博文
郑宇 谢幸 GPS
||
Contents
1 基于位置服务的分析与展望
2 基于无线传感器网络拓扑结构的物联网定位模型
3 郑宇 谢幸
[1] Towards mobile intelligence: Learning from GPS history data for collaborative recommendation
[2]
[3] 基于用户轨迹挖掘的智能位置服务
[4]
[1] 基于位置服务的分析与展望
李清泉 乐 阳
CCF通讯 2010
关键词:基于位置的服务 空间信息服务 空间定位
1 引言
who, when, what, where
基于位置服务的情景可通俗地表示为:你在哪里、什么身份、附近有什么资源

基于位置服务的4个基本组成部分:用户、通信网络、定位、服务与内容提供商
2 关键技术

2.1 定位技术
2.2 电子地图技术
2.3 信息分析和挖掘技术
2.4 自适应表达

3 基于位置服务的典型应用
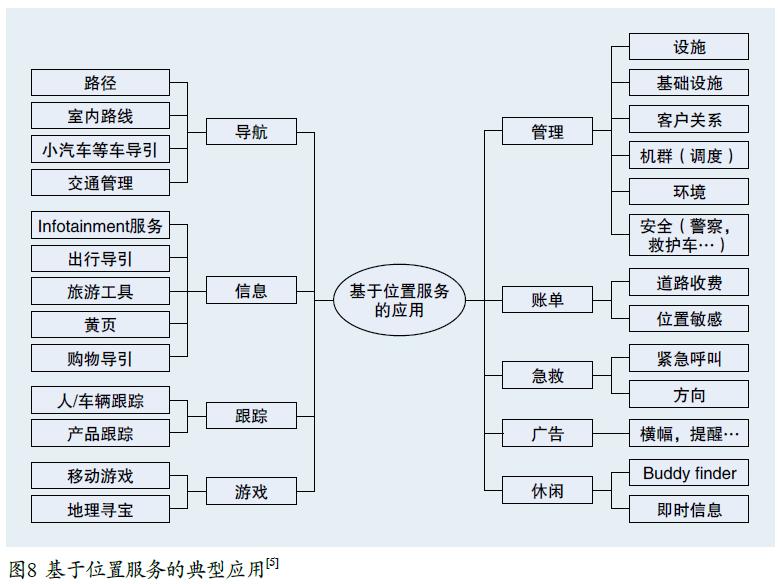
4 结语
[2] 基于无线传感器网络拓扑结构的物联网定位模型
顾晶晶 陈松灿 庄毅
顾晶晶 陈松灿 庄毅
计算机学报 2010, Sept
摘要:
无线传感器网络是物联网(Internet of Things)的重要组成部分(利用其实现物联网中目标的定位技术已
成为研究热点之一,由于受环境、障碍物、网络攻击和硬件错误等诸多因素的影响(传感器节点所采集的数据易产
生较大误差(形成错误数据(从而对定位造成严重影响9尽管已发展出了众多定位算法和模型(但针对错误数据实
现定位的研究还较罕见(尤其在国内(几乎是空白9文中针对上述问题,旨在利用网络(几何)拓扑结构信息(提出一
种用局部信息刻画全局分布密度信息的新颖物联网定位模型!鲁棒的局部保持的典型相关分析定位模型LE-RLPCCA
成为研究热点之一,由于受环境、障碍物、网络攻击和硬件错误等诸多因素的影响(传感器节点所采集的数据易产
生较大误差(形成错误数据(从而对定位造成严重影响9尽管已发展出了众多定位算法和模型(但针对错误数据实
现定位的研究还较罕见(尤其在国内(几乎是空白9文中针对上述问题,旨在利用网络(几何)拓扑结构信息(提出一
种用局部信息刻画全局分布密度信息的新颖物联网定位模型!鲁棒的局部保持的典型相关分析定位模型LE-RLPCCA
与现有同类典型方法在真实环境中的实验结果相比,LE-RLPCAA具有更高的定位鲁棒性和稳定性
关键词:物联网,无线传感器网络,定位,拓扑结构,错误数据,鲁棒性
3 郑宇 谢幸
[1-] Towards mobile intelligence: Learning from GPS history data for collaborative recommendation
Vincent W. Zheng, Yu Zheng, Xing Xie, Qiang Yang
Artificial Intelligence 184–185 (2012) 17–37
Abstract:
With the increasing popularity of location-based services, we have
accumulated a lot of
location data on the Web. In this paper, we are interested in answering
two popular
location-related
queries in our daily life: (1) if we want to do something such
as
sightseeing or dining in a large city like Beijing, where should we go? (2)
If we want
to visit a place such as the Bird’s Nest in Beijing Olympic park, what can
we do there?
We develop a mobile
recommendation system to answer these queries. In our system,
we first model the users’
location and activity histories as a user–location–activity rating
tensor. Because each user has limited data, the resulting rating tensor is
essentially
very sparse. This makes our recommendation task difficult. In order to
address this data
sparsity problem,
we propose three algorithms based on collaborative
filtering. The first
algorithm merges all the users’ data together, and uses a collective matrix
factorization
model to provide general recommendation (Zheng et al., 2010 [3]). The second algorithm
treats each user differently and uses a collective tensor and matrix
factorization model to
provide personalized recommendation (Zheng et al., 2010 [4]). The third algorithm is a
new algorithm which further improves our previous two algorithms by using a
rankingbased
collective tensor and matrix factorization model. Instead of trying to
predict the
missing entry values as accurately as possible, it focuses on directly
optimizing the ranking
loss w.r.t. user preferences on the locations and activities. Therefore, it
is more consistent
with our ultimate goal of ranking locations/activities for recommendations.
For these three
algorithms, we also exploit some additional information, such as user–user
similarities,
location features, activity–activity correlations and user–location
preferences, to help the
CF tasks. We extensively evaluate our algorithms using a real-world GPS
dataset collected
by 119 users over 2.5 years. We show that all our three algorithms can
consistently
outperform the competing baselines, and our newly proposed third algorithm
can also
outperform our other two previous algorithms.
Keywords: GPS, Location, Activity, Mobile recommendation, Collaborative filtering, Personalization
1. Introduction
2. Problem statement
4. Data modeling
5. Mobile recommendations
6. Experimental setup on real-world data
6.1. GPS users, devices and data
6.1. GPS users, devices and data
[3-] 基于用户轨迹挖掘的智能位置服务
郑 宇 谢 幸
CCF通讯 2010-6
关键词:基于位置的服务 GPS轨迹 轨迹数据挖掘
1 用户轨迹数据的产生
2 轨迹和基于位置的服务
3 理解个人历史轨迹
3.1 地图匹配
3.1 地图匹配
3.2 交通方式判别
4 基于多人轨迹数据的大众旅游推荐
5 个性化朋友和地点推荐

https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-468147-544831.html
上一篇:review: 网络编码中的优化问题研究
下一篇:并行计算
扫一扫,分享此博文