博文
ABBS: Chaperone function and mechanism of small heat-shock p
|||
Chaperone function and mechanism of small heat-shock proteins
Xinmiao Fu
State Key Laboratory of Protein and Plant Gene Research, School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 2014, 46: 347–356; doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmt152
Small heat-shock proteins (sHSPs) are ubiquitous ATP-independent molecular chaperones that play crucial roles in protein quality control in cells. They are able to prevent the aggregation and/or inactivation of various non-native substrate proteins and assist the refolding of these substrates independently or under the help of other ATP-dependent chaperones. Substrate recognition and binding by sHSPs are essential for their chaperone functions. This review focuses on what natural substrate proteins an sHSP protects and how it binds the substrates in cells under fluctuating conditions. It appears that sHSPs of prokaryotes, although being able to bind a wide range of cellular proteins, preferentially protect certain classes of functional proteins, such as translation-related proteins and metabolic enzymes, which may well explain why they could increase the resistance of host cells against various stresses. Mechanistically, the sHSPs of prokaryotes appear to possess numerous multi-type substrate-binding residues and are able to hierarchically activate these residues in a temperature-dependent manner, and thus act as temperature-regulated chaperones. The mechanism of hierarchical activation of substrate-binding residues is also discussed regarding its implication for eukaryotic sHSPs.
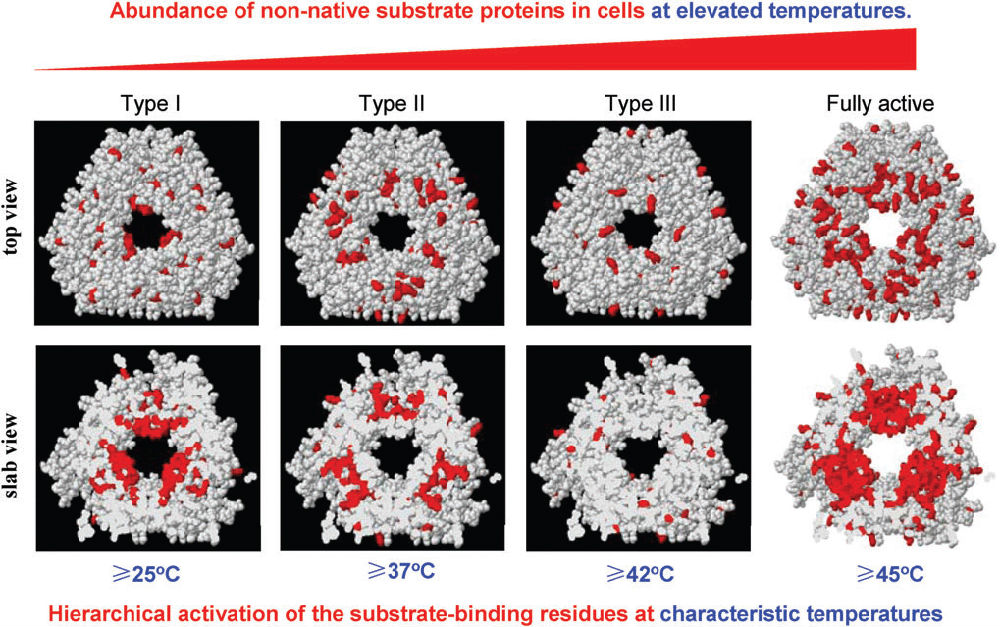
A mechanism of hierarchically activating multi-type substrate-binding residues of sHSPs underlies their heat shock-enhanced chaperone
activities
全文: http://abbs.oxfordjournals.org/content/46/5/347.full
相关论文:
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-592748-944883.html
上一篇:ABBS: Casticin suppresses self-renewal and invasion of lung
下一篇:ABBS: Isolation and culture of hepatic stellate cells from