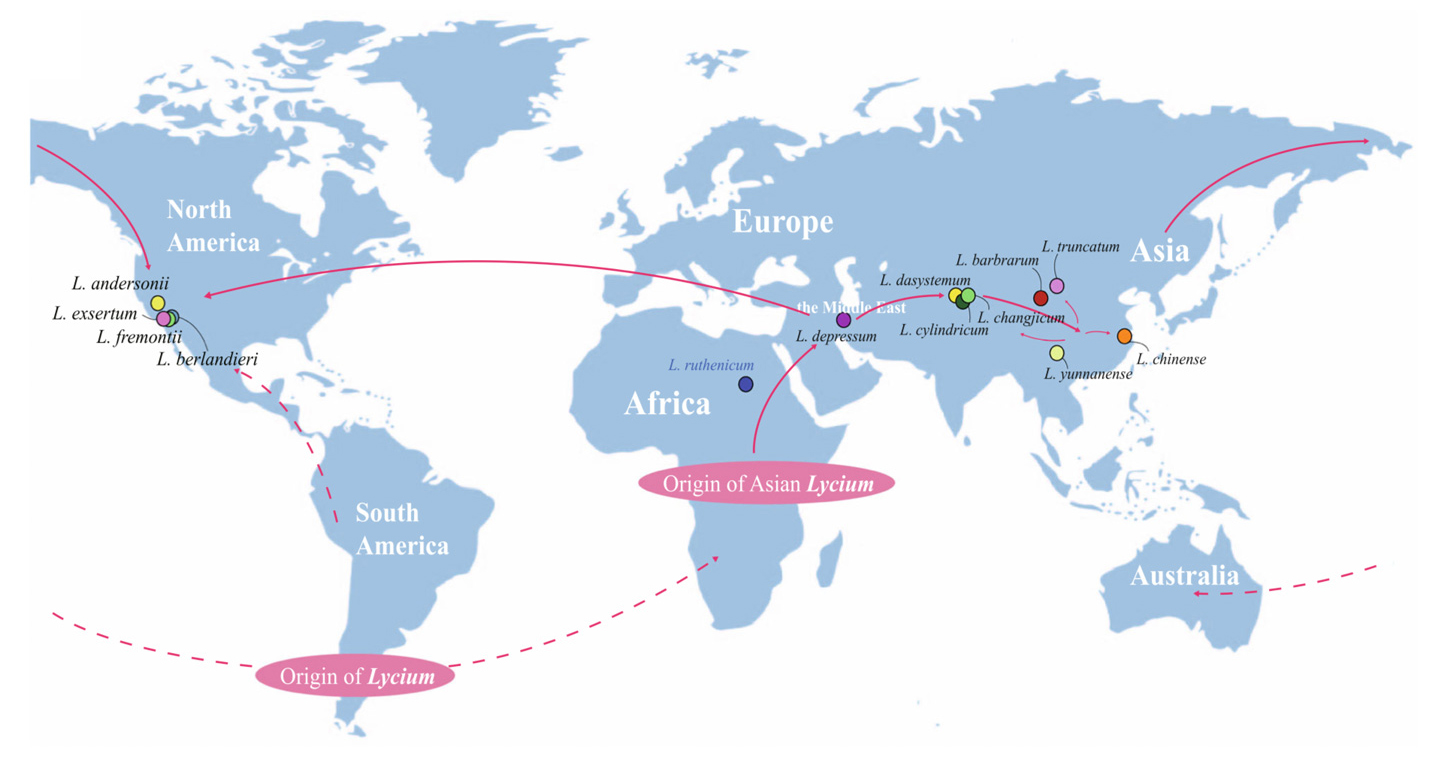
枸杞属是茄科(Solanaceae)的一个具有重要经济价值的植物类群,约包含80个种,在北半球和南半球呈片段化的分布模式。虽然目前茄科已经有几种草本植物进行了全基因组测序,但到目前为止,还没有茄科木本植物的基因组序列。本文中,作者对13种多年生枸杞属木本植物的基因组进行了测序,着重关注了枸杞(Lycium barbarum)。整合其他已测序的茄科植物基因组分析显示,迄今为止所有已测序的茄科植物共有一次全基因组三倍化(WGT)事件,该事件发生在茄科和旋花科植物分化后不久。作者鉴定了茄科植物中新的基因家族,以及基因家族的扩展和收缩。基于自交不亲和相关基因家族的鉴定,作者推测杂交热点富集了可能作用于枸杞配子体自交不亲和途径中发挥作用的基因。在枸杞果实发育和成熟过程中,LC和CNR同源基因的表达极低,表明这两个基因在枸杞和番茄之间的功能多样化。此外,枸杞中存在额外的FLC类MADS-box基因,这可能与枸杞的多年生开花周期有关。枸杞和番茄在木质素生物合成途径中基因的差异表达,可能说明了木本和草本植物的分化。作者进一步的分析显示,枸杞从非洲迁移到亚洲,然后从亚洲迁移到北美。本文的研究结果为茄科植物的起源、演化以及多样性提供了新的视野。
通讯作者
** 刘仲健 **
个人简介: 1978-1982年,华南农业大学,学士。 研究方向:被子植物进化;植物分子系统学;基因组学;开花分子调控机制。
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-02152-8
Journal: Communications Biology
Published date: June 03, 2021
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-3158122-1290512.html
上一篇:eLife:ABA-GA双稳态开关作用于拟南芥种子萌发时间的表型变异
下一篇:Nature Communications:HSFA2/HSFA3异聚复合物介导热胁迫后的转录记忆
全部作者的其他最新博文
- • Plant Physiology:CsMADS3促进柑果中的叶绿素降解和类胡萝卜素合成(华中农业大学)
- • Molecular Plant:LBD11-ROS反馈调节作用于拟南芥的维管形成层增殖和次生生长(浦项科技大学)
- • Science Advances:根结线虫通过调控植物的CLE3-CLV1模块,促进侵染进程(日本熊本大学)
- • Nature Communications:油菜素内酯参与植物营养生长期转变的分子机制解析(浙江农林大学)
- • Current Biology:光合作用产生的蔗糖驱动侧根“生物钟”(德国弗莱堡大学)
- • PNAS:花同源异型基因在叶中被抑制、花中被激活的分子机制(南卡罗来纳大学)