博文
PNAS:植物中维生素E生物合成途径的一个关键水解酶被鉴定到
||
Genome-wide association identifies a missing hydrolase for tocopherol synthesis in plants
通讯单位:Michigan State University
Significance
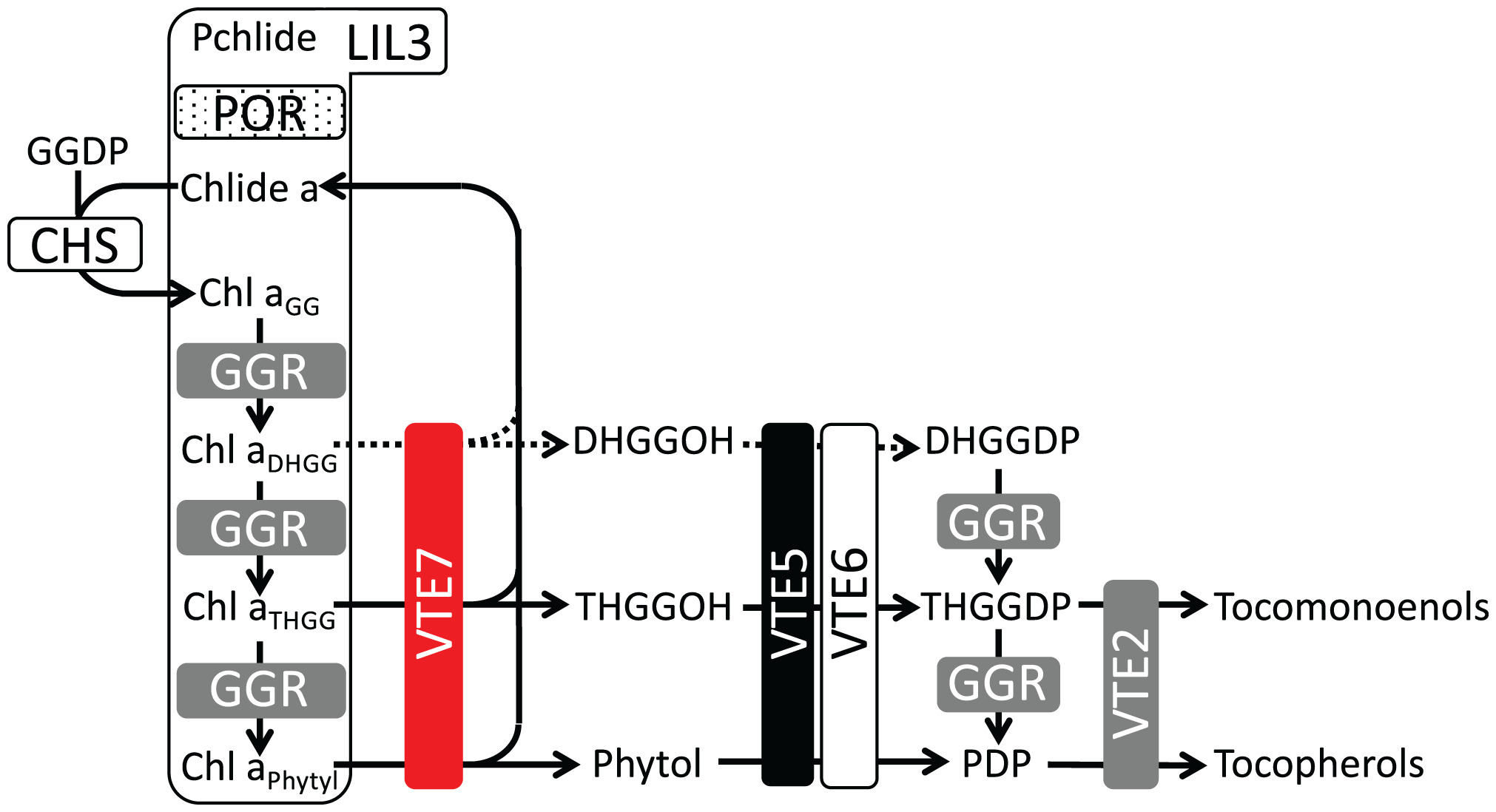
Tocopherols (vitamin E) are plant-synthesized, lipid-soluble antioxidants whose dietary intake, primarily from seed oils, is essential for human health. Tocopherols contain a phytol-derived hydrophobic tail whose in vivo source has been elusive. The most significant genome-wide association signal for Arabidopsis seed tocopherols identified an uncharacterized, seed-specific esterase (VTE7) localized to the chloroplast envelope, where tocopherol synthesis occurs. VTE7 disruption and overexpression had large impacts on tissue tocopherol contents with metabolic phenotypes consistent with release of prenyl alcohols, including phytol, during chlorophyll synthesis, rather than from the bulk degradation of thylakoid chlorophylls as has long been assumed. Understanding the source of phytol for tocopherols will enable breeding and engineering plants for vitamin E biofortification and enhanced stress resilience.
