博文
云师大生物质能课题组已在国际权威环境科学类期刊发表学术论文3篇
|||
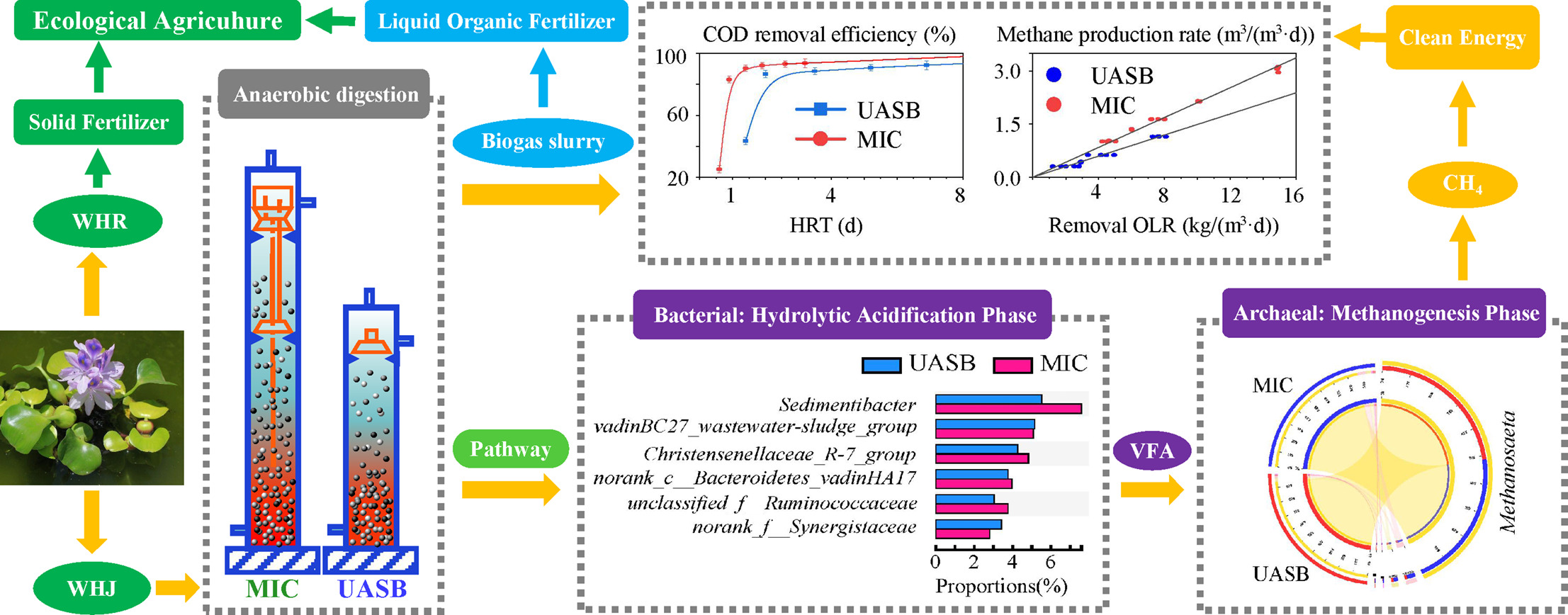
2020年7月10日《Science of The Total Environment》 在线发表了云南师范大学环境科学学院生物质能课题组张无敌研究员的最新研究成果《不同反应器处理水葫芦汁的能源效率和微生物群落关系的比较研究》。这是今年生物质能第3篇高质量研究论文,标志着云南师范大学生物质能研究进入了研究快车道。第一作者为在读博士生刘健峰博士,通讯作者为:张无敌研究员
Comparison of long-term energy efficiency and microbial community dynamics of different reactors in response to increased loadings of water hyacinth juice
Science of The Total Environment,Available online 10 July 2020, 140812
Highlights:
1. MIC and UASB reactors were examined for their maximum WHJ treatment
capacity limits.
MIC和UASB反应器处理水葫芦汁潜力得到了研究;
2. MIC exhibited a higher energy conversion rate and stronger performance than
UASB.
与UASB反应器相比,MIC反应器显示了更高的能源回收率和处理能力;
3.The methane production rate and removal OLR showed a linear relationship.
甲烷产率和有机负荷呈现出了较好的线性关系;
MIC and UASB reactors had similar predominant methanogens: Methanosaeta.
4. UASB反应器和MIC反应器处理水葫芦汁反应得出,产甲烷优势菌群均为鬃毛甲烷菌属(Methanosaeta);
Acetoclastic methanogenesis was the dominant metabolic pathway in WHJ
treatment
UASB反应器和MIC反应器处理水葫芦汁中主要为乙酸型产甲烷代谢路径;
二、上流式厌氧污泥床与改进型内循环反应器高效处理高COD废水的启动过程研究,
第一作者为在读博士生刘健峰博士,通讯作者为:张无敌研究员
Novel start-up process for the efficient degradation of high COD wastewater
with up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket technology and a modified internal
circulation reactor,Bioresource Technology 308 (2020) 123300
Highlights
A novel start-up process (NSP) was developed and verified in UASB and MIC reactors.
NSP time of MIC reactors (46 days) was less than that of UASB reactors (52 days).
NSP (23,500 mg/L) had higher influent COD than traditional startups (250–6500 mg/L).
The biogas production rate of MIC was three times higher than that of the UASB.
Methane was dominately generated through acetoclastic pathway by Methanosaeta.
三、常规沼气发酵生态系统甲烷排放通量的评价研究
第一作者为在读硕士生曾锦,通讯作者为:徐锐教授
Evaluation of methane emission flux from a typical biogas fermentation ecosystem in China,Journal of Cleaner Production,Volume 257, 1 June 2020, 120441
Highlights
CH4 emission fluxes from a typical hydraulic biogas digester in China were studied.
The diurnal and monthly variations from January to July were characterized.
Different environmental factors had various influences on the CH4 emission fluxes.
Leak of CH4 emission has non-negligible effect on the methane conversion factor.
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-454141-1242452.html
上一篇:一个合影引起来的涟漪
下一篇:云南师范大学生物质能研究方向带头人——张无敌研究员
全部作者的其他最新博文
- • 云师大地理学部王金亮教授团队在top期刊《Science of The Total Environment》发表研究成果
- • 云师大化工学院赵学博士在top期刊《Coordination Chemistry Reviews》发表第二篇综述文章
- • 云师大能环学院梁承月在《Journal of Environmental Management》上发表最新研研究成果
- • 云师大化工学院李如春在《Separation and Purification Technology》发表最新研究成果
- • 云师大能环学院王云峰教授等在国际知名新能源期刊《Renewable Energy》上发表最新研
- • 云师大能环学院余琼粉教授在国际知名期刊《Energy Conversion and Managemen》发表最新研究成果