博文
[转载]CPB封面文章和亮点文章 | 2021年第10期
||

Chang-Wei Sun(孙昌伟), Yu Sun(孙宇), Jia-Chen Duan(端家晨), Guang-Tai Xue(薛广太), Yi-Chen Liu(刘奕辰), Liang-Liang Lu(陆亮亮), Qun-Yong Zhang(张群永), Yan-Xiao Gong(龚彦晓), Ping Xu(徐平), and Shi-Ning Zhu(祝世宁)
Chin. Phys. B, 2021, 30 (10): 100312

通讯波段的高频谱纯度可预知单光子源在量子信息领域具有重要的应用,特别是中红外波段单光子源还可以被应用于长距离量子通信、成像和气体测量等领域。一般来说,高频谱纯度光子源常使用窄带滤波的方法制备,这将大大降低单光子源的预知效率。因此在实验上如何制备高频谱纯度单光子源且保持高的预知效率一直是一个亟需解决的关键问题。
本文利用扩展相位匹配原理,在极化周期20.35 μm,长度25 mm的单块掺镁铌酸锂晶体中实现了1644 nm到4922.9 nm的宽调谐的高频谱纯度和高预知效率单光子源。整个波长范围中,在宽带滤波片的滤波效率大于80%的情况下可将光谱纯度提升至0.95以上。本文除了从理论上进行数值模拟,还对实验制备的光子源进行联合谱强度测量(JSI)和二阶关联测试(g2(0)),实验结果与数值模拟结果吻合得很好。本文的研究有助于获得高品质的中红外波段单光子源和推动中红外量子信息技术的发展。
原文链接
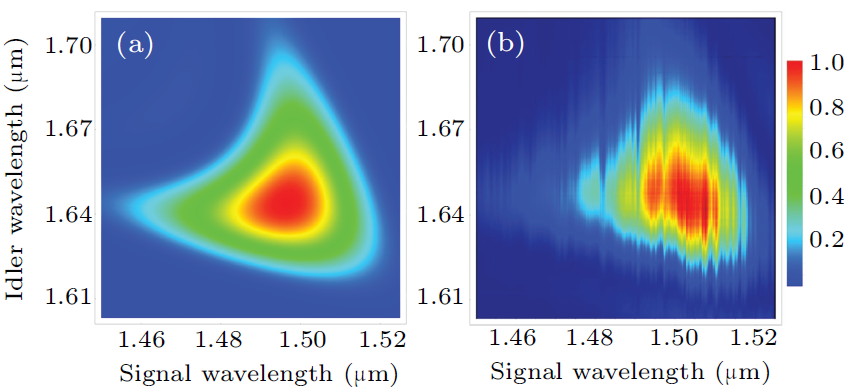
Fig. 4. (a) Numerical simulation of the JSI. The pump wavelength λp = 783.4 nm, the bandwidth of pump laser ∆λp = 9 nm, the crystal length L=25 mm, the temperature is 26℃. (b) Experimental measured JSI. The experimental configuration is same as the numerical simulation.

LnCu3(OH)6Cl3 (Ln = Gd, Tb, Dy): Heavy lanthanides on spin-1/2 kagome magnets
Ying Fu(付盈), Lianglong Huang(黄良龙), Xuefeng Zhou(周雪峰), Jian Chen(陈见), Xinyuan Zhang(张馨元), Pengyun Chen(陈鹏允), Shanmin Wang(王善民), Cai Liu(刘才), Dapeng Yu(俞大鹏), Hai-Feng Li(李海峰), Le Wang(王乐), and Jia-Wei Mei(梅佳伟)
Chin. Phys. B, 2021, 30 (10): 100601