生育酚(维生素E)是一种植物合成的脂溶性抗氧化剂,其饮食摄入量主要来自种子油,对人类健康至关重要。生育酚含有植物酚衍生的疏水尾巴,其体内来源一直难以捉摸。拟南芥种子生育酚最显著的全基因组关联信号确定了一个定位于叶绿体被膜上的未鉴定的种子特异性酯酶(VTE7),在那里发生生育酚的合成。VTE7的中断和过表达对组织中生育酚的含量有很大的影响,其代谢表型与叶绿素合成过程中包括植物醇在内的戊烯醇的释放一致,而不是长期以来认为的类囊体叶绿素的大量降解。了解生育酚中植物酚的来源将有助于培育和设计维生素E生物强化和增强抗逆性的植物
Abstract
背景:The tocopherol biosynthetic pathway, encoded by VTE genes 1 through 6, is highly conserved in plants but most large effect quantitative trait loci for seed total tocopherols (totalT) lack VTE genes, indicating other activities are involved.
VTE基因1-6编码的生育酚生物合成途径在植物中高度保守,但大多数种子总生育酚(TOTALT)的大效应数量性状座位都缺乏VTE基因,这表明VTE基因还参与了其他活动。
研究内容:A genome-wide association study of Arabidopsis seed tocopherols showed five of seven significant intervals lacked VTE genes, including the most significant, which mapped to an uncharacterized, seed-specific, envelope-localized, alpha/beta hydrolase with esterase activity, designated AtVTE7. Atvte7 null mutants decreased seed totalT 55% while a leaky allele of the maize ortholog, ZmVTE7, decreased kernel and leaf totalT 38% and 49%, respectively. Overexpressing AtVTE7 or ZmVTE7 partially or fully complemented the Atvte7 seed phenotype and increased leaf totalT by 3.6- and 6.9-fold, respectively. VTE7 has the characteristics of an esterase postulated to provide phytol from chlorophyll degradation for tocopherol synthesis, but bulk chlorophyll levels were unaffected in vte7 mutants and overexpressing lines. Instead, levels of specific chlorophyll biosynthetic intermediates containing partially reduced side chains were impacted and strongly correlated with totalT. These intermediates are generated by a membrane-associated biosynthetic complex containing protochlorophyllide reductase, chlorophyll synthase, geranylgeranyl reductase (GGR) and light harvesting-like 3 protein, all of which are required for both chlorophyll and tocopherol biosynthesis. We propose a model where VTE7 releases prenyl alcohols from chlorophyll biosynthetic intermediates, which are then converted to the corresponding diphosphates for tocopherol biosynthesis.
对拟南芥种子生育酚的全基因组关联研究表明,7个显著区间中有5个缺失VTE基因,其中最显著的区间定位于一种未鉴定的、种子特异的、被膜定位的具有酯酶活性的α/β水解酶,命名为AtVTE7。Atvte7缺失突变体使种子总数减少55%,而玉米直系的泄漏等位基因ZmVTE7使籽粒和叶片总数分别减少38%和49%。过量表达AtVTE7或ZmVTE7部分或完全补充了Atvte7种子的表型,并使叶片总数分别增加了3.6倍和6.9倍。Vte7具有酯酶的特征,可以为生育酚的合成提供叶绿素降解过程中的植酸,但在vte7突变体和高表达品系中,整体叶绿素水平不受影响。相反,含有部分还原侧链的特定叶绿素生物合成中间体的水平受到影响,并与totalT密切相关。这些中间体是由一个膜相关的生物合成复合体产生的,该复合体含有原叶绿素还原酶、叶绿素合成酶、香叶基香叶基还原酶(GGR)和类捕光蛋白,所有这些都是叶绿素和生育酚生物合成所必需的。我们提出了一个模型,VTE7从叶绿素生物合成中间体中释放戊烯醇,然后将其转化为相应的二磷酸,用于生育酚的生物合成。
研究意义:该研究基于基因组关联分析鉴定了在生育酚生物合成中的关键α/β水解酶ABH,并阐明了该酶的功能及介导生育酚合成的代谢机制。研究结果完善了生育酚生物合成途径,有助于培育和改造植物以进行维生素 E 生物强化和增强抗逆能力。
原文链接:https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2113488119
Journal: PNAS
First Published: May 31, 2022
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-3420203-1342706.html
上一篇:Plant Com:澳大利亚西澳大学Mylne团队解析拟南芥除草剂磺草灵靶标的晶体结构和作用机制
下一篇:New Phytologist:韩国中央大学发现一个调控旱胁迫耐受性的泛素化酶