博文
带有氯气的电极提供了高功率和能量密度
||
带有氯气的电极提供了高功率和能量密度
诸平
据威利公司(Wiley)2023年1月3日报道,带有氯气的电极提供了高功率和能量密度(Electrode with chlorine gas provides high power and energy density)。
超级电容器(Supercapacitors)是一种补充可充电电池的能量存储设备,甚至可以部分取代可充电电池。目前的超级电容器没有足够的能量密度,因此寿命不够长。一种用“呼吸”电极("breathing" electrode)制造超级电容器的新方法要优越得多。正如中英开发团队于2022年11月20日在德国《应用化学国际版》(Angewandte Chemie International Edition)杂志网站上发表的论文中解释的那样,他们从一种蜥蜴(lizard)身上获得了灵感,这种蜥蜴在潜入水中时会带着一个气泡呼吸。详见Xiaotong Fan, Kai Huang, Long Chen, Haipeng You, Menglei Yao, Hao Jiang, Ling Zhang, Cheng Lian, Xiangwen Gao, Chunzhong Li. High Power‐ and Energy‐Density Supercapacitors through the Chlorine Respiration Mechanism. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, First published: 20 November 2022. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202215342. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202215342
今天,超级电容器的应用包括补偿医院或数据处理中心等设施的短期停电,以及缓冲电子设备的消耗峰值。通过制动能量充电的超级电容器帮助现代有轨电车和公共汽车节省电力。太阳能企业也对稳定电压波动越来越感兴趣。
与可充电电池(rechargeable batteries)相比,超级电容器是能量存储的“短跑运动员”:它们可以在很短的时间内产生非常大的电流(高功率密度)。然而,它们是可怜的“长跑运动员”,因为即使用电量低,它们也坚持不了很长时间(能量密度低)。现代电能存储需要结合这两种特性,并具有低重量。不幸的是,到目前为止,提高能量密度的方法总是以功率密度为代价,这是超级电容器发展的绊脚石。
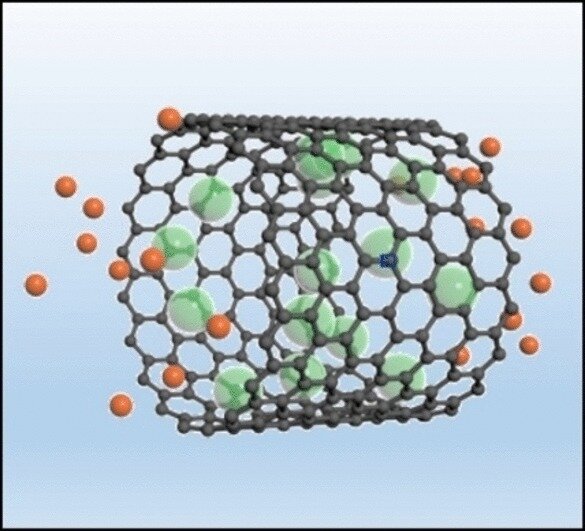
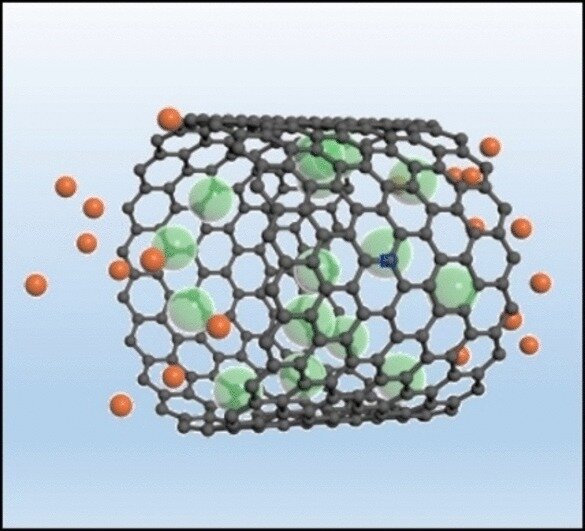
由中国上海的华东理工大学(East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai, China)和英国牛津大学(University of Oxford, UK)的陈龙(Long Chen音译)、连成(Cheng Lian音译)、高向文(Xiangwen Gao音译)和李春忠(Chunzhong Li音译)领导的团队现在已经开始克服这一挑战。他们的灵感来自一只小蜥蜴。变色蜥蜴(Anolis lizards)生活在陆地上,但当它们潜入水中寻找食物时,也可以在水下呼吸。为了做到这一点,它们带着一个气泡,气泡附着在头上的一层鳞片上。在水下,它们反复地呼吸这个气泡。新开发的电极由多孔碳材料制成(最有利的是直径约3 nm的多孔碳纳米管),当它淹没在食盐溶液中作为电解质时,也可以附着一层气体。然而,使用的气体不是空气,而是氯气。
在充电和放电期间,除了超级电容器通常的电荷分离(charge separation)之外,该电极还经历氧化还原反应( redox reaction)。充电后,电极将电子转移到氯气(chlorine gas)中,将氯气还原为氯离子,氯离子进入电极“呼出”的溶液中。放电时,氯离子(chloride ions)被氧化成氯(Cl2),这将气体返回到电极“吸入”的电极孔中。通过使用各种分析方法,该团队证明没有氯气(chlorine gas)逃离电极。气体薄层中的快速还原/氧化(rapid reduction/oxidation)和快速传质极大地增加了超级电容器的能量密度,同时保持极高的功率密度。即使经过数千次循环,容量仍然保持在相同的高水平。
上述介绍,仅供参考。欲了解更多信息,敬请注意浏览原文或者相关报道。
Deconvoluting the data: Charge density distributions of electric double layers
We report an unprecedentedly high power- and energy-density supercapacitor through the chlorine respiration in porous carbon materials. Both electrochemical results and theoretical calculations show that porous carbon with pore size around 3 nm delivers the best chlorine evolution and adsorption performance.
Supercapacitor represents an important electrical energy storage technology with high-power performance and superior cyclability. However, currently commercialized supercapacitors still suffer limited energy densities. Here we report an unprecedentedly respiring supercapacitor with chlorine gas iteratively re-inspires in porous carbon materials, that improves the energy density by orders of magnitude. Both electrochemical results and theoretical calculations show that porous carbon with pore size around 3 nm delivers the best chlorine evolution and adsorption performance. The respiring supercapacitor with multi-wall carbon nanotube as the cathode and NaTi2(PO4)3 as the anode can store specific energy of 33 Wh kg−1 with negligible capacity loss over 30 000 cycles. The energy density can be further improved to 53 Wh kg−1 by replacing NaTi2(PO4)3 with zinc anode. Furthermore, thanks to the extraordinary reaction kinetics of chlorine gas, this respiring supercapacitor performs an extremely high-power density of 50 000 W kg−1.
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-212210-1370520.html
上一篇:廉价荧光染料的完整调色板
下一篇:运动抑制胰岛素的产生