自旋1/2的笼目反铁磁体是研究阻挫磁性和寻找量子自旋液体的重要平台。由于其他相互作用的影响,例如Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya (DM)相互作用、单离子各向异性等,笼目磁体倾向于形成具有某种特殊磁结构的磁有序态,比如“q=0”, “√3×√3”等。YCu3(OH)6Cl3虽由于DM相互作用形成“q=0”的磁结构,但Cu2+的完美笼目晶格使其成为理想的笼目反铁磁体。
本文通过水热合成,成功制备了和YCu3(OH)6Cl3同结构的LnCu3(OH)6Cl3 (Ln = Gd, Tb, Dy),将重稀土离子引入了这个具有“q=0”磁有序的笼目磁体。在通过变温XRD初步排除结构相变后,通过系统的热力学测量(磁化率、比热等)发现:相较于轻稀土(Nd, Sm, Eu),重稀土离子虽然很大程度上影响该体系的低温磁性和热力学行为,但仍对Cu2+-笼目晶格的本征磁性影响有限。本文补充了重稀土离子对YCu3(OH)6Cl3体系的磁性影响研究,使得LnCu3(OH)6Cl3(Ln = Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy)化合物成为进一步系统分析稀土对Cu2+-笼目晶格的阻挫磁性影响的绝佳材料平台。
原文链接
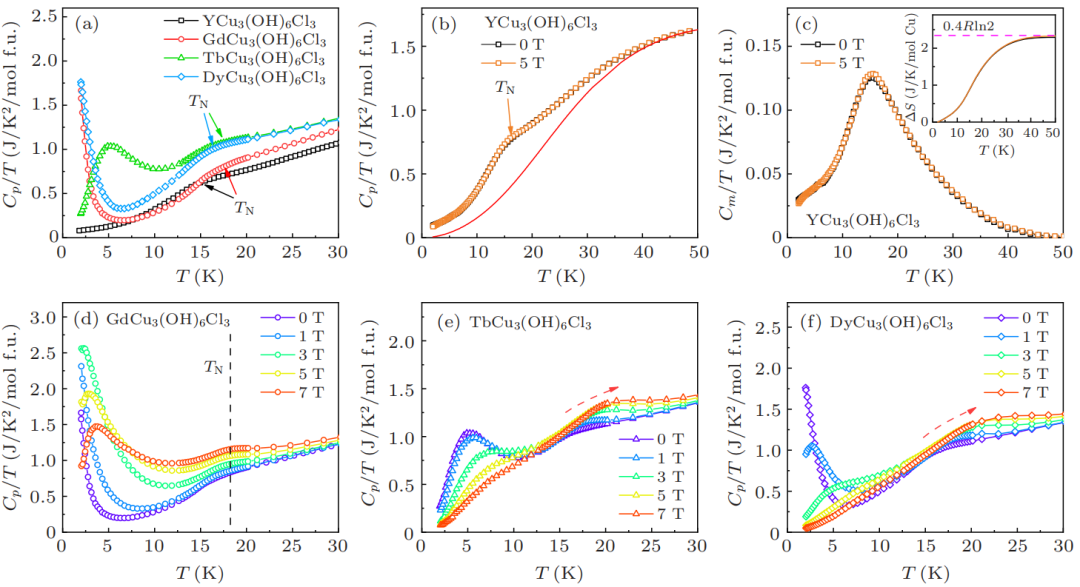
Fig. 6. (a) Specific heat for YCu3(OH)6Cl3 and LnCu3(OH)6Cl3 (Ln = Gd, Tb, Dy). (a) Cp/T for YCu3(OH)6Cl3 and LnCu3(OH)6Cl3 under zero field. (b) The Cp/T of YCu3(OH)6Cl3. The red solid line is phonon-contribution fitting. (c) Magnetic specific heat Cm/T of YCu3(OH)6Cl3 after subtracting phonon-contribution. Inset is magnetic entropy per Cu2+. (d)-(f) Temperature-dependent specific heat under different magnetic fields for GdCu3(OH)6Cl3, TbCu3(OH)6Cl3 and DyCu3(OH)6Cl3, respectively.

