博文
Developmental Cell:水稻一个mRNA m5C甲基转移酶作用于高温适应
||
OsNSUN2-Mediated 5-Methylcytosine mRNA Modification Enhances Rice Adaptation to High Temperature
First author: Yongyan Tang; Affiliations: CAS Institute of Botany (中科院植物所): Beijing, China
Corresponding author: Kang Chong
Extreme weather events can cause heat stress that decreases crop production. Recent studies have demonstrated that protein degradation and rRNA homeostasis as well as transcription factors are involved in the thermoresponse in plants. However, how RNA modifications contribute to temperature stress response in plant remains largely unknown. Herein, we identified OsNSUN2 as an RNA 5-methylcytosine (m5C) methyltransferase in rice. osnsun2 mutant displayed severe temperature- and light-dependent lesion-mimic phenotypes and heat-stress hypersensitivity. Heat stress enhanced the OsNSUN2-dependent m5C modification of mRNAs involved in photosynthesis and detoxification systems, such as β-OsLCY, OsHO2, OsPAL1, and OsGLYI4, which increased protein synthesis. Furthermore, the photosystem of osnsun2 mutant was vulnerable to high ambient temperature and failed to undergo repair under tolerable heat stress. Thus, OsNSUN2 mutation reduced photosynthesis efficiency and accumulated excessive reactive oxygen species upon heat treatment. Our findings demonstrate an important mechanism of mRNA m5C-dependent heat acclimation in rice.
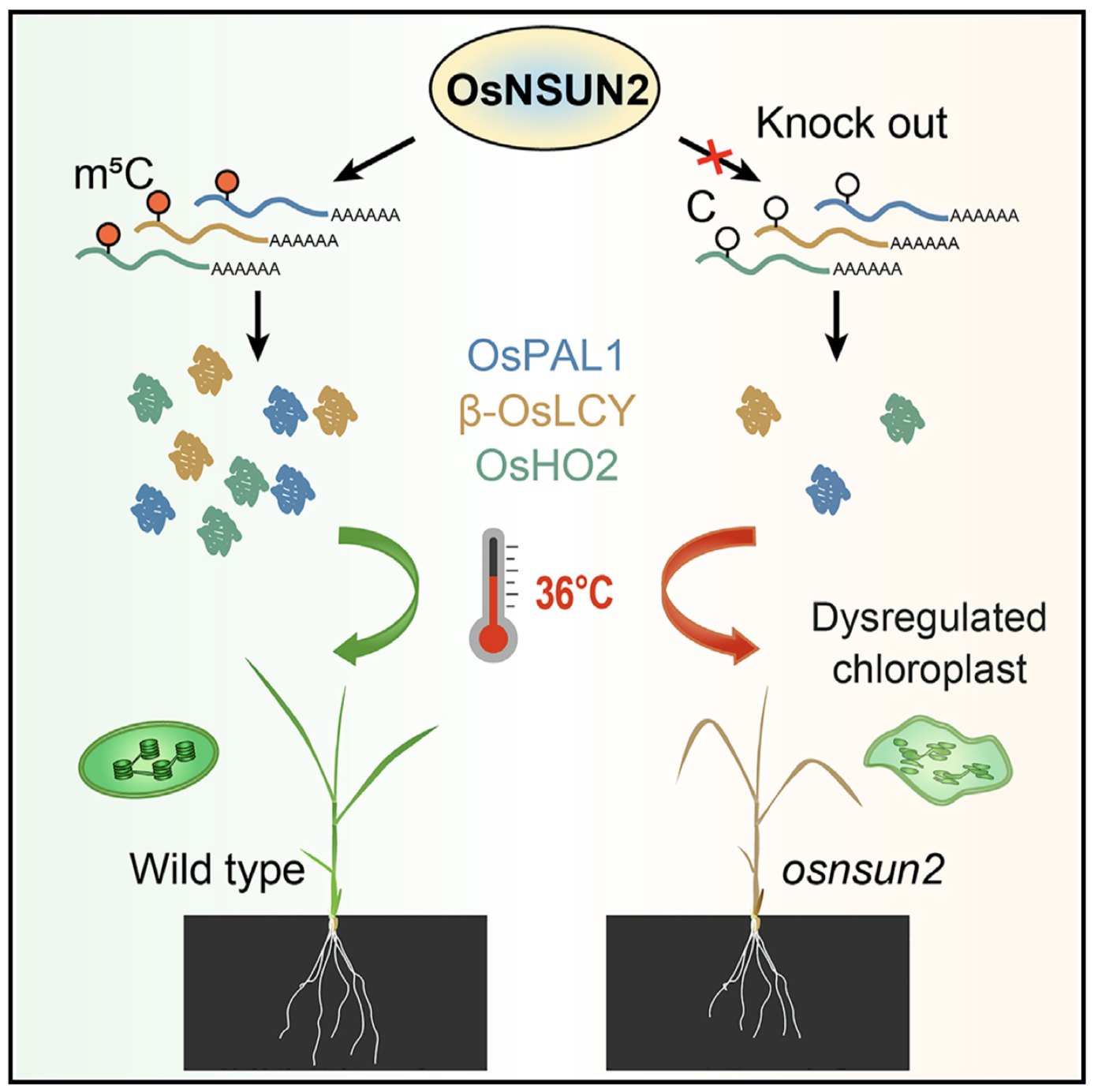