Dual mechanisms of Bcl-2 regulation in IP3-receptor-mediated Ca2+ release: A computational study
Hong Qi(祁宏), Zhi-Qiang Shi(史志强), Zhi-Chao Li(李智超), Chang-Jun Sun(孙长君), Shi-Miao Wang(王世苗), Xiang Li(李翔), and Jian-Wei Shuai(帅建伟)
Chin. Phys. B, 2021, 30 (10): 108704

肌醇1,4,5-三磷酸受体(IP3R)介导的钙离子(Ca2+)释放在细胞存活和死亡的调控中发挥着关键作用,Bcl-2蛋白在很多肿瘤细胞中高表达。实验发现Bcl-2蛋白可通过直接或间接机制抑制IP3R释放Ca2+的能力。然而,这两种机制均比较复杂,导致人们对其缺乏深刻的理解;更重要的是,人们尚不清楚这两种机制孰强孰弱以及二者耦合在一起的效果。
本文作者对这两种机制构建了微分方程模型,并针对上述问题开展了相关研究。首先,模拟了直接和间接机制模型在两种不同Bcl-2水平下Ca2+浓度随时间的变化,并与实验结果进行了比较。其次,采用单参数和双参数分岔分析,从全局角度证明了Bcl-2蛋白在直接和间接机制模型中均能抑制钙信号。然后,通过数学分析阐明在抑制钙信号方面,间接机制比直接机制更有效。最后,预测这两种机制会协同抑制钙信号。本研究结果有助于促进人们对Bcl-2蛋白调节IP3R介导的Ca2+释放机制的理解;因Bcl-2小分子抑制剂已进入临床试验阶段,本研究对癌症药物的研发有一定的参考意义。
原文链接
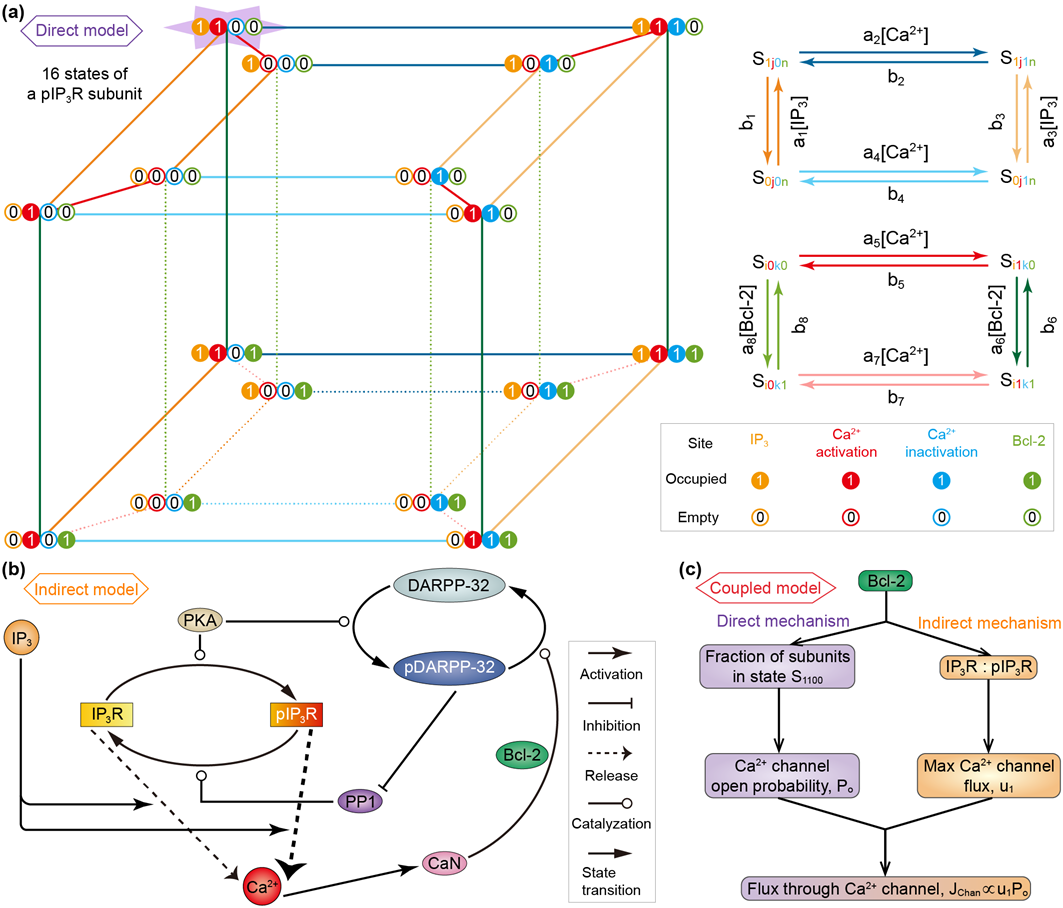
Fig. 1. (a) Kinetic schemes of the direct mechanism model. For simplify, it is assumed that all IP3Rs are phosphorylated (pIP3R). Left: Each subunit of pIP3R has one IP3 binding site, two Ca2+binding sites, and one Bcl-2 binding site. These sites can be occupied (represented by 1) or empty (represented by 0), and thus there are sixteen possible states (see from the top view). Right: The kinetics on the top and bottom faces of the inner and outer cubes as well as the kinetics between the two cubes. (b) Schematic diagram of the indirect mechanism model. The reversible conversion between phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated forms of IP3R is catalyzed by PKA and PP1. IP3 binds to IP3R/pIP3R and modulates Ca2+ release. The release of Ca2+ from pIP3R is stronger than that from IP3R. An increase in Ca2+ level leads to activation of CaN, which dephosphorylates pDARPP-32 into DARPP-32. During this process, Bcl-2 serves as a platform docking CaN and pDARPP-32. PKA catalyzes DARPP-32 into pDARPP-32, which is an inhibitor of PP1. (c) Mechanism of the coupled model. The direct and indirect mechanisms are linked by Bcl-2 regulation of flux through Ca2+ channel, i.e., IP3R and pIP3R. The direct mechanism influences the channel open probability by determining the fraction of channel subunits in state S1100, while the indirect mechanism influences the maximal channel flux by determining the IP3R-to-pIP3R ratio.

SPECIAL TOPIC — Ion beam modification of materials and applications
SPECIAL TOPIC — Quantum computation and quantum simulation
SPECIAL TOPIC —Twistronics
SPECIAL TOPIC — Machine learning in condensed matter physics
SPECIAL TOPIC — Phononics and phonon engineering
SPECIAL TOPIC — Water at molecular level
SPECIAL TOPIC — Optical field manipulation
SPECIAL TOPIC — Modeling and simulations for the structures and functions of proteins and nucleic acids
SPECIAL TOPIC —Terahertz physics
SPECIAL TOPIC — Ultracold atom and its application in precision measurement
SPECIAL TOPIC — Topological 2D materials
SPECIAL TOPIC — Active matters physics
SPECIAL TOPIC — Physics in neuromorphic devices
SPECIAL TOPIC — Advanced calculation & characterization of energy storage materials & devices at multiple scale
TOPICAL REVIEW — Advanced calculation & characterization of energy storage materials & devices at multiple scale
TOPICAL REVIEW — Quantum dot displays
TOPICAL REVIEW — CALYPSO structure prediction methodology and its applications to materials discovery
SPECIAL TOPIC — A celebration of the 100th birthday of Kun Huang
TOPICAL REVIEW — A celebration of the 100th birthday of Kun Huang
SPECIAL TOPIC — Strong-field atomic and molecular physics
TOPICAL REVIEW — Strong-field atomic and molecular physics
TOPICAL REVIEW — Topological semimetals
SPECIAL TOPIC — Topological semimetals
SPECIAL TOPIC — Photodetector: Materials, physics, and applications
TOPICAL REVIEW — Photodetector: Materials, physics, and applications
TOPICAL REVIEW — Fundamental research under high magnetic fields
Virtual Special Topic — High temperature superconductivity
Virtual Special Topic — Magnetism and Magnetic Materials

官网:http://cpb.iphy.ac.cn https://iopscience.iop.org/journal/1674-1056
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-3377544-1312810.html
上一篇:[转载]CPB2021年第9期编辑推荐文章
下一篇:[转载]CPB2021年第10期编辑推荐文章