极端气候事件会导致热胁迫,引起作物的减产。最近的研究显示蛋白降解和rRNA内稳态,以及转录因子会参与植物的温度响应。然而,植物中RNA修饰是如何作用于温度胁迫响应还不清楚。本文中,作者在水稻中鉴定到了一个RNA 5-甲基胞嘧啶(m5C)甲基转移酶OsNSUN2。osnsun2突变体会表现出严重的温度和光依赖性病变模拟表型和热胁迫超敏反应。热胁迫会增强参与光合与排毒系统相关基因mRNA上依赖于OsNSUN2的m5C修饰,比如说β-OsLCY、OsHO2、OsPAL1以及OsGLYI4基因,最终增加这些基因编码蛋白的合成。此外,osnsun2突变体的光合系统容易受到高温环境的损坏,并且在正常可承受范围的热胁迫条件下不能正常修复。因此,OsNSUN2突变在热处理下会降低光合效率,并积累过剩的活性氧物质。本文的研究揭示了水稻中一个mRNA m5C依赖性的热适应机制。
Highlights
OsNSUN2 is the major mRNA m5C methyltransferase in rice
OsNSUN2是水稻中主要的mRNA m5C甲基转移酶
m5C regulates mRNA translation
m5C调控mRNA翻译
m5C modulates chloroplast homeostasis
m5C调控叶绿体的内稳态
m5C enhances rice adaptation to high temperature
m5C增强水稻对于高温的适应
通讯:种康(http://sourcedb.ib.cas.cn/cn/expert/200904/t20090403_45020.html)
个人简介:1984年,兰州大学,学士;1988年,兰州大学,硕士;1993年,兰州大学,博士。
研究方向:1. 小麦开花与春化作用分子机理;2. 水稻感受低温信号的分子应答机制;3. 水稻激素信号互作调控器官发生的分子网络。
doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2020.03.009
Journal: Developmental Cell
Published date: April 09, 2020
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-3158122-1229573.html
上一篇:Nature Genetics:草棉、亚洲棉及陆地棉基因组揭示棉花A基因组演化
下一篇:bioRxiv:雌雄异株林木美洲黑杨的性别决定基因鉴定
全部作者的其他最新博文
- • Plant Physiology:CsMADS3促进柑果中的叶绿素降解和类胡萝卜素合成(华中农业大学)
- • Molecular Plant:LBD11-ROS反馈调节作用于拟南芥的维管形成层增殖和次生生长(浦项科技大学)
- • Science Advances:根结线虫通过调控植物的CLE3-CLV1模块,促进侵染进程(日本熊本大学)
- • Nature Communications:油菜素内酯参与植物营养生长期转变的分子机制解析(浙江农林大学)
- • Current Biology:光合作用产生的蔗糖驱动侧根“生物钟”(德国弗莱堡大学)
- • PNAS:花同源异型基因在叶中被抑制、花中被激活的分子机制(南卡罗来纳大学